Genetics is an area of biology that studies the mechanisms of heredity or biological inheritance.
To study the ways in which genetic information is transmitted in individuals and populations, there are several areas of knowledge that relate to genetics. classical such as molecular biology, ecology, evolution, and more recently genomics, in which bioinformatics is used to treat Dice.
Basic concepts
Get to know the main genetic concepts and understand about each one of them:
Haploid and Diploid Cells

Haploid cells (n) have only one set of chromosomes. Thus, in animals, sex cells or gametes are haploid. These cells have half the number of chromosomes of the species.
Diploid (2n) cells are those that have two sets of chromosomes, such as the zygote, which has a set of chromosomes originating from the mother and a set originating from the father. They are diploid cells, neurons, cells from the epidermis, bones, among others.
chromosomes
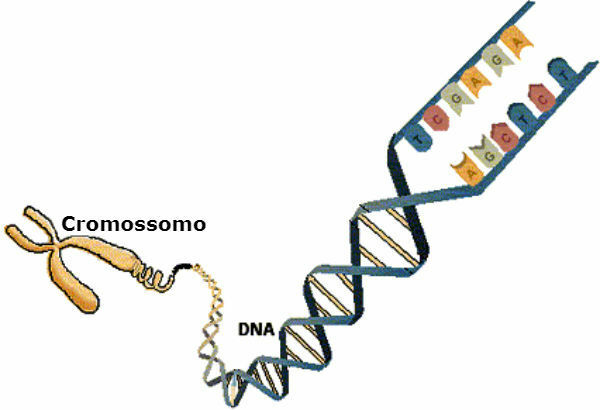
You chromosomes they are sequences of the DNA molecule, in the form of a spiral, that present genes and nucleotides.
The number of chromosomes varies from one species to another, it is represented by n.
For example, the fly Drosophila it has 8 chromosomes in body cells and 4 in gametes. The human species has a total number of 46 chromosomes in diploid cells and 23 in gametes.
Homologous Chromosomes
Each chromosome present in the sperm will match in the chromosomes of the egg.
In other words, the chromosomes of each gamete are homologous, since they have genes that determine a certain characteristic, organized in the same sequence in each one of them.

Learn more about homologous chromosomes.
genes
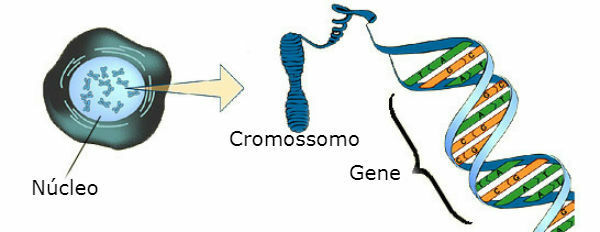
Genes are these sequential DNA fragments, responsible for encoding information that will determine the production of proteins that will act in the development of the characteristics of each being alive.
They are considered the functional unit of heredity.
You allele genes are those that occupy the same locus on homologous chromosomes and are involved in the determination of the same character.
They are responsible for determining a certain characteristic, for example, fur color in rabbits, they have variations, determining different characteristics, for example, brown or white fur. Furthermore, they occur in pairs, one of maternal origin and the other of paternal origin.
know more about Genes and Chromosomes.
Alleles and Multiple Alleles

An allele is each of several alternative forms of the same gene that occupy a locus on the chromosome and act to determine the same character. You multiple alleles occur when genes have more than two allelic forms.
In this case, more than two alleles are present in determining a character.
Homozygotes and Heterozygotes
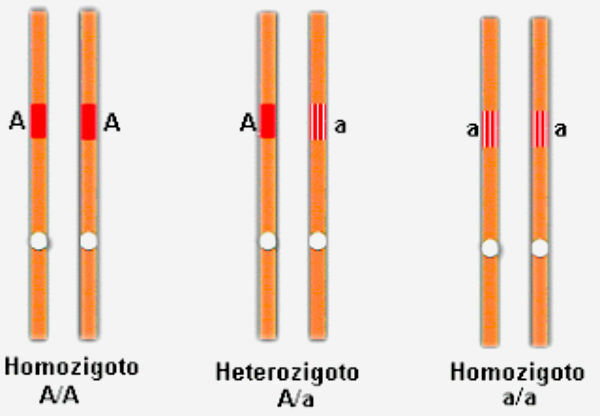
Homozygous beings are those that have identical allele gene pairs (AA/aa), that is, they have identical allele genes.
Meanwhile, heterozygotes characterize individuals who have two distinct allele genes (Aa).
know more about Homozygous and Heterozygous.
Dominant and Recessive Genes
When a heterozygous individual has a dominant allele gene, it expresses itself by determining a certain characteristic. Dominant genes are represented by capital letters (AA, BB, VV) and expressed phenotypically in heterozygosity.
When the allele gene is not expressed in that individual, it is a recessive gene. Recessive genes are represented by lowercase letters (aa, bb, vv) where phenotypes are expressed only in homozygosis.
know more about Dominant and Recessive Genes.
Phenotype and Genotype
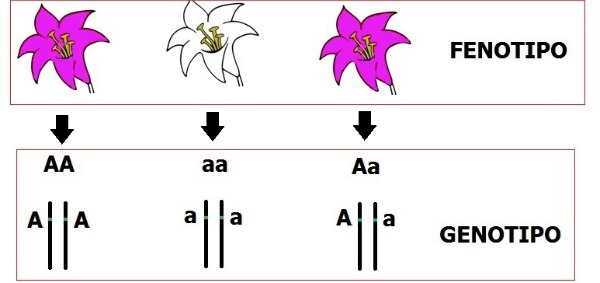
Genotype is the set of information contained in genes, thus, twin brothers have the same genotype because they have the same genes. It represents the individual's genetic makeup.
The phenotype, on the other hand, is the expression of genes, that is, it is the set of characteristics that we see in living beings, by example, eye color, blood type, color of flowers on a plant, color of fur on a cat, among others.
know more about Phenotype and Genotype.
Inheritance Linked to Sex
Sex chromosomes are those that determine the sex of individuals.
Women have 2 X chromosomes, while men have an X and a Y chromosome. In this way, it is the male gamete that determines the sex of the children.
As the X chromosomes have many more genes than the Y, some of the X genes have no corresponding allele on the Y, thus determining sex chromosome-linked or sex-linked inheritance.
know more about Inheritance Linked to Sex.

O color blindness and hemophilia are examples of diseases determined by genes present on the X chromosome. Color blindness, which is a type of color blindness, is a condition produced by a mutant allele responsible for producing one of the visual pigments.
Learn more about Genetics, read also:
- Genetic Diseases
- Mendel's Laws
- Genetic engineering
- Project human genome


