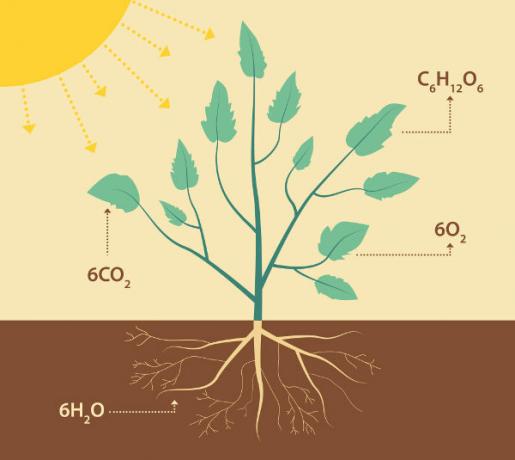
THE photosynthesis is a photochemical process that consists in the production of energy through sunlight and carbon fixation from the atmosphere.
It can be summarized as the process of transforming light energy into chemical energy. The term photosynthesis has as meaning synthesis by light.
Photosynthesis process

Photosynthesis is a process that takes place inside the plant cell, from CO2 (carbon dioxide) and H2O (water), as a way to produce glucose.
Plants, algae, cyanobacteria and some bacteria carry out photosynthesis and are called chlorophyll beings, because they have an essential pigment for the process, chlorophyll.
Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts, an organelle present only in plant cells, and where the pigment chlorophyll, responsible for the green color of plants, is found.
Pigments can be defined as any type of substance capable of absorbing light. Chlorophyll is the most important pigment in plants for the absorption of photon energy during photosynthesis. Other pigments also participate in the process, such as carotenoids and phycobilins.
Absorbed sunlight has two basic functions in the photosynthesis process:
- Boost electron transfer through compounds that donate and accept electrons.
- Generate a proton gradient necessary for the synthesis of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate - energy).
Also read about plant parts.
photosynthesis equation
In summary, we can clarify the photosynthesis process through the following reaction:
H2O and CO2 are the substances needed to carry out photosynthesis. Chlorophyll molecules absorb sunlight and break down H2O, releasing O2 and hydrogen. Hydrogen joins CO2 and forms glucose.
This process results in the general photosynthesis equation, which represents an oxidation-reduction reaction. H2O donates electrons, like hydrogen, to reduce CO2 to form carbohydrates in the form of glucose (C6H12O6).
However, the photosynthetic process is more detailed and takes place in two stages, as we will see below.
Photosynthesis steps
Photosynthesis is divided into two stages: the light phase and the dark phase.
light phase
The clear, photochemical or luminous phase, as the name defines it, are reactions that occur only in the presence of light and take place in the lamellae of the thylakoids of the chloroplast.
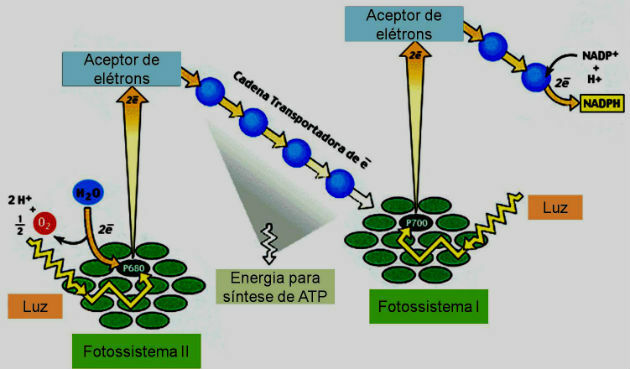
The absorption of sunlight and the transfer of electrons takes place through photosystems, which are sets of proteins, pigments and electron transporters, which form a structure in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplast.
There are two types of photosystems, each with about 300 chlorophyll molecules:
- Photosystem I: Contains a P reaction center700 and preferentially absorbs light of a wavelength of 700 nm.
- Photosystem II: Contains a P reaction center680 and absorbs light preferably of wavelength at 680 nm.
The two photosystems are linked by an electron transport chain and act independently but complementary.
Two important processes take place in this phase: photophosphorylation and photolysis of water.
Photophosphorylation
Photophosphorylation is basically the addition of a P (phosphorus) to ADP (Adenosine diphosphate), resulting in the formation of ATP.
The moment a photon of light is captured by the antenna molecules of the photosystems, its energy is transferred to the reaction centers, where chlorophyll is found. When the photon hits the chlorophyll, it becomes energized and releases electrons that have gone through different acceptors and formed, along with H2O, ATP and NADPH.
Photophosphorylation can be of two types:
- acyclic photophosphorylation: The electrons that were released by chlorophyll do not return to it, but to the other photosystem. Produces ATP and NADPH.
- Cyclic Photophosphorylation: The electrons return to the same chlorophyll that released them. Form only ATP.
water photolysis
The photolysis of water consists of breaking down the water molecule by the energy of sunlight. The electrons released in the process are used to replace the electrons lost by chlorophyll in photosystem II and to produce the oxygen we breathe.
The general equation of photolysis or Hill reaction is described as follows:
Thus, the water molecule is the ultimate electron donor. The ATP and NADPH formed will be used for the synthesis of carbohydrates from CO2. However, this will happen in the next step, the dark phase.
dark phase
The dark phase, pentose cycle or Calvin cycle can occur in the absence and presence of light and happens in the chloroplast stroma. During this phase, glucose will be formed from CO2. Thus, while the light phase provides energy, in the dark phase carbon fixation takes place.

Check out a summary of how the Calvin cycle occurs:
1. Carbon fixation
- At each turn of the cycle, a CO molecule2 is added. However, it takes six complete turns to produce two molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and one molecule of glucose.
- Six molecules of ribulose diphosphate (RuDP), with five carbons, bind to six molecules of CO2, producing 12 molecules of phosphoglyceric acid (PGA), with three carbons.
2. Production of organic compounds
- The 12 molecules of phosphoglyceric acid (PGAL) are reduced to 12 molecules of phosphoglyceric aldehyde.
3. Regeneration of diphosphate ribulose
- Of the 12 phosphoglyceric aldehyde molecules, 10 combine with each other to form 6 RuDP molecules.
- The two remaining phosphoglyceric aldehyde molecules serve to initiate the synthesis of starch and other cellular components.
The glucose produced at the end of photosynthesis is broken down and the energy released allows cell metabolism to take place. The process of breaking down glucose is the cellular respiration.
Importance of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the basic process of transforming energy in the biosphere. It supports the base of the food chain, in which the feeding of organic substances provided by green plants will produce food for heterotrophic beings.
Thus, photosynthesis has its importance based on three main factors:
- Promotes CO capture2 atmospheric;
- Performs the renewal of the O2 atmospheric;
- It drives the flow of matter and energy in ecosystems.
Photosynthesis and Chemosynthesis
Unlike photosynthesis that requires light to occur, chemosynthesis happens in the absence of light. It consists in the production of organic matter from mineral substances.
It is basically a two-step process performed only by autotrophic bacteria to obtain energy. In the first step, inorganic substances are oxidized and, in the second step, carbon dioxide undergoes reduction, leading to the production of organic compounds.
1st step: Inorganic Compound + O2 → Oxidized Inorganic Compounds + Chemical Energy
2nd stage: CO2 + H2O + Chemical Energy → Organic Compounds + O2
Learn more, read also:
- carbon cycle
- oxygen cycle
- Botany: the study of plants