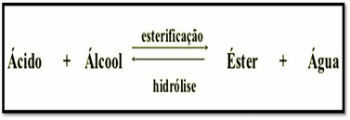
Esterification is a reversible chemical reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol, producing ester and water.
The reaction can be described as follows:
CARBOXYLIC ACID + ALCOHOL → ESTER + WATER
The esterification reaction is slow, requiring an increase in temperature and the presence of a catalyst to accelerate its speed. This process is called Fischer Esterification.
The inverse reaction to esterification is called Ester Hydrolysis. In this case, from ester and water, carboxylic acid and alcohol are produced.
Esterification reactions
The general equation of an esterification reaction is as follows:
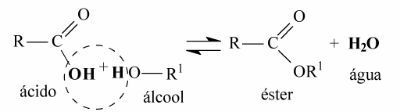
Note that water is formed by the union of the hydroxyl group (OH) of the carboxylic acid with the hydrogen (H) of the alcohol.
The remainder of the carbon chain of the carboxylic acid and alcohol join together to form the ester.
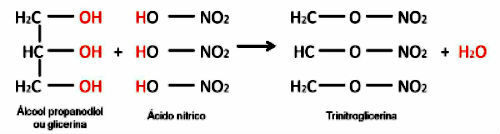
Esterification can also take place between an inorganic acid or secondary or tertiary alcohol.
In this case, the formation of water will occur in a different way: the hydroxyl group will come from the alcohol and the hydrogen from the acid.
An example is the reaction between an inorganic acid and the formation of an inorganic ester. The three molecules of organic acid (nitric acid) react with glycerin and form trinitroglycerin (nitrate ester), an explosive.
applications
Obtaining esters is important for the production of different types of products. See some examples:
Flavorings in food industries
Fischer esterification is the main means for the production of esters in industrial plants, especially foodstuffs.
Flavorings are esters that give aroma and flavor to industrialized products such as candies, sweets, soft drinks and juices.
Examples of esters used as flavorings are:
- ethyl ethanoate: apple aroma
- octyl ethanoate: orange aroma
- Ethyl Butanoate: pineapple aroma
Biodiesel
Biodiesel is obtained through a transesterification reaction.
The process consists of mixing vegetable oil or animal fat (triglycerides) in methanol or ethanol, in the presence of a catalyst.
One of the products of the reaction is glycerin, which can be used to manufacture cosmetics, foods and medicines.
Read too:
- Transesterification reaction
- Neutralization reaction
- Saponification reaction: ester hydrolysis