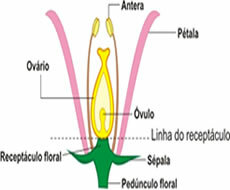
You human body organs they are formed by the grouping of tissues, which in turn are formed by the grouping of cells.
For our organism to function in an integrated way, the organs of the human body constitute a system, where each one acts in a specific way to perform a certain function. It is the set of systems that make up the organism.
Below, we are going to know the main organs of the human body systems and with them they act in our organism.
Main organs of the digestive system
The organs of digestive system they are responsible for absorbing the nutrients we consume, helping throughout the digestion process so that what is not used can be discarded by the body.
The main organs of this system are:
Pharynx

THE pharynx it is a tubular organ with muscular walls that connects the throat to the esophagus.
It is responsible for carrying out the passage of inhaled air and ingested food to the other organs of the respiratory and digestive systems, respectively.
Therefore, the pharynx is a common organ of the digestive and respiratory system.
Esophagus
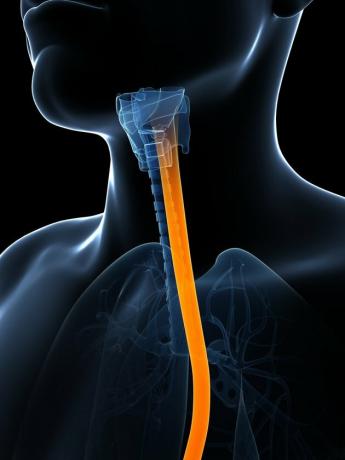
O esophagus it is a tubular organ with muscular walls, responsible for carrying food to the stomach after being transported through the pharynx.
Stomach

O stomach it is shaped like a pouch and is located in the abdomen, between the esophagus and the small intestine.
It is responsible for the partial digestion of food, turning the bolus into chyme.
Liver
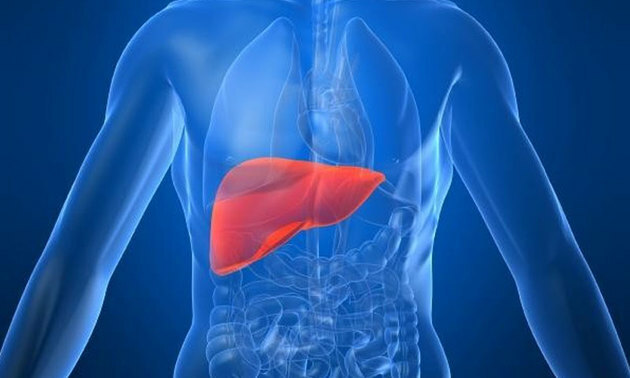
O liver is located in the region of the abdomen, below the diaphragm. It is the largest gland in the human body and develops both endocrine and exocrine activity.
It is responsible for storing and filtering substances, in addition to synthesizing fat and producing bile.
intestines
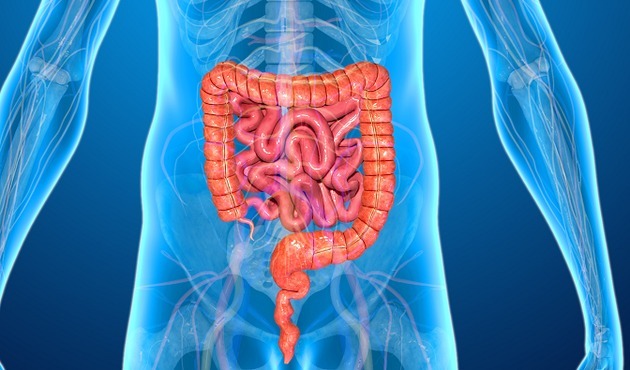
In the human body, it is in the intestines that water and nutrients are absorbed during the digestive process. They are divided into two types.
- O small intestine it is a tubular organ located between the stomach and the large intestine. It is responsible for the absorption of nutrients and is divided into three parts: duodenum, jejunum and ileum.
- O large intestine It is a tubular organ responsible for water absorption, storage and elimination of solid waste and is divided into three parts: cecum, colon and rectum.
Major organs of the respiratory system
The organs of respiratory system they are responsible for the breathing process, that is, the absorption of oxygen and the elimination of carbon dioxide that is removed from the cells. The main organs of this system are:
Larynx
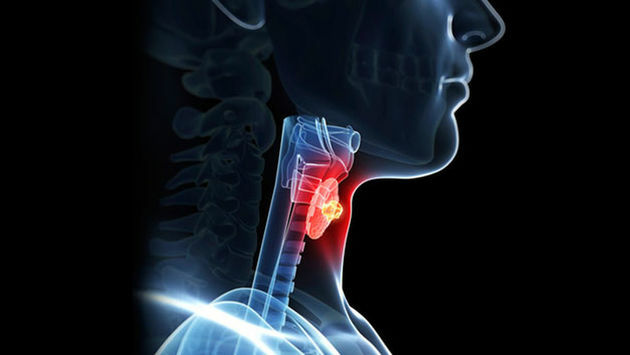
THE larynx it is the main organ of speech, as it aggregates the vocal cords. It is located in the neck, between the pharynx and the trachea.
It receives air from the pharynx and prevents food from passing into the trachea, through the epiglottis, which closes at the time of swallowing.
Trachea

THE trachea it is a hollow tubular organ composed of cartilaginous rings. It is located between the larynx and the bronchi.
Its function is to heat, humidify, filter the air and thus transport it to the lungs.
Lungs
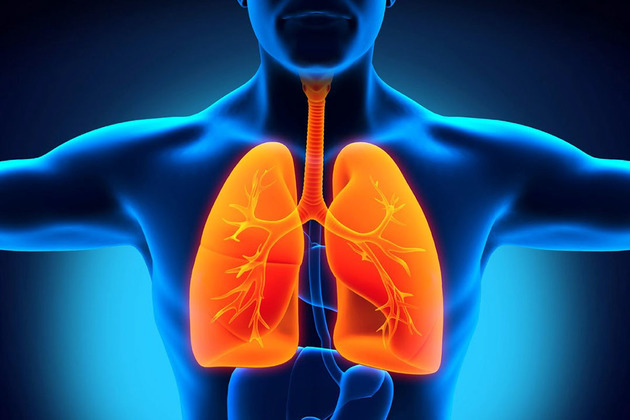
The human body is made up of two lungs, which have a pyramidal shape, spongy consistency and are located in the rib cage.
It is responsible for exchanging gases so that the blood is oxygenated and eliminates carbon dioxide (CO2) of the body.
bronchi
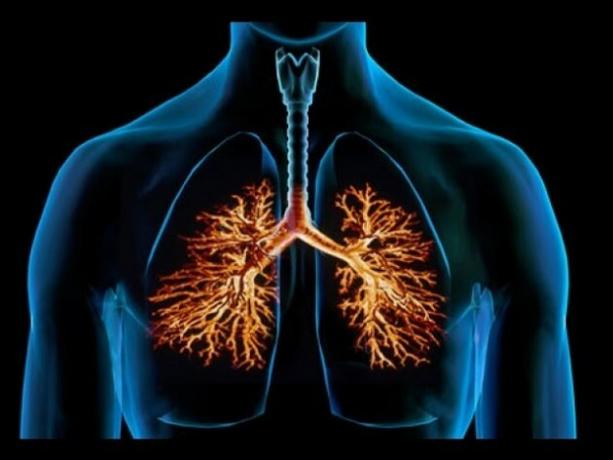
You bronchi they are two tubular organs that connect the trachea to the lungs. They branch out into smaller and smaller tubes called bronchioles
The function of the bronchi is to carry air into the lungs.
Main organs of the endocrine system
The organs of endocrine system are responsible for the production of hormones, which in turn are released into the blood to reach target organs. The main organs of this system are:
Hypophysis
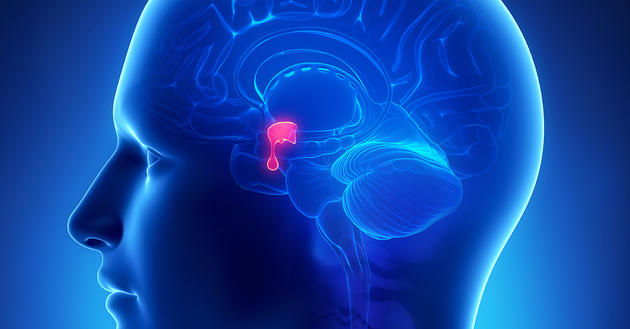
THE hypophysis, pituitary gland or master gland, is a small gland located in the brain.
It is responsible for producing hormones, regulating sexual cycles and controlling the activities of other glands.
Thyroid

THE thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck region. It is one of the largest glands in the human body.
It has important functions in the body, such as regulation of growth, development, fertility, menstrual cycles and emotional control.
parathyroids
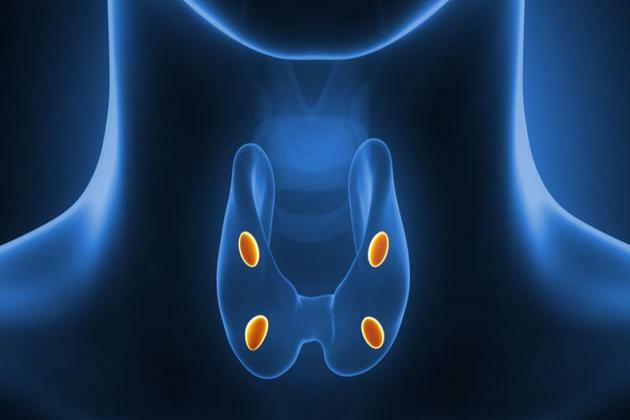
At parathyroids they are four small glands, located around the thyroid.
Its functions are: regulating the amount of calcium in the blood and the production of hormones.
adrenals
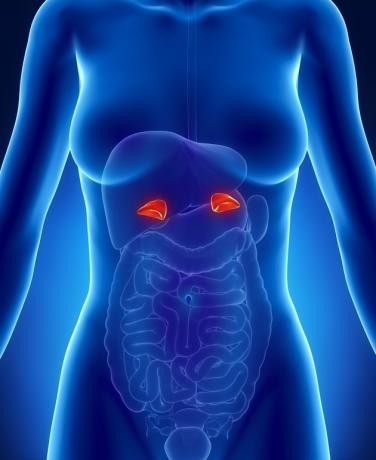
At adrenal glands or adrenals are formed by the cortex and medulla.
They are located above the kidneys and their main function is the production and release of hormones.
pancreas

O pancreas it is a mixed gland responsible for the production of hormones (endocrine system) and pancreatic juice (digestive system).
It is located behind the stomach, between the duodenum and spleen.
Main organs of the circulatory system
The organs of circulatory system or cardiovascular they are responsible for transporting nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide and hormones through the blood. The main bodies that make up this system are:
Heart

O heart, the central organ of the circulatory system, is a hollow muscular organ responsible for pumping blood mediated by two movements: systole (contraction) and diastole (relaxation).
Thus, while the right side pumps venous blood to the lungs, the left side pumps arterial blood to various parts of the body.
Blood vessels
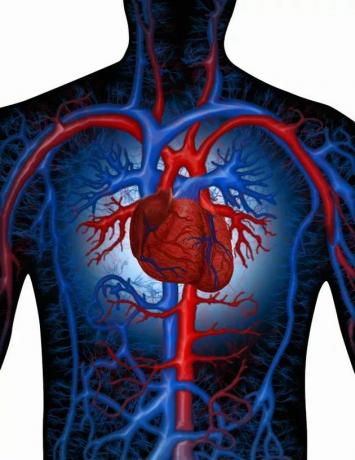
You blood vessels, places where blood circulates throughout the body, are tubular organs distributed throughout the body.
They are formed by veins and arteries, which in turn form capillaries.
Major organs of the nervous system
The organs of nervous system they are responsible for the organisms' communication, that is, they control the voluntary and involuntary movements of the body, emitting and capturing stimuli and messages.
To perform this function, the main organs of this system are:
Brain
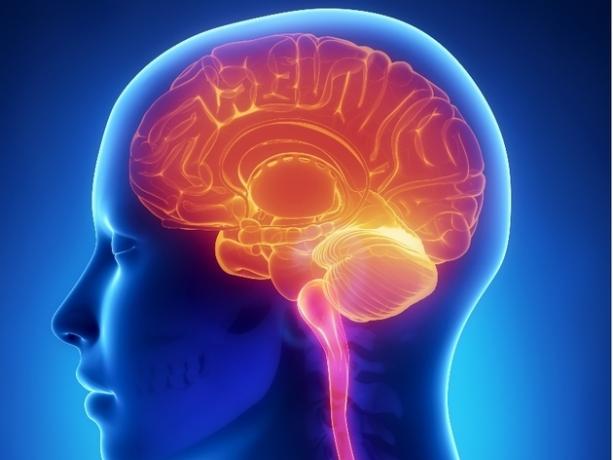
O brain is divided into right hemisphere and left hemisphere.
It is the most important organ of the nervous system, responsible for the production of hormones, as well as the transport, organization and storage of information. It is considered the organism's command center.
Cerebellum
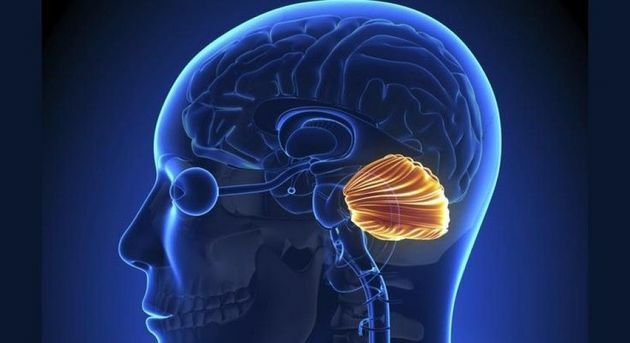
O cerebellum it is an organ located below the brain. It has very important functions such as movement, reflex, muscle contraction and body balance.
Spinal cord
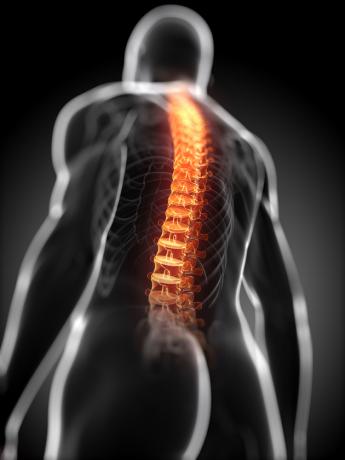
THE spinal cord is a cylindrical cord located in the spine, in the inner canal of the vertebrae.
It is responsible for the production and conduction of nerve impulses from the body to the brain, that is, it communicates between the body and the nervous system.
Main organs of the urinary and excretory systems
The organs of urinary system and excretor their main function is to filter impurities from the blood and, for this to occur, these organs carry out the production and elimination of urine. The main organs of this system are:
Kidneys

The human body is made up of two kidneys, bean-shaped organs that can measure up to 12 cm. They are reddish-brown in color and are located in the back of the abdomen.
Its main functions are: filtering substances, eliminating toxic substances, producing hormones and urine.
Bladder
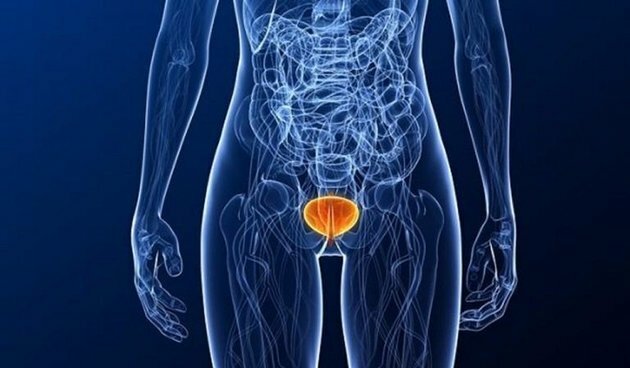
The bladder is the hollow, bag-shaped muscular organ located in the lower abdomen. It is responsible for storing urine, which can reach 800 ml.
Main organs of the reproductive system
The reproductive system has different characteristics and organs for men and women.
The main bodies of the female reproductive system they are:
ovaries

You ovaries they are two oval-shaped organs located in the pelvic cavity of women.
Its function is based on the production of the female hormone, estrogen, as well as the production of eggs, the female sex gametes.
Uterus

Located inside the pelvic cavity the uterus it is a muscular organ, hollow and elastic. He is responsible for menstruation, pregnancy and childbirth.
Its main function is to shelter the fetus after it is fertilized.
Read too:
- Pregnancy and Childbirth
- Normal Delivery and Cesarean Delivery
Clitoris
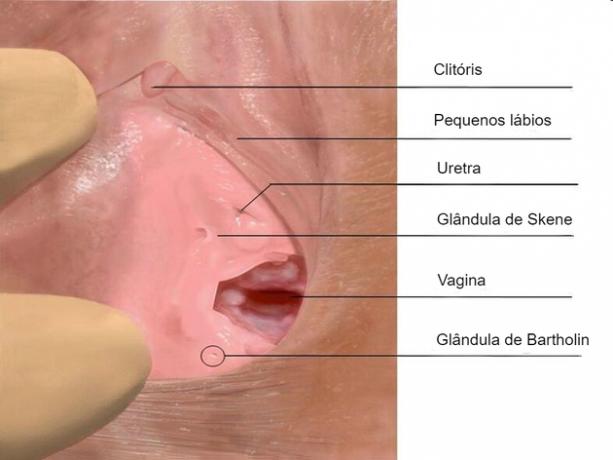
O clitoris it is the female erectile sex organ and is located at the top of the vulva.
Its main function is to provide female pleasure (orgasm), since its structure is formed by numerous nerve endings.
The main bodies of the male reproductive system they are:
Penis
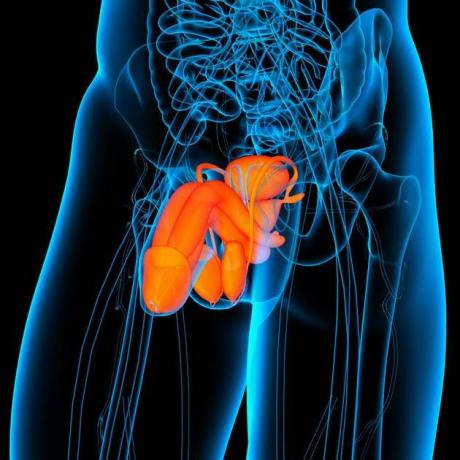
O penis it is the male, external, cylindrical sex organ, which is also part of the urinary system.
For it, there is the elimination of urine and semen, through the urethra canal. It is still responsible for male sexual pleasure.
Prostate
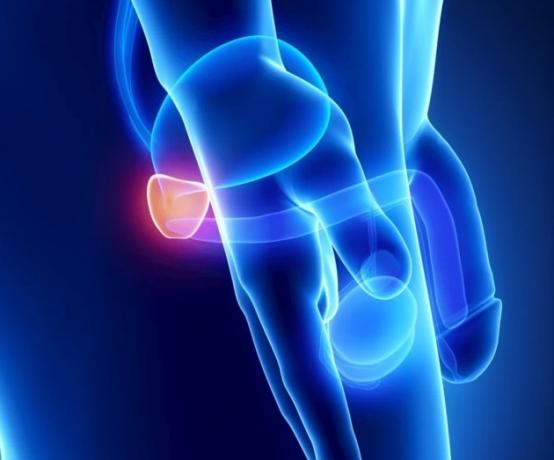
THE prostate is a round-shaped exocrine gland located below the bladder.
It is responsible for the production of a substance that serves to protect sperm.
Testicles

The testes are two male sex glands, oval in shape and located in the scrotum.
Its functions correspond to the production of hormones and male sex gametes, the sperm.
other organs of the human body
Other important organs make up the human body and help the body to function in perfect harmony. These bodies are:
Spleen

O spleen, located in the upper left region of the abdominal cavity, is an oval organ that is part of the lymphatic system.
Its functions are: production and destruction of red blood cells.
Skin
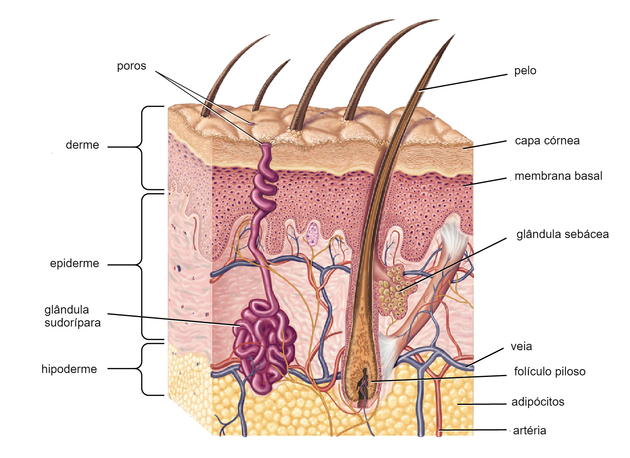
THE skin it is the outer covering of the body, considered the largest and heaviest organ in the body.
She is part of the integumentary system and its main functions are: protection, nutrient reserve and temperature balance.
Read too:
- Dermis
- Epidermis
- hypodermis
- Skin Layers
Appendix
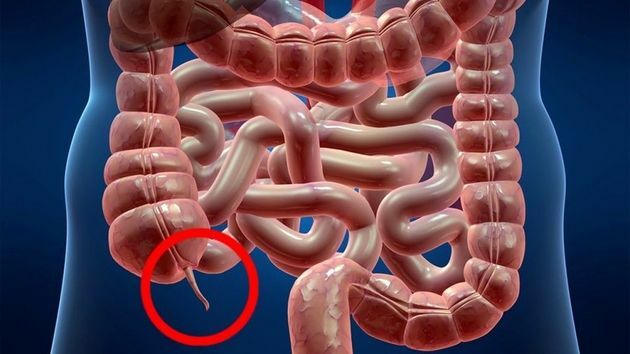
O appendix is a small, hollow, pouch-shaped organ located at the beginning of the large intestine.
Its function is to harbor bacteria that aid in digestion and lymphocytes that contribute to the body's defense. It has a relationship with the immune system.
Now that you know more about the organs of the human body, learn about:
- Human Body
- Parts of the human body
- members of the human body
- bones of the human body
- human body cells
- human body tissue
- human body systems
- Nerves of the human body
- Muscles of the human body
- Organs of the human body without which you can survive
- 8 superpowers of human body cells