Botany is the branch of Biology dedicated to the study of plants.
The term botany derives from Greek botané, which means “plant”.
It covers physiology, morphology, plant ecology and taxonomy, that is, all the characteristics, interactions and functioning of plants.
Historic
During Antiquity, naturalists already sought to divide living beings into groups according to their similar characteristics.
For this, the observation of species was fundamental. Initially, there were only two groups: the animal kingdom and the vegetable kingdom.
In this way, the first classifications of living beings began to appear and, consequently, the study of botany. The first studies in the area arose in Ancient Greece.
The beginning of botany was marked by the publication of the works Plantarum History ‘History of Plants" and De Causis Plantarum "On the Causes of Plants", both written by Theophrastus (371 a. Ç. - 287 a. C.), philosopher and successor of Aristotle. Theophrastus is considered the "Father of Botany".
Botany continued to evolve from the contribution of various naturalists. The advance in the area was driven by the publication of books, scientific expeditions and the creation of herbaria and botanical gardens.
Currently, botany is divided into several specialties and phylogenetics has contributed to a better understanding of plant evolution.
Features
The main characteristics of the plants are:
- eukaryotic cells: nucleus delimited by nuclear membrane;
- autotrophic beings: produce their own food;
- Photosynthesizers: carry out photosynthesis, the process for obtaining food and energy.
plant cell
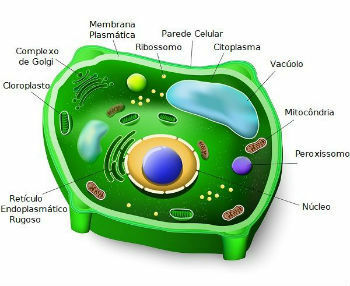 Plant cell and its structures
Plant cell and its structures
The plants are constituted by the plant cells. They differ from animal cells in that they have vacuoles, chloroplasts and a cell wall.
The vacuoles are organelles that occupy most of the cytoplasm. They are responsible for storing substances and regulating the entry of water into the cell, controlling its turbidity.
Chloroplasts are unique organelles in plant cells. It is the place where chlorophyll, the pigment necessary for carrying out photosynthesis, is found.
The cell wall of vegetables is made up of the polysaccharide cellulose. It is responsible for support, resistance and protection against pathogens.
plant histology
Plant cells form the tissues of plants, they are the object of study of plant histology.
Plant tissues are divided into:
- meristematic fabrics: are responsible for plant growth and permanent tissue formation.
- permanent fabrics: are differentiated and classified according to the function they perform.
Plant Parts
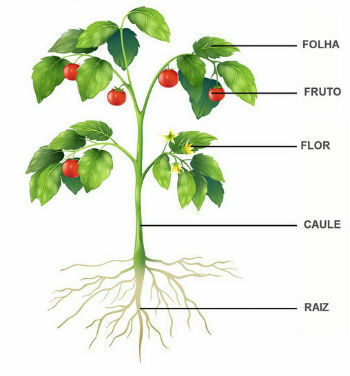 plant parts
plant parts
At plant parts they are: roots, leaves, stem, flowers and fruits. Each one of them performs a function that guarantees the plant's survival.
- Source: Absorption and conduction of substances. In some cases, they can store energetic substances.
- Sheets: Responsible for photosynthesis, respiration and perspiration.
- Stalk: Support and transport of substances.
- Flowers: Responsible for reproduction.
- fruits: Dispersion of seeds, ensuring the survival of the species.
Some plants do not have flowers and fruits, as we will see below in the plant groups.
plant kingdom
O Plant Kingdom or Plant includes eukaryotic, autotrophic and photosynthetic beings. It is considered the plant kingdom.
In the Vegetal Kingdom we can distinguish the groups of vascular plants (with conductive vessels) and the avascular plants (without conductive vessels):
- Vascular Plants: Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms and Angiosperms.
- Avascular Plants: Bryophytes.
Bryophytes
 Bryophyte, the simplest group of plants
Bryophyte, the simplest group of plants
At bryophytes represent small plants that inhabit humid environments. The group is represented by the mosses and livers.
These plants do not have conductive tissue. Thus, the transport of substances takes place from cell to cell, through diffusion.
Reproduction can be asexual or sexual. Most species are dioecious, that is, there are female and male plants. The others are monoecious, that is, hermaphrodites.
Sexual reproduction depends on the water that transports the male anterozoids to the female plant.
Pteridophytes
 Fern, an example of pteridophyte
Fern, an example of pteridophyte
At pteridophytes they are plants that have conductive and seedless vessels. They are represented by ferns, ferns and horsetails.
Reproduction can be asexual or sexual. In asexual reproduction, budding occurs. While the sexuada depends on water to meet the male and female gametes.
gymnosperms

Araucaria
At gymnosperms they are plants that have seeds but do not produce fruit. The characteristic of the group is to present the seeds "naked", that is, not surrounded by fruit.
The best known plant in this group is the Araucaria or Paraná Pine.
The reproductive structure of the group is the strobile which can be male or female. Female strobiles are known as pine cones.
Angiosperms
 Angiosperms are the most complex vegetables
Angiosperms are the most complex vegetables
At angiosperms they are the most complex plants that exist in nature. They are the only ones that have seeds, flowers and fruits.
This is the most numerous and diversified group in nature, with more than 250,000 species.
The flower is the reproductive structure of angiosperm plants. The fruit is the result of the development of the flower's ovary after fertilization. The fruit protects the seed that will give rise to a new plant.
The reproduction of angiosperms depends on the pollination, which represents the transfer of the pollen grain from the male part of the flower to the female part.
Want to know more about Angiosperms? Read too:
- germination
- Types of flowers and their functions
- Types of fruits
- Root types
- fruit
Importance of plants
Plants are closely related to the life of human beings. They present a series of environmental utilities and services:
- food
- Medicines
- human well being
- Supply of wood
- temperature regulation
- Maintenance of the rain regime
Furthermore, plants are the producing beings and the basis of food chains.
Curiosity
On April 17, National Botany Day is celebrated.