You Time zones, also called time zones, are each of the 24 time zones drawn by an imaginary line from one pole to the other of the terrestrial globe.
The purpose of this division is to standardize the calculation of time across planet Earth.
Due to geopolitical issues, each nation may adopt a certain time as a reference, which can lead to distortions.
Before this methodology, clocks were set in each city that passed through or, as in the Middle Ages, by the apparent solar time at noon.
Time zones corrected this by instituting an average solar time. However, this standardization process only began in 1878, when Sanford Fleming, based on his astronomy studies, proposed the division of the world into 24 vertical bands.
Later, in 1884, at the "International Conference on the First Meridian", held by representatives of 25 countries in Washington, the planetary standardization of the hour was adopted and agreed upon.
Fundamental concepts for understanding time zones
Meridians
The meridians are the semicircumferences that connect the poles and divide the globe into two hemispheres: the western (west of the GMT) and the east (east of the GMT). They determine the multiples of 15° that make up the total of 360° of the Earth's circumference.
At the intersection between these lines, which is wider as it approaches the Equator, we will have the same timetable running from North to South.

Greenwich Mean Time
The Greenwich Meridian is the longitudinal landmark to determine the “Greenwich Mean Time” (GMT). Therefore, Longitude 0° would pass over Greenwich, near London. East of this mark, count to 180° positive and, to the west of it, to 180° negative.

How to calculate Time Zones?
This methodology takes into account the rotation movement from Earth, counterclockwise to the East. Thus, we advance the hours of the time zones to the East, and we delay the hours to the West of the GMT (Greenwich Mean Time, in Portuguese Greenwich Mean Time).
So, to determine the time zones of a location, we have to know its geographic coordinates.
To complete the rotation, planet Earth takes approximately 23 hours, 56 minutes and 4 seconds. The proportion is 1h for every 15° of rotation, that is, 1° every 4 minutes.
Thus, in 24 hours, the Earth will have completed the 360° turn.
In each 15º of longitude we have a time zone that is equivalent to one hour, being the Greenwich Meridian the longitudinal zero mark of the Earth. Therefore, from it we can count the imaginary vertical lines (of one hour each), which increase if located to the east of the globe, or decrease if located to the west.
Parallel lines (latitudes), in turn, determine the average width of the spindles. For this reason, on the equator the time zone will be 1667 km, while in the tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, the width will be 1529 km. It continues to decrease, until reaching the poles, where the average width of the spindles will be 289.4 km.
Exercise
(UFSM-RS) Look at the map below and answer the question below.
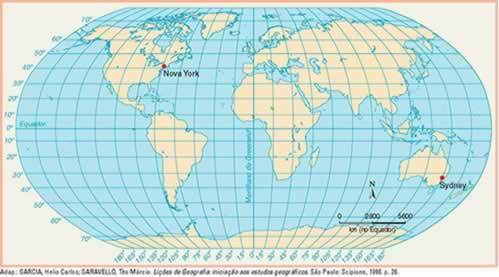
Disregarding local daylight saving times, the geographic coordinates of the map also allow us to deduce that a sports competition that takes place in Sydney, at 4 pm, is watched on TV, live, in New York at):
a) 7 hours.
b) 8 hours.
c) 2 hours.
d) 1 hour.
it's midnight.
Letter d) 1 hour.
Time Zones in Brazil
Located in the Western Hemisphere, Brazil has 4 time zones and, in relation to the Greenwich Meridian (GMT), it has its delayed time varying from two to five hours less:
- Zone 1 (-2GMT): It has two hours less than the Greenwich Meridian.
- Zone 2 (-3GMT): it has three hours less than the Greenwich Meridian, corresponds to the official time zone in Brazil (Brasilia-DF time).
- Zone 3 (-4GMT): It has four hours less than the Greenwich Meridian.
- Zone 4 (-5GMT): It has five hours less than the Greenwich Meridian.
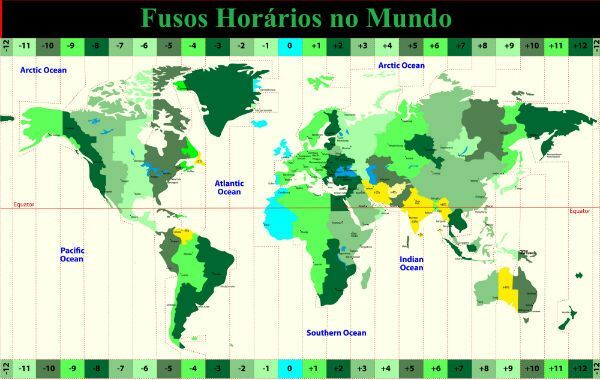
World Time Zone
Among the world time zones, the following stand out:
- European Time Zone (GMT + 1), which covers most of Europe and West Africa;
- USA Time Zone (GMT – 5) which covers the United States and northwestern South America;
- Russian Time Zone (GMT + 3), which comprises European Russia, Arabian Peninsula and East Africa.
Some fun facts about Time Zones
- China has four time zones, but only adopts Beijing time for the entire nation
- The time difference between São Paulo and Japan is 12 time zones, that is, 12 hours. So, when it's 9am in São Paulo, it's already 9pm in Japan.
- The official time zone for Antarctica is GMT 0.00.
- Changing time zones quickly can cause a type of stress called jet lag, characterized by irritability and altered sleep and appetite patterns.
- Russia, due to its great extension, has 11 time zones in its territory.

