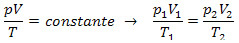Converging or diverging lenses are finite and transparent media, with at least one of their surfaces curved, that deflect light rays that pass through them.
Convergents approach and concentrate the rays at a point, after striking parallel to the lens. Divergent ones, on the other hand, scatter and scatter light rays.
The lens geometry and the refractive index of its material determine this behavior.
If the refractive index of the lens material is greater than that of the outside, the lenses are classified as:
Converging lenses
The thin-edged lenses are converging.

Converging lenses are indicated for correction of Hyperopia and Presbyopia.
divergent lenses
Thick-edged lenses are divergent.
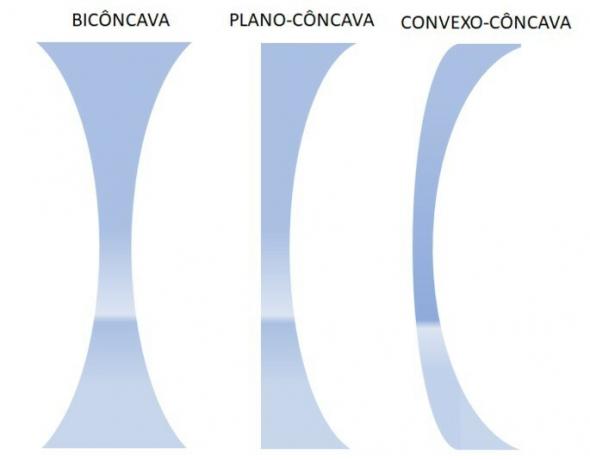
Divergent lenses are indicated for myopia correction.
If the refractive index of the middle of the lens is lower than that of the outer medium, then divergent lenses become convergent, and vice versa.
Slim Spherical Lens
Thin spherical lenses have negligible thickness in relation to the radii of curvature. In his study, lenses are represented by double arrows, perpendicular to the main axis.
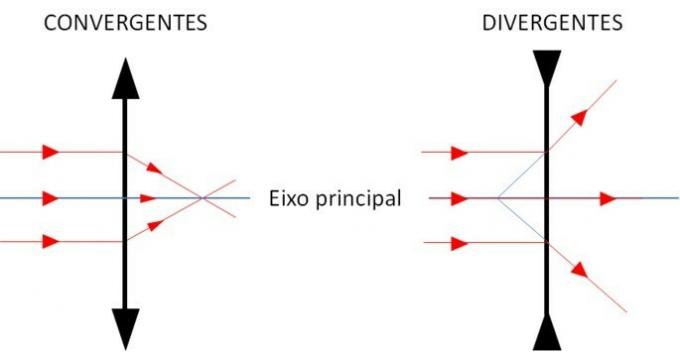
Image focus (Fi)
It is the meeting point of light rays (converging lens), or their extensions (lens divergent), after the beam falls parallel to the main axis, and emerges when passing through it, as in picture above.
O focus real image happens with converging lenses.

the fowith virtual image happens with divergent lenses.

Object focus (Fo)
It is a point on the main axis, symmetrical to the Fi image focus. These points are located on opposite sides of the lens, and the same distance from the optical center.
A ray of light that falls on the lens, having passed through the object focus, emerges parallel to the main axis.
Focal length f, is the length from the optical center to the image focus or object focus.

anti-main points
These are points on the main axis that are twice the focal length f from the optical center. These are the anti-major object (Ao) and anti-major image (Ai) points.
Learn more about:
Spherical Lenses
Light - refraction, reflection and propagation means
Physics Formulas