O Protectionism it is an economic policy aimed at protecting the internal market from external competition.
This policy has been used since the 16th century with Mercantilism and its measures are currently applied by several countries.
Summary
The main characteristics of protectionism are that it makes it difficult for foreign products and services to enter in order to protect the national market.
To achieve this, the government raises import tax rates, creates sanitary, economic and political customs barriers, subsidizes national industry or agriculture.
These measures are intended to prevent the entry of imported products from harming the domestic market.
Even though it has lost its effectiveness with the globalization, several countries still use protectionist measures in favor of increasing profits and the internal market.
This doctrine is supposedly seen as “disloyal” by several scholars in the field. On the one hand, the country is losing ground on the world economic scene. On the other hand, protectionism aims to protect and strengthen the country's internal economy through the monopoly of the internal market.
In this way, better living and working conditions are guaranteed for the inhabitants, as well as the increase in job offers and the development of new technologies.
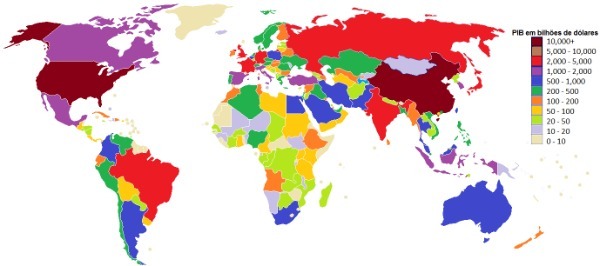
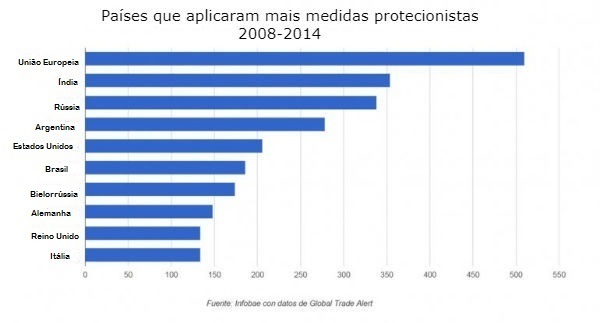
According to World Trade Organization (WTO), a survey conducted in 2013, Brazil leads the ranking of countries that use too many protectionist laws, which makes external commercial transactions difficult in certain sectors.
This does not mean, however, that jobs and the increase in domestic consumption are guaranteed through the application of protectionist laws.
In the opinion of some economists, there are not many benefits in using protectionist measures in the face of a globalized world economic scenario.
After all, protectionism can generate an increase in domestic products, but also a loss of trade opportunities with countries and also delays in the political, social, economic and technological spheres.
Types of Protectionism
Although there is no difference between protectionism and the rates applied in economic spheres, there are those who divide protectionism in two ways, namely:
- trade protectionism: countries establish quotas for certain products;
- Customs Protectionism: when fees for importing the product are high.
Agricultural Protectionism
Agricultural protectionism is characterized by the protection that the government establishes for certain sectors of agriculture.
It is usually done through subsidies, farmer credit facilities and tax breaks. With this, the final product will be cheaper and can be sold in the domestic or foreign market at a more competitive price.
Free Comerce
Opposed to the theory of protectionism is Free Trade, also called "free trade".
This idea defends that trade between countries should not be restricted, thus facilitating commercial, political and economic exchanges as stated in the economic liberalism.
read more:
- Mercantilism
- Characteristics of Mercantilism
- Trade balance
- Bourgeoisie
- Financial Capitalism