The skull is a bone box whose function is to protect the brain and organs of smell, vision and hearing, as well as the external organs of the respiratory and digestive system. It is made up of 28 bones.
It is one of the components of the skeletal system of the head and is located in the upper part of the body and attached to the neck.
Skull Functions
The main functions of the skull are:
- Shelter and protect the brain and the sensitive organs of the head;
- Protect nerves and blood vessels;
- Allow air and food to pass through the existing openings;
- Acting in the chewing process from the action of the jaw, jaw and teeth.
skull anatomy

The skull is separated into three parts, which are the neurocranium, viscerocranium and middle ear. Get to know each of them below.
neurocranium
O neurocranium corresponds to the superior and posterior-inferior part of the skull, it is the rounded framework that surrounds the brain and the inner ears. It can also be called a skull box.
See the main bones of the neurocranium in the table below:
| Neurocranial bones | Description |
|---|---|
| Occipital | It has a large, oval perforation responsible for allowing communication between the brain and the spinal canal. |
| Sphenoid | It is a unique irregular bone located at the base of the skull before the temporal and basilar portion of the occipital bone. |
| Parietal | It is a pair bone, being responsible for forming the roof of the skull. Its shape is flat and has two faces, four edges and four angles. |
| Temporal | It is an extremely important pair bone for our body, as the hearing aid is located inside it. |
| Front | This is a wide, flat bone that is located forward and upward. It has two portions, one vertical and one horizontal, where the orbital and nasal cavities are located. |
| Ethmoid | It is a light, spongy bone that has an irregular shape and is located in the anterior part of the skull. |
viscerocranium
At the viscerocranium are the facial bones that relate to the respiratory, digestive, and sensory systems.
Also known as the splanchnocranium, the viscerocranium is made up of the bones shown in the table below.
| Bones of the visceral skull | Description |
|---|---|
| tear | It is the bone that houses the lacrimal sac and is responsible for supporting the contents of the orbit. |
| vomer | It is a bone that makes up the nasal septum, thus creating a division between the two sides of the nasal cavity. |
| Jaw | It is the bone that forms the largest portion of the face and contains most of the muscle tissue. It is responsible for facial expressions. |
| Nasal | It's a pair of bones located in the face that make the initial contour of the nose. |
| Palatine | It is a bone that is located between the maxilla and the sphenoid bone. It is L-shaped and is responsible for forming the posterior portion of the hard palate and the floor of the nasal cavity. |
| Zygomatic | It is the bone responsible for bridging the neurocranium and viscerocranium. It is he who forms the cheekbones. |
| Jaw | It is the bone that forms the chin and the lower contour of the face. It is what allows a person to open their mouth to eat, chew and speak. |
| lower nose shell | It is located along the lateral wall of the nasal cavity. |
middle ear

O middle ear it is formed by three double bones. Get to know each of them in the table below.
| Middle ear bones | Description |
|---|---|
| Hammer | It is the largest ossicle in the ear. It is connected to the eardrum by the tympanic membrane and the anvil. |
| Anvil | It is located between the malleus and the stapes. |
| stirrup | It is the smallest bone in the human body, measuring about 3 millimeters. Its function is to provide support and is connected to the anvil and the inner ear. |
cranial sutures
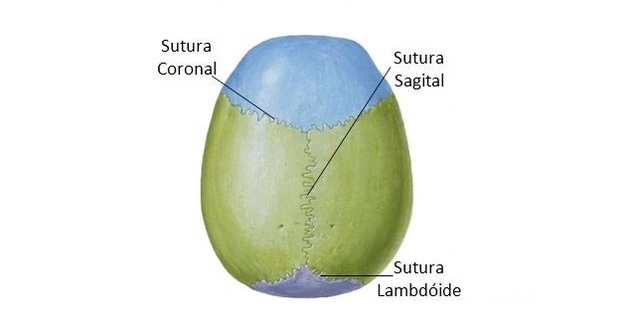
Cranial sutures are joints that allow mobility to the bones of the skull, in addition to serving to connect one bone to another.
The sutures are closed after the age of 30 or 40 years.
The table below describes the most important sutures.
| Suture | Description |
|---|---|
| Coronal | Located between the frontal and parietal bones. |
| Sagittal | Separates the parietal bones. |
| Lamboid | It occurs horizontally between the occipital bone and the parietal bone. |
cranial fossae
In addition to the sutures, the skull is also made up of holes, which are the places where nerves and blood vessels pass. Most of these holes are located at the base of the skull.
The skull also has cranial fossae, which are described in the table below.
| cranial fossa | Description |
|---|---|
| anterior cranial fossa | Composed of frontal, sphenoid and ethmoid bones. |
| middle cranial fossa | Formed by the sphenoid and temporal bones. |
| posterior cranial fossa | Composed of the temporal and occipital bones. |
Skull bone malformation
See below some anomalies related to bone malformation of the skull.
craniofacial stenosis
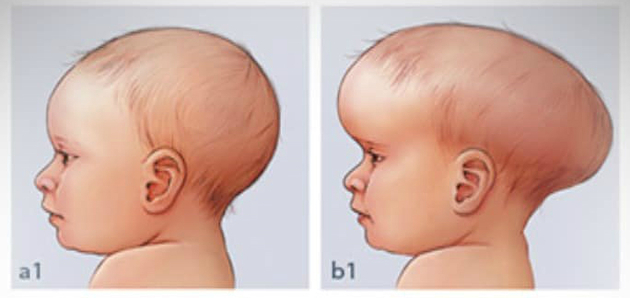
Also known as craniosynostosis, this is a bone malformation in the skull. The cause is related to the absence or premature closure of cranial and facial sutures.
It is not known for sure why this occurs, but it is estimated that it affects an average of every 2,000 children in the world. Diagnosis is made from radiological exams or CT scans.
Treatment can be made according to the severity of the craniofacial stenosis. If the impact is related to esthetics, surgery is optional, but if closing the cranial sutures puts the child's life at risk, surgery becomes essential.
cleft palate
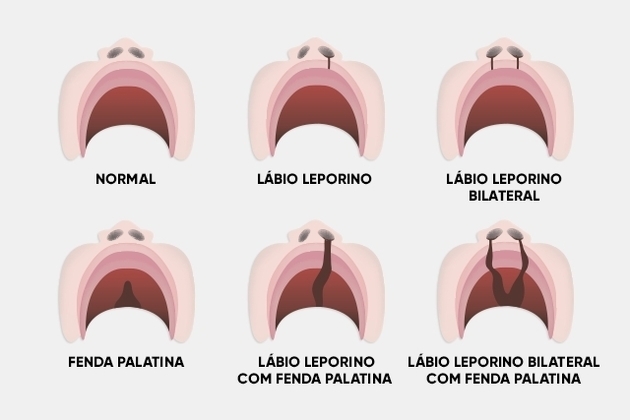
Popularly known as cleft lip, cleft lip is an anomaly caused by non-closure of structures in the palate or lip region. It is a malformation that occurs between the fourth and tenth week of pregnancy.
The opening can reach different sizes, reaching the entire roof of the mouth (hard palate) and the base of the nose or only part of them.
The cause of cleft palate is not known for sure, but some factors are considered to be risk factors, such as: nutritional deficiency and maternal diseases during pregnancy, use of certain medications and use of alcohol and tobacco.
Take the opportunity to check out our video lesson related to the subject:
Also read about:
- bones of the human body
- bone classification
- Human anatomy
- members of the human body