The endoplasmic reticulum is a organelle which is related to the synthesis of organic molecules. There are 2 types of crosshairs: the smooth and the rough, that has different forms and functions.
The rough is associated with ribosomes and protein synthesis, while the smooth produces lipids. the crosshairs are membranous structures composed of flat bags and located in the cytosol of the cell.
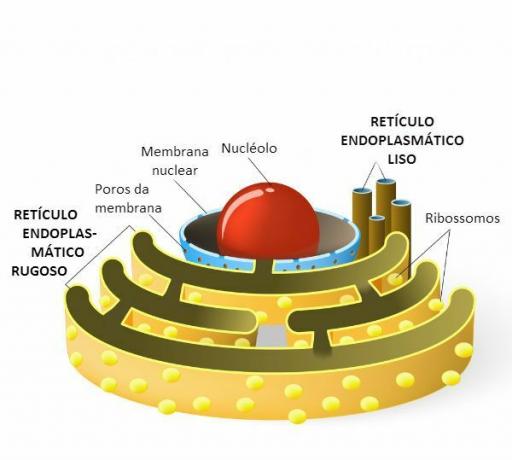 Representation of smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum. Note the ribosomes in the rugosa and the connection with the cell nucleus.
Representation of smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum. Note the ribosomes in the rugosa and the connection with the cell nucleus.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
The endoplasmic reticulum, when associated with ribosomes acquires a rough appearance, which is why it is called rough or grainy. It is located in the cytoplasm, close to the core, its membrane being a continuation of the outer nuclear membrane.
RER Functions
The proximity to the nucleus makes the protein synthesis more efficient, since the RER can quickly send a signal to the nucleus to start the DNA transcription process, and even when there are deformed proteins or unfolded (inactive), there is a specific signal to improve the process, otherwise it will be signaled that the cell must be forwarded to a programmed death (apoptosis).
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum does not have ribosomes attached to its membrane and so it looks smooth.
REL functions
Your role is basically to participate in the production of molecules of lipids, in particular phospholipids that will make up the cell membrane. However, depending on the cell type where it is, the REL will have different functions. So, for example, he may be more involved in the production of steroid hormones from cholesterol, or with regulation of calcium levels in the cytoplasm of striated muscle cells.
See too: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells