THE Supply and Demand Law it is a phenomenon that determines the prices of products in the market.
Basically, when there is a lot of supply, prices go down, and when there is a lot of demand for a product and a shortage of it, prices go up.
Definition of Market, Supply and Demand
First of all, it is necessary to define what the market, supply and demand are:
- Marketplace – the space where companies offer their products to consumers;
- Offer – when companies offer products to the market;
- Search – when customers want to buy and consume products.
Operation of the Supply and Demand Law
Search
- When demand increases, price increases.
- When demand decreases, the price also decreases.
Example:
We want to buy a bottle of water on a summer's day at the beach.
Many people want to drink water and so the demand for water increases. Certainly, the merchant will sell it for a price higher than that of the winter or if it was cold.
Offer
- When supply increases, price decreases.
- When the supply decreases, the price increases.
Example:
Let's continue with our water bottle.
If several people offered bottles of water, the price will have to decrease so that they can be sold.
On the other hand, if there were only one person selling water on this beach, the price to pay for it would be high, because everyone would be willing to pay a good price to quench their thirst.
Price variation
Prices tend to vary due to a number of factors. However, when many people want the same product, prices tend to increase.
This is because manufacturers know that the consumer will be willing to pay more money for the same product if it is difficult to find it.
Likewise, when no one wants to buy a certain product, its price tends to decrease, as only then can the manufacturer sell it.
Breakeven Point, Supply and Demand
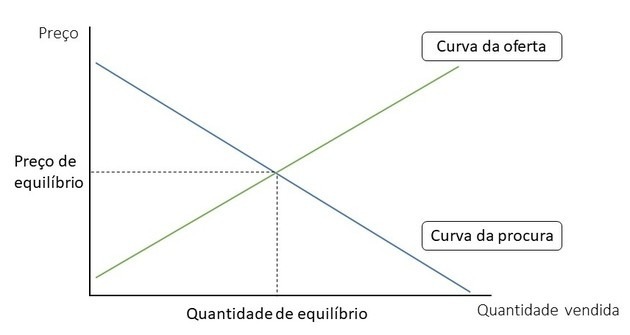
Ideally, if supply were equal to demand or vice versa, there would be a break-even point
In this way, the balance between supply and demand would make prices stay at a reasonable level. That is, neither too expensive nor too cheap.
However, prices tend to follow similar values, as the consumer would not accept paying an extremely high or low price for the same product.
Liberal theorists argue that the Law of Supply and Demand is governed by the “invisible hand”. According to the economic liberalism, there is the “rationality of supply” and the “rationality of demand” when prices are adjusted naturally.
In this way, the market is self-regulating, making prices accessible to most consumers.
read more:
- Liberalism
- neoliberalism
- Adam Smith
- Characteristics of Capitalism