Connective tissue it is a connecting tissue, composed of a large amount of extracellular matrix, cells and fibers.
Its main functions are to provide support and fill spaces between tissues, in addition to nourishing them.
There are special types of connective tissue, each with a specific function. This varies mainly according to the composition of the matrix and the type of cells present.
Connective Tissue Types
THE classification of the different connective tissues can be made according to the material and type of cells that compose it.
THE extracellular matrix, which is the substance between cells, has variable consistency. It can be: gelatinous (loose and dense connective tissue), liquid (blood), flexible (cartilaginous), or rigid (bone).
Thus, it can be divided into connective tissue itself and connective tissues with special properties, namely: adipose, cartilaginous, bone and blood.
Connective Tissue Properly Said
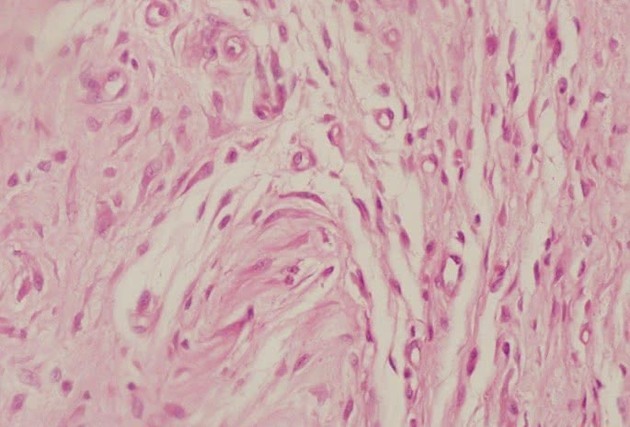
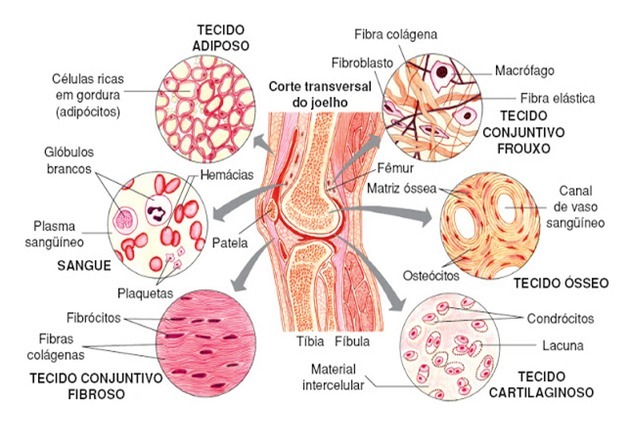
This fabric, as the name implies, is the typical
binding fabric. It acts in the support and filling of tissues and, in this way, helps them to stay together, structuring the organs.Its extracellular matrix is abundant, composed of a gelatinous part (hyaluronate polysaccharide) and three types of protein fibers: collagen, elastic and reticular.
There are two subtypes of connective tissue itself, classified according to the amount of matrix present, they are:
loose connective tissue
It consists of little extracellular matrix, with many cells and few fibers.
This makes the fabric flexible and poorly resistant to mechanical pressure. Some cells are resident, such as fibroblasts and macrophages and others are transient, such as: lymphocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils.
It is found throughout the body, involving organs. It also serves as a passageway to blood vessels, thus being important in tissue nutrition.
dense connective tissue
It has large amount of extracellular matrix, with a predominance of collagen fibers, arranged without great organization. There are few cells present, among them the fibroblasts.
It is found below the epithelium, in the dermis, giving resistance to mechanical pressure, thanks to its many fibers. It is also widely found in tendons.
Also read about epithelial tissue
adipose connective tissue
It is a type of connective tissue with special properties. Its function is energy reserve and also protection against cold and impacts.
It consists of little extracellular matrix, with a considerable amount of reticular fibers and many special cells, the adipocytes, which accumulate fat.
Cartilaginous Connective Tissue

It's composed by large amount of extracellular matrix, however, it is more rigid in this tissue than in the connective tissue itself. This is due to the presence of glycosaminoglycans associated with proteins, in addition to fine collagen fibers.
In the cartilages, made up of this tissue, the chondrocytes, cells that are housed within gaps in the matrix.
Due to its special consistency, the cartilaginous tissue supports various regions of the body, but with a certain flexibility.
Bone Connective Tissue
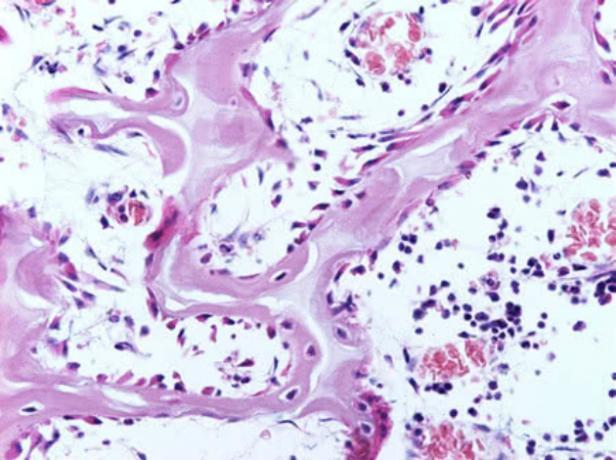
It is a more rigid tissue, present in bones and responsible for support and movement.
Is composed of abundant extracellular matrix, rich in collagen fibers and special molecules (proteoglycans and glycoproteins). The matrix is calcified by the deposition of crystals (formed from calcium phosphate) on the fibers.
The special tissue cell, the osteocyte, lies within gaps in the rigid matrix. It is a mature cell originated from the osteoblasts, young bone cells.
Blood Connective Tissue
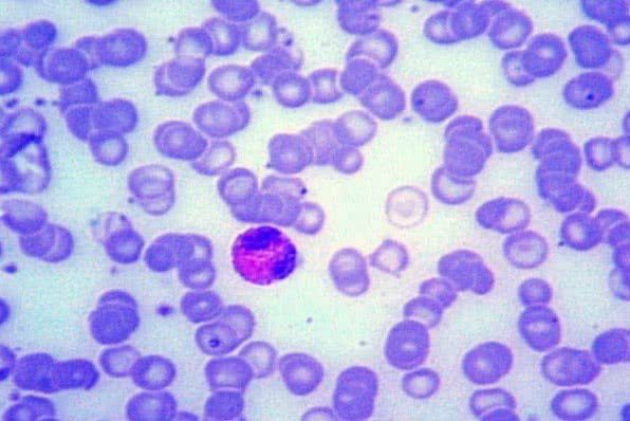
It is a special fabric whose matrix is in liquid state. This substance is called plasma, in it are the blood cells: red blood cells (red blood cells) and White blood cells (leukocytes) and the platelets (cell fragments).
Hematopoietic or hemocytopoietic tissue is responsible for the formation of blood cells and blood components. He is present in the bone marrow, located inside some bones.
Roles
Each type of connective tissue has specific types of cells and its extracellular matrix contains different molecules and fibers that determine its function.
- Fills spaces between different fabrics and structures;
- It participates in the nutrition of cells from other tissues that do not have vascularization, as it facilitates the diffusion of nutrients, in addition to gases, between blood and tissues;
- Energy reserve in adipose cells;
- It acts in the body's defense through its cells;
- It produces blood cells in the bone marrow.
Video
To reinforce what was presented about connective tissue types and their characteristics, watch the video below.
Read too:
- human body tissue
- nerve tissue
- Muscle tissue
- Histology
- animal histology