The distance between two points is the measure of the line segment that joins them.
We can calculate this measure using Analytical Geometry.
Distance between two points on the plane
In the plane, a point is fully determined knowing an ordered pair (x, y) associated with it.
To know the distance between two points, we will initially represent them in the Cartesian plane, and then calculate this distance.
Examples:
1) What is the distance between point A (1.1) and point B (3.1)?
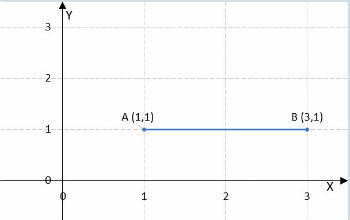
d (A, B) = 3 - 1 = 2
2) What is the distance between point A (4.1) and point B (1,3)?
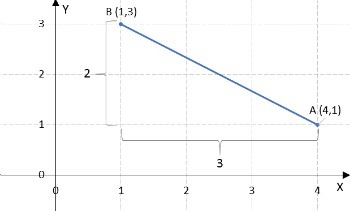
Note that the distance between point A and point B is equal to the hypotenuse of the right triangle with legs 2 and 3.
So, we will use the Pythagorean theorem to calculate the distance between the given points.
[d(A, B)]2 = 32 + 22 = √13
Formula of distance between two points on the plane
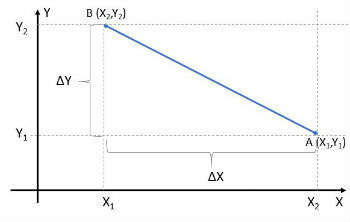
To find the distance formula, we can generalize the calculation done in example 2.
For any two points, such as A(x1yy1) and B (x2y2), we have:
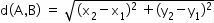
To learn more, read also:
- plane geometry
- Cartesian Plan
- straight
Distance between two points in space
We use a three-dimensional coordinate system to represent points in space.
A point is fully determined in space when there is an ordered triple (x, y, z) associated with it.
To find the distance between two points in space, initially we can represent them in the coordinate system and from there, perform the calculations.
Example:
What is the distance between point A (3,1.0) and point B (1,2.0)?

In this example, we see that point A and B belong to the xy plane.
The distance will be given by:
[d(A, B)]2 = 12 + 22 = √5
Formula of the distance between two points in space

To learn more, read also:
- Spatial Geometry
- Line Equation
- Math Formulas
Solved Exercises
1) A point A belongs to the abscissa axis (x axis) and is equidistant from points B (3.2) and C (-3.4). What are the coordinates of point A?
As point A belongs to the abscissa axis, then its coordinate is (a, 0). So we have to find the value of a.
(0 - 3)2 + (a - 2)2 = (0 + 3)2 + (to -4)2
9 + to2 - 4th +4 = 9 + a2 - 8th + 16th
4th = 12
a = 3
(3.0) are the coordinates of point A.
2) The distance from point A (3,a) to point B (0.2) is equal to 3. Calculate the ordinate value a.
32 = (0 - 3)2 + (2 - a)2
9 = 9 + 4 - 4a +a2
The2 - 4th +4 = 0
a = 2
3) ENEM - 2013
In recent years, television has undergone a real revolution, in terms of image quality, sound and interactivity with the viewer. This transformation is due to the conversion of the analog signal to the digital signal. However, many cities still do not have this new technology. Seeking to bring these benefits to three cities, a television station intends to build a new transmission tower, which sends a signal to antennas A, B and C, which already exist in these cities. The locations of the antennas are represented in the Cartesian plane:
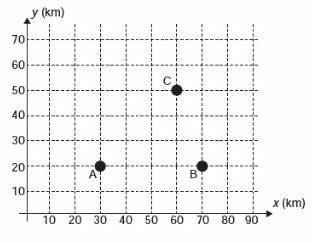
The tower must be located at an equidistant location from the three antennas. The proper place for the construction of this tower corresponds to the coordinate point
a) (65; 35)
b) (53; 30)
c) (45; 35)
d) (50; 20)
e) (50; 30)
Correct alternative e: (50;30)
See too: distance between two points exercises
4) ENEM - 2011
A neighborhood of a city was planned in a flat region, with parallel and perpendicular streets, delimiting blocks of the same size. In the following Cartesian coordinate plane, this neighborhood is located in the second quadrant, and the distances in the
axes are given in kilometers.
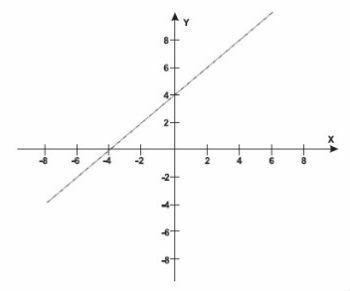
The straight line of equation y = x + 4 represents the planning of the route of the underground subway line that will cross the neighborhood and other regions of the city.
At point P = (-5.5), a public hospital is located. The community asked the planning committee to plan a subway station so that its distance to the hospital, measured in a straight line, would not be more than 5 km.
In response to the community's request, the committee correctly argued that this would be automatically satisfied, as the construction of a station at the point was already planned.
a) (-5.0)
b) (-3.1)
c) (-2.1)
d) (0.4)
e) (2.6)
Correct alternative b: (-3.1).
See too: exercises on analytic geometry