The Valence Layer is the last layer of an atom's electronic distribution. As it is the outermost layer, it is also the furthest from the atomic nucleus.
According to the Octet Rule, the valence shell needs eight electrons to stabilize.
Thus, atoms acquire stability when they have 8 electrons in the valence shell. This happens with noble gases, they have the complete valence layer. The only exception is the element Helium which has 2 electrons.
The other elements need to make chemical bonds to receive the missing electrons and reach the eight electrons in the valence shell.
The valence shell electrons are the ones that participate in the bonds, as they are the most external.
Electrosphere Layers
According to the Rutherford-Bohr atomic model, electrons revolve around the atomic nucleus, in different energetic layers.
There are seven layers designated by the letters K, L ,M, N, O, P and Q. Each supports a maximum number of electrons.
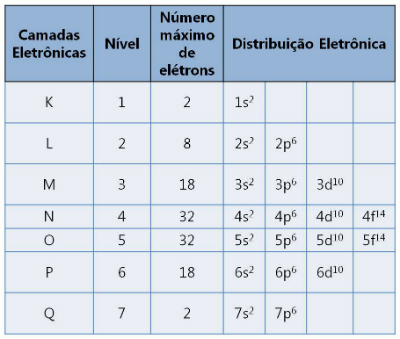 Electronic layers and the numbers of electrons they support
Electronic layers and the numbers of electrons they support
Read too:
- Bohr's atomic model
- Rutherford Atomic Model
- Noble Gases
- Octet Rule
How to determine the Valencia Layer?
The valence layer can be determined in two ways: Eletronic distribution and Periodic table.
To determine the valence layer through electronic distribution, the Linus Pauling diagram.
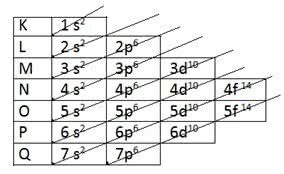 Pauling diagram
Pauling diagram
Recall that the Pauling diagram follows the increasing order of energy. The last layer obtained in the electronic distribution is the valence layer.
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p6 6s2 4f14 5d10 6p6 7s2 5f14 6d10 7p6
So, in the valence layer, the most energetic sublevel is the last layer.
Examples:
Nitrogen - N
Atomic Number: 7
Electronic distribution: 1s2 2s2 2p3
Valencia layer: 2s2 2p3, N has 5 electrons in the valence shell.
Iron - Fe
Atomic Number: 26
Electronic distribution: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6
Valencia layer: 4s2, Fe has 2 electrons in the valence shell.
Chlorine - Cl
Atomic Number: 17
Electronic distribution: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5
Valencia layer: 3s2 3p5, Cl has 7 electrons in the valence shell.
Oxygen - O
Atomic number: 8
Electronic distribution: 1s2 2s2 2p4
Valencia layer: 2s2 2p4, oxygen has 6 electrons in the valence shell.
Carbon - C
Atomic number: 6
Electronic distribution: 1s2 2s2 2p2
Valencia layer: 2s2 2p2, carbon has 4 electrons in the valence shell.
Also read about Quantum Numbers.
So far, the examples used have been with ground state elements. But the same principle can be used for ions, cations and anions. See the example:
Chloride Anion - Cl-
Chlorine's atomic number is 17. If it were in its ground state, the number of electrons would be equal to the number of protons. However, in this case there is a gain of 1 electron.
First, make the electronic distribution for the Chlorine element:
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5
With the gain of an extra electron, add in the last layer:
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6. So there are 8 electrons in the valence shell (3s2 3p6).
See too: Exercises on electronic distribution.
To determine the valence layer through the periodic table, it is necessary to identify the period and the element family.
Thus, while 1A family has 1 valence electron, 2A has 2, and so on. The chemical elements contained in it periodic table family have the same number of electrons in the valence shell.
However, this is only valid for groups 1, 2, 13, 14, 15, 16 and 17 which have the following numbers of electrons in the valence shell 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7, respectively.
For elements where this relationship is not possible, electronic distribution should be used.
Do not forget! At chemical bonds arise from the need to stabilize atoms and thus form molecules. This is done by donating electrons from the valence shell, which, because they are farther from the nucleus, have a tendency to donate.
Also read about Molecular Geometry.
Exercises
1. Find the valence layer of the following elements:
Bromine
35br
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p5
Bromine's valence shell (7A family) has 7 electrons. That's because 4s2 and 4p5 belong to the N layer, while 3d10 belongs to layer M.
Aluminum
13Al
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1
The aluminum valence shell (3A family) has 3 electrons.
2. (UFSC) The number of electrons in each sublevel of the strontium atom (38Sr) in ascending order of energy is:
a) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2
b) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 4p6 3d10 5s2
c) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 5s2
d) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4p6 4s2 3d10 5s2
e) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3p6 3s2 4s2 4p6 3d10 5s2
a) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2
3. (IFSP/2013) The number of electrons in the valence shell of the calcium atom (Z = 20), in the ground state, is
to 1
b) 2
c) 6
d) 8
e) 10
b) 2
Check entrance exam questions with a commented resolution in: Exercises on the Periodic Table.