When we talk about blood circulation, we immediately imagine the human circulation: with blood running in blood vessels thanks to the impulse generated by the heart. However, not all organisms have this way of transporting blood. Let's get to know the main existing types of circulation below.
→ open and closed circulation
We commonly observe blood flowing through blood vessels, however, this does not happen in all animals. Using this feature as a classification criterion, we have two types of circulation:
Open or incomplete circulation: In this type of circulation, the blood passes through a main vessel and is released into cavities (gaps) in the body for the occurrence, directly with the cells, of gas exchange. This circulation is seen in arthropods and molluscs.
Closed circulation: In this type of circulation, blood flows only inside blood vessels. Among the best known types of blood vessels, we can mention the arteries, veins and capillaries. This type of circulation occurs in all vertebrates and annelids.
→ Single and double circulation
There is also the classification that is based on the analysis of how many times the blood passes through the heart in a complete circuit throughout the body. In this case, we have two types of circulation:
-
Simple circulation: blood passes through the heart only once. This case is observed in the fish, in which blood rich in carbon dioxide (venous) leaves the heart towards the gills, where it is oxygenated (arterial blood) and goes to the body. In the body, gas exchange occurs and blood returns to the heart rich in carbon dioxide, starting a new cycle.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
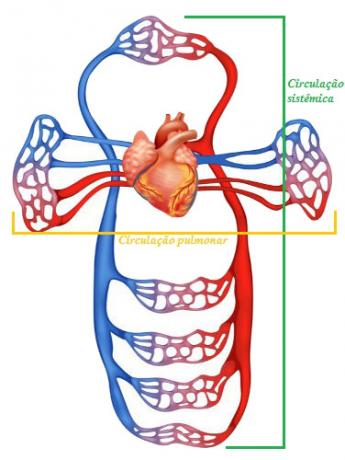
In dual circulation, we can observe the pulmonary and systemic circulation
Double circulation: blood passes through the heart twice. The circuit that takes blood from the heart to the lung and from the lung back to the heart is called the pulmonary circulation. The circuit that takes blood from the heart to the tissues of the body and from there to the heart is called systemic circulation.
→ Complete and incomplete circulation
Analyzing whether or not there is a mixture of blood rich in carbon dioxide and blood rich in oxygen, we can classify the double circulation in:
Incomplete circulation: a mixture of oxygen-rich blood and carbon dioxide-rich blood occurs and can be observed in amphibians and reptiles. The first group has a heart with three cavities, which allows for the mixing of blood. In reptiles, non-crocodilians have a heart with three cavities and crocodilians have a heart with four cavities, but the mixture occurs in a structure called the foramen of Bakery.
Full circulation: blood rich in carbon dioxide does not mix with blood rich in oxygen. It takes place in birds and mammals. These two groups have a heart with four cavities: two atria and two ventricles.
Heads up:In human beings, circulation is closed, double and complete!
By Ma. Vanessa dos Santos
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SANTOS, Vanessa Sardinha dos. "Types of blood circulation"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/tipos-circulacao-sanguinea.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.