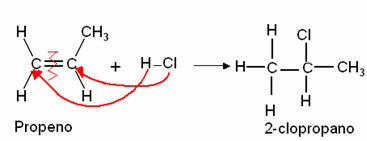
The chemical elements correspond to the grouping of atoms that have the same amount of protons, that is, the same atomic number.
Currently, there are 118 chemical elements, 92 of which are natural (found in nature) and 26 are artificial and artificially produced.
Representation
All known chemical elements are present in the periodic table. They are represented by an acronym, where the first letter is capitalized. If this acronym has two letters, the second will be lowercase, for example:
Iron Element – acronym Fe
In addition, the periodic table provides some important information about the element. The main ones are: name, symbol, atomic number, atomic mass and electronic distribution.

Periodic Classification of Chemical Elements
In the periodic table, the elements are increasingly organized in relation to the atomic number.
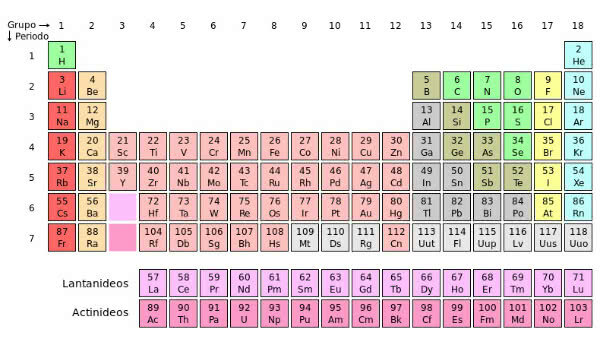
They are grouped into:
Periods: are the seven horizontal lines of the periodic table, where the elements have the same number of electronic layers:
- 1st period: 2 elements
- 2nd period: 8 elements
- 3rd period: 8 elements
- 4th Period: 18 elements
- 5th Period: 18 elements
- 6th Period: 32 elements
- 7th Period: 32 elements
The 6th and 7th periods have a particularity. In them are inserted the series of lanthanides and actinides. However, it is common to find the elements of these groups below the table to optimize space.
columns: the columns, groups or families, are the 18 vertical lines that appear on the periodic table.
Families A and B have 8 groups each:
- 1A Family: Alkaline Metals (lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium and francium).
- 2A Family: Alkaline-Earth Metals (beryl, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium and radio).
- 3A Family: Boron family (boron, aluminum, gallium, indium, thallium and nihonium).
- 4A Family: Carbon family (carbon, silicon, germanium, tin, lead and flerovium).
- 5A Family: Nitrogen family (nitrogen, phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, bismuth and Muscovy).
- 6A Family: Chalcogens (oxygen, sulfur, selenium, tellurium, polonium, livermorium).
- 7A Family: Halogens (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, astatine and tenessine).
- 8A Family: Noble Gases (helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, radon and oganessonium).
You transition elements (transition metals) represent the 8 families of series B:
- 1B family: copper, silver, gold and roentgen.
- 2B family: zinc, cadmium, mercury and copernicus.
- 3B Family: scandium, yttrium and lanthanide series (15 elements) and actinides (15 elements).
- 4B Family: titanium, zirconium, hafnium and rutherfordium.
- 5B family: vanadium, niobium, tantalum and dubnium.
- Family 6B: chromium, molybdenum, tungsten and seaborgium.
- 7B Family: manganese, technetium, rhenium and bohrium.
- 8B family: iron, ruthenium, osmium, hassium, cobalt, rhodium, iridium, meitnerium, nickel, palladium, platinum, darmstadium.
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry - IUPAC recommends that we should preferentially use the term group, numbered from 1 to 18 from left to right, to refer to the gathering of elements with similar characteristics, rather than families.
Also read about the History of the Periodic Table.
Element Properties
Chemical elements have two types of properties:
Periodic Properties: vary periodically with the increase or decrease of their atomic numbers, they are:
- atomic radius
- Atomic Volume
- Absolute Density
- Melting Point and Boiling Point
- Electronic Affinity
- Ionization Energy
- electronegativity
- electropositivity
Aperiodic Properties: do not vary periodically, that is, do not vary at regular intervals. For example:
- Atomic Mass
- Specific heat
All Chemical Elements
Below is a table in alphabetical order that brings together all chemical elements, their symbols, atomic numbers and atomic masses.
Atomic masses in parentheses correspond to the most stable isotopes of radioactive elements.
| Element | Symbol | Atomic Number | Atomic Mass |
|---|---|---|---|
| actinium | B.C | 89 | (227) |
| Aluminum | Al | 13 | 26,9815 |
| Americium | Am | 95 | (243) |
| Antimony | Saturday | 51 | 121,75 |
| argon | Air | 18 | 39,948 |
| arsenic | At | 33 | 74,9216 |
| astatine | At | 85 | (210) |
| Barium | Ba | 56 | 137,34 |
| Berkelium | Bk | 97 | (247) |
| Beryllium | be | 4 | 9,0122 |
| Bismuth | Bi | 83 | 209 |
| Bohrius | bh | 107 | (262,1) |
| Boron | B | 5 | 10,811 |
| Bromine | br | 35 | 79,909 |
| Cadmium | CD | 48 | 112,40 |
| Calcium | Here | 20 | 40,08 |
| California | Cf | 98 | (251) |
| Carbon | Ç | 6 | 12,01115 |
| Cerium | Ce | 58 | 140,12 |
| Cesium | Cs | 55 | 132,905 |
| Lead | Pb | 82 | 207,19 |
| chlorine | Cl | 17 | 35,453 |
| Cobalt | Co | 27 | 58,93 |
| Copper | Ass | 29 | 63,55 |
| Copernicus | Cn | 112 | 285 |
| Krypton | Kr | 36 | 83,80 |
| Chrome | Cr | 24 | 51,996 |
| curium | cm | 96 | (247) |
| Darmstadium | Ds | 110 | (269) |
| dysprosium | Dy | 66 | 162,50 |
| Dubnium | Db | 105 | (262) |
| Einsteinium | are | 99 | (252) |
| Sulfur | s | 16 | 32,064 |
| erbium | Er | 68 | 167,26 |
| Scandium | Sc | 21 | 44,956 |
| Tin | Yn | 50 | 118,69 |
| Strontium | Mr | 38 | 87,62 |
| europium | Me | 63 | 151,96 |
| fermium | end | 100 | (257) |
| Iron | Faith | 26 | 55,847 |
| Flerovius | Fl | 114 | 289 |
| Fluorine | F | 9 | 18,9984 |
| Phosphor | P | 15 | 30,9738 |
| francium | Fr | 87 | (223) |
| gadolinium | Gd | 64 | 157,25 |
| Gallium | Ga | 31 | 69,72 |
| Germanium | Ge | 32 | 72,59 |
| Hafnium | Hf | 72 | 178,49 |
| Hassius | hs | 108 | (265) |
| Helium | he | 2 | 4,0026 |
| Hydrogen | H | 1 | 1,00797 |
| holmium | ho | 67 | 164,930 |
| Indian | In | 49 | 114,82 |
| Iodine | I | 53 | 126,9044 |
| iridium | Go | 77 | 192,2 |
| Ytterbium | Yb | 70 | 173,04 |
| Yttrium | Y | 39 | 88,905 |
| Lanthanum | There | 57 | 138,91 |
| Laurencio | Lr | 103 | (260) |
| Lithium | read | 3 | 6,941 |
| library | Lv | 116 | 292 |
| lutetium | Lu | 71 | 174,97 |
| Magnesium | mg | 12 | 24,312 |
| Meitnerium | Mt | 109 | (269) |
| Manganese | Mn | 25 | 54,9380 |
| Mendelevium | Md | 101 | (258) |
| Mercury | Hg | 80 | 200,59 |
| Molybdenum | Mo | 42 | 95,94 |
| Muscovy | Mc | 115 | 288 |
| neodymium | Na | 60 | 144,24 |
| neon | Huh | 10 | 20,183 |
| Neptunium | Np | 93 | (237) |
| Nihon | Nh | 113 | 284 |
| Niobium | Nb | 41 | 92,906 |
| Nickel | Ni | 28 | 58,69 |
| Nitrogen | N | 7 | 14,0067 |
| nobelio | At the | 102 | (259) |
| Oganesone | Og | 118 | 294 |
| osmium | You | 76 | 190,2 |
| Gold | Au | 79 | 196,967 |
| Oxygen | O | 8 | 15,9994 |
| Palladium | Pd | 46 | 106,4 |
| Platinum | Pt | 78 | 195,09 |
| Plutonium | pu | 94 | (244) |
| Polonium | Dust | 84 | (209) |
| Potassium | K | 19 | 39,098 |
| Praseodymium | Pr | 59 | 140,907 |
| Silver | Ag | 47 | 107,870 |
| Promethium | pm | 61 | (145) |
| Protactinium | Pan | 91 | (231) |
| Radio | Frog | 88 | (226) |
| radon | Rn | 86 | (222) |
| Rhenium | Re | 75 | 186,2 |
| Rhodium | Rh | 45 | 102,905 |
| Roentgen | Rg | 111 | (272) |
| Rubidium | Rb | 37 | 85,47 |
| Ruthenium | ru | 44 | 101,07 |
| Rutherford | Rf | 104 | (261 |
| Samarium | Yes | 62 | 150,35 |
| Seaborgium | Sg | 106 | (263,1) |
| Selenium | if | 34 | 78,96 |
| Silicon | Yes | 14 | 28,086 |
| Sodium | At | 11 | 22,9898 |
| Thallium | Tl | 81 | 204,37 |
| Tantalum | OK | 73 | 180,948 |
| technetium | Tc | 43 | (98) |
| Tellurium | You | 52 | 127,60 |
| tenesino | ts | 117 | 294 |
| Terbium | Also | 65 | 158,924 |
| Titanium | You | 22 | 47,90 |
| Thorium | Th | 90 | 232,0 |
| Thulium | have | 69 | 168,934 |
| Tungsten | W | 74 | 183,85 |
| Uranium | U | 92 | 238 |
| Vanadium | V | 23 | 50,942 |
| xenon | X and | 54 | 131,38 |
| Zinc | Zn | 30 | 65,38 |
| Zirconium | Zr | 40 | 91,22 |
Check entrance exam questions with a commented resolution in Exercises on the Periodic Table and unpublished questions on the subject in Exercises on Organizing the Periodic Table.