Cycle of carbon it is a biogeochemical cycle, that is, a process that guarantees carbon recycling, allowing this element to interact with the environment and also with living beings. In this cycle, we see how carbon moves through the atmosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere.
Stages of the carbon cycle
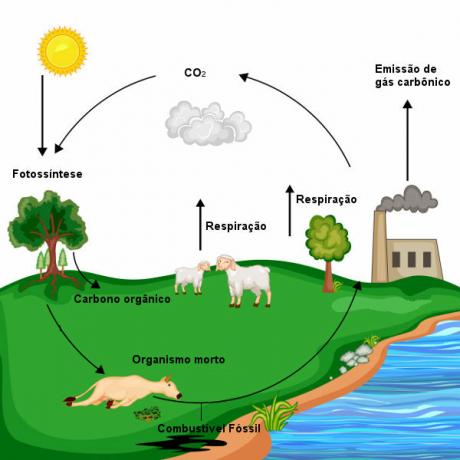
The carbon cycle can be divided into two cycles that occur at different speeds: the geological carbon cycle it's the biological carbon cycle. These two cycles, while easier to understand separately, are intertwined. Learn more about them:
Geological carbon cycle
is responsible for regulate the movement of carbon through the atmosphere, hydrosphere and lithosphere and stands out for being a cycle Late. Carbon, as we know, is found in soils, rocks, aquatic environments, such as in oceans, and in the atmosphere.
Carbon dioxide (CO2), present in the atmosphere, is soluble in water, so a continuous exchange between CO2 in the atmosphere and the aquatic environment
. Another form of movement happens when the CO2dissolves in rainwater, producing H2CO3, which is an acidic solution, which facilitates the erosion of silicate rocks.O weathering process (set of processes that lead to the disintegration of rocks) also causes the release of Ca ions2+ and HCO3. These ions can be taken to the ocean and used by marine organisms to form shells. These shells, when the animal dies, are deposited in the environment and accumulate, forming part of the sediment at the bottom of the oceans. This sediment later forms limestone rocks. the CO2 can still be released by volcanoes to atmosphere.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Biological carbon cycle
involves the living beings of the planet and can occur in terrestrial and aquatic environments. photosynthetic organismss are responsible for removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. In the process of photosynthesis, these organisms use CO2 and release oxygen (O2). In photosynthesis, carbon is used to make organic molecules.
Living beings need organic matter to survive. while the autotrophic are capable of producing organic molecules, heterotrophs need to consume these molecules from other living beings, this being the case, for example, of human beings. In this way, through the organic matter, the carbon passes through the chains and webs food.
Living beings are also responsible for releasing carbon dioxide into the environment. The release occurs by two processes: the process ofbreathing and the process ofdecomposition. In breathing, organisms use oxygen and release carbon dioxide in the process. In the decomposition, there is the release of carbon dioxide and Water.
It is also important to highlight that, in recent years, human beings have contributed to the increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels. Activities like the logging and the use of fossil fuels have guaranteed a significant increase of this gas in the atmosphere, and, with this, an increase in the so-called greenhouse effect has been observed.
Read more about:Brazilian environmental problems
greenhouse effect and global warming
We call a greenhouse effect a natural phenomenon which guarantees a warming the earth's surface, essential for the survival of life on the planet. This effect is achieved thanks to the presence of gases in the atmosphere, called greenhouse gases, which are capable of retaining part of the heat coming from the Sun. Among these are carbon dioxide and methane gas.

In recent years, what has been observed is a growing increase in the emission of these greenhouse gases. Carbon dioxide, for example, is added to the atmosphere on a large scale through processes such as burning fossil fuels. Increased CO concentration2 in the atmosphere is related to the increase in the greenhouse effect and an increase in the temperature of the planet, which is known as global warming.
The increase in the planet's average temperature is an issue that deserves attention, as this warming can trigger serious problems. Among the main consequences of global warming, we can mention:
Increased rainfall in some regions and long periods of drought in others;
Melting of glaciers;
Sea level rise;
Lost of biodiversity;
Supply problems;
Increased cases of some diseases, such as dengue and malaria.
If you are more interested in the themes of this topic, read our texts: Greenhouse effect and Global warming.
Know more: Climate changes
Importance of the carbon cycle
The carbon cycle is essential for the survival of life on the planet, since the carbon is an element that is part of the structure of all organic molecules. In addition, this element is present in much of the material that makes up our planet, such as rocks, oceans and the atmosphere.
Mind Map: Carbon Cycle

* To download the mind map in PDF, Click here!
carbon cycle summary
Carbon is an element found in several reservoirs on the planet, such as rocks and the atmosphere.
Carbon forms the structure of organic molecules.
The carbon cycle involves a geological cycle and a biological cycle, which are interlinked.
In the geological cycle, carbon moves through the atmosphere, hydrosphere and lithosphere, while in the biological cycle, carbon moves through living beings.
Photosynthesis, respiration and decomposition processes are essential for the carbon cycle.
The action of human beings has caused an increase in carbon dioxide available in the atmosphere, accentuating the greenhouse effect and contributing to global warming.
Global warming is responsible for triggering changes on our planet, among which we can cite sea level rise, melting glaciers, extreme droughts and loss of biodiversity.
Read too:Global Warming and Species Extinction
By Ma. Vanessa dos Santos