Test your knowledge with 10 questions about the classification of living beings and use the comments after the feedback to clarify your doubts.
question 1
Biological classification, also called taxonomy, is a system that groups living beings according to:
a) The closest ancestor and observed patterns
b) The greatest number of species and the ecosystem
c) The way they feed and the habitat
d) Common characteristics and evolutionary kinship relationships
Correct alternative: d) Common features and evolutionary kinship relationships.
The taxonomy (taxis = arrangement, order; nomos = law) performs the description and nomenclature of living beings through common characteristics and evolutionary kinship relations.
This classification system was created due to the need to order and classify known species.
The classification takes into account, for example, morphological, genetic, physiological and reproductive aspects associated with evolutionary kinship.
question 2
A species can be defined as:
a) A living being with morphological differentiation.
b) A type of animal or plant.
c) A set of similar organisms that share unique characteristics among themselves.
d) A community of living beings that live in the same place.
Correct alternative: c) A set of similar organisms that share unique characteristics with each other.
The species is the unit of classification of living beings. These organisms are beings capable of reproducing and generating offspring.
Thus, a species is a group of individuals that, in addition to the morphological characteristics that make them visibly similar, have the ability to reproduce among themselves.
question 3
Indicate the descending order of biological classification.
a) Kingdom ⇒ Order ⇒ Class ⇒ Phylum ⇒ Gender ⇒ Family ⇒ Species
b) Kingdom ⇒ Phylum ⇒ Class ⇒ Order ⇒ Family ⇒ Genus ⇒ Species
c) Kingdom ⇒ Family ⇒ Order ⇒ Class ⇒ Phylum ⇒ Genus ⇒ Species
d) Kingdom ⇒ Phylum ⇒ Gender ⇒ Order ⇒ Family ⇒ Class ⇒ Species
Correct alternative: b) Kingdom ⇒ Phylum ⇒ Class ⇒ Order ⇒ Family ⇒ Genus ⇒ Species.
Karl von Linée developed in 1735 a system with 7 taxonomic categories, which became known as Linnaeus' taxonomy and is organized from the most comprehensive classification to the narrowest of the following form:
Kingdom ⇒ Phylum ⇒ Class ⇒ Order ⇒ Family ⇒ Genus ⇒ Species.
For example, the biological classification of a domestic dog is:
Kingdom – Animalia
Phylum - Chordata
Class – Mammalia
Order - Carnivora
Family – Canidae
Gender - Kennels
Species – familiar kennels
Learn more about classification of living beings.
question 4
What are the 5 realms in which living things are classified?
a) Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista and Eukarya.
b) Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Eubacteria and Monera.
c) Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Virus and Archaea.
d) Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista and Monera.
Correct alternative: d) Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista and Monera.
The 5 Kingdoms was a classification proposed in 1969 by Whittaker. Are they:
Animalia: heterotrophic, eukaryotic and multicellular organisms.
Plantae: eukaryotic, autotrophic and chlorophyll organisms.
Fungi: unicellular or multicellular eukaryotic organisms.
Protista: eukaryotic, autotrophic or heterotrophic and unicellular or multicellular organisms.
Monera: prokaryotic, unicellular, autotrophic or heterotrophic organisms.
Note that viruses are not included in this classification, as they are acellular beings. The classification into 5 Kingdoms mainly takes into account the type of nutrition and cell organization.
Another way to classify living beings is through 3 domains, based on biochemical characteristics:
Archaea: chemotrophic and prokaryotic organisms
Bacteria: unicellular organisms and prokaryotes
Eukarya: eukaryotic organisms
See too: Living beings and non-living beings
question 5
About phylogenetic trees, it is correct to state that:
a) Represent the kinship between indefinite members.
b) Represent the evolutionary kinship relationships.
c) Represent the genealogy of living beings with morphological differences.
d) Represent the junction between different species of an ecosystem.
Correct alternative: b) Represent evolutionary kinship relationships.
The branches presented in a phylogenetic tree demonstrate how the evolution of species occurred over time.
This description is important for studying the history of species through a graphical representation.
A cladogram is a kind of phylogenetic tree, without describing elapsed time. See the diagram below.
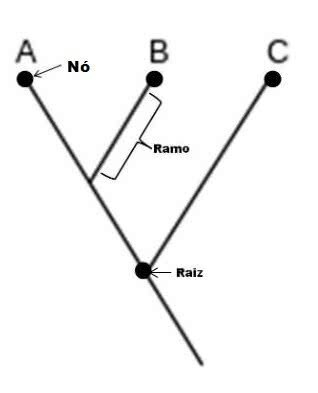
Root: probable ancestral group or species.
Node: Indicates a cladogenetic event.
Branch: lead to one or more end groups.
Learn more about Phylogeny and Evolution theory.
question 6
Correctly list the two columns below.
I. Animals
II. Vegetable
III. protists
IV. Fungi
V. Bacteria
SAW. Virus
( ) comprise protozoa and algae.
( ) They are intracellular parasites
( ) comprises bacteria and cyanobacteria (blue or cyanophyceous algae).
( ) mushrooms, molds, wooden ears, lichens are examples of this kingdom.
( ) is formed by autotrophic organisms (they produce their own food) and chlorophylls.
( ) are beings that have the ability to move around and most of them generate descendants through sexual reproduction.
The correct sequence is:
there; II; III; IV; V; SAW
b) III; V; II; I; IV; IV
c) II; V; IV; SAW; III; I
d) I; IV; V; SAW; III; II
e) III; SAW; V; IV; II; I
Correct answer: e) III; SAW; V; IV; II; I.
Animals are beings that have the ability to move and most generate descendants through sexual reproduction.
Vegetables are autotrophic (they produce their own food) and chlorophyll organisms.
Protists include protozoa and algae.
Fungi are represented by mushrooms, molds, wooden ears and lichens.
Bacteria are represented by bacteria and cyanobacteria (blue or cyanophyceous algae).
Viruses are intracellular parasites.
Read too: What are living beings?
question 7
(PUC-RJ) The maned wolf and the jaguar are two specimens of our fauna threatened with extinction. The following diagram shows the main taxonomic categories to which these animals belong:
Maned wolf: Cordado > mammal > carnivore > canid > Chrysocyon > C. brachyurus Puma: Chordate > mammal > carnivore > felid > Felis > F. concolor
The analysis of the diagram allows us to say that the two animals are close in the same category until:
the class.
b) phylum.
c) family.
d) gender.
e) order.
Correct alternative: e) order.
The taxonomic classification follows the order Kingdom ⇒ Phylum ⇒ Class ⇒ Order ⇒ Family ⇒ Genus ⇒ Species.
Therefore, we can say that the maned wolf and the jaguar are beings that are close in the same category until order, carnivorous, which groups animals that feed on meat and fat.
question 8
(FUVEST) Consider the following characteristics attributed to living beings:
I. Living things are made up of one or more cells.
II. Living beings have genetic material interpreted by a universal code.
III. When considered as populations, living beings change over time.
Assuming that having all these characteristics is a mandatory requirement to be classified as a "living being", it is correct to state that:
a) viruses and bacteria are living beings because they both meet requirements I, II and III.
b) viruses and bacteria are not living beings, because both do not meet requirement I.
c) viruses are not living beings because they meet requirements II and III, but not requirement I. d) viruses are not living beings because they meet requirement III but not requirements I and II. e) viruses are not living beings, as they do not meet requirements I, II and III.
Correct alternative: c) viruses are not living beings because they meet requirements II and III, but not requirement I.
Viruses are beings made up of genetic material, DNA or RNA, surrounded by a protective cover, so they are acellular beings.
They are known as intracellular parasites, as they only perform their functions in a host organism. These organisms have a high mutating power.
Learn more about Characteristics of Living Beings.
question 9
(Unicamp-SP) According to the binomial nomenclature system established by Linnaeus, the scientific name Felis catus applies to all domestic cats such as Angora, Siamese, Persian, Abyssinian and piebald. The wild cat (Felis silvestris), the lynx (Felis lynx) and the puma or puma (Felis concolor) are species related to the cat.
a) To which genus do all the animals mentioned belong?
Correct answer: Felis gender.
b) Why are all domestic cats designated by the same scientific name?
Correct answer: Because they belong to the same species.
c) Which of the following names correctly designates the family to which these animals belong: Felinaceae, Felidae, Felini, Felinus or Felidaceae? Justify.
Correct answer: Felidae, as nomenclatures ending in "idae" correspond to the family name according to the classification system.
question 10
(PUC-RIO). Considering that all living things need a carbon source to build their organic molecules, the essential difference between autotrophs and heterotrophs, respectively, is:
a) use organic carbon and inorganic carbon.
b) use inorganic carbon and organic carbon.
c) use carbon from water and air.
d) use methane and carbon dioxide.
e) perform aerobic respiration and fermentation.
Correct alternative: b) use inorganic carbon and organic carbon.
Autotrophic beings are those who have the ability to produce their own food. These organisms, usually green because of the chlorophyll pigment, use carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere as a source of carbon, which is an inorganic carbon, in the photosynthesis process to obtain nutrients and energy.
Heterotrophic beings get nutrients and energy by feeding on other living beings, taking advantage of their carbon sources, therefore organic carbon.
Keep testing your knowledge with the lists:
- Exercises on Ecology
- Virus Exercises
- Exercises on Fungi
- Exercises on Genetics


