Electromagnetism is the branch of physics that studies the relationship between the forces of electricity and magnetism as a single phenomenon. It is explained by the magnetic field.
Origin
Michael Faraday (1791-1867) discovered the electrical effects produced by magnetism. Through these effects, called electromagnetic induction, he explained the nature and properties of magnetic fields.
Faraday explained that the magnetic field is produced by electrical charges generated from friction between bodies which, in turn, undergo attraction or repulsion.
That is to say, it is possible to generate energy by moving a magnet close to an inductor or a conductor. This movement causes the electrons to move, resulting in electrical voltage, or energyelectromagnetic.
This happens due to the polarity existing in the matter of any body: positive charge (proton), negative charge (electron) and neutral charge (neutron).
The place where this force is concentrated is called the electric field.
The strength of electrical charges is calculated using Coulomb's Law. In addition to this law, the understanding of the magnetic field triggered many discoveries concerning electricity.
But it was James Clark Maxwell (1831-1879) who managed to bring together the existing knowledge about electricity and magnetism.
Maxwell studied the effect in an inverse way to that presented by Faraday. Thus, showing the variation of the electric field under the magnetic field, he proposed 4 equations, the so-called Maxwell equations, which are embedded in the concept of classical electromagnetism.
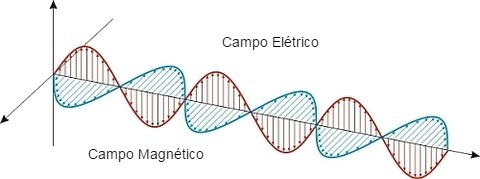
The Scottish physicist showed the existence of fieldselectromagnetic. It is the concentration of electrical and magnetic charges, which move like waves. For this reason, they are called electromagnetic waves and propagate at the speed of light. Light is an example of an electromagnetic wave!
Microwaves, radios and devices used in radiography exams are other examples of the presence of electromagnetic waves.
Continuesyourresearch:
- Electricity
- Magnetism
- Physics Formulas
- Magnetic Force
- Faraday's Law
- Lenz's Law
- electromagnetic induction