O Eastern Europe it is formed by countries located in the center of the European continent.
This term indicates a number of countries that have had a different historical and cultural trajectory than Western European countries.
We can also call it Eastern Europe or Eastern Europe.
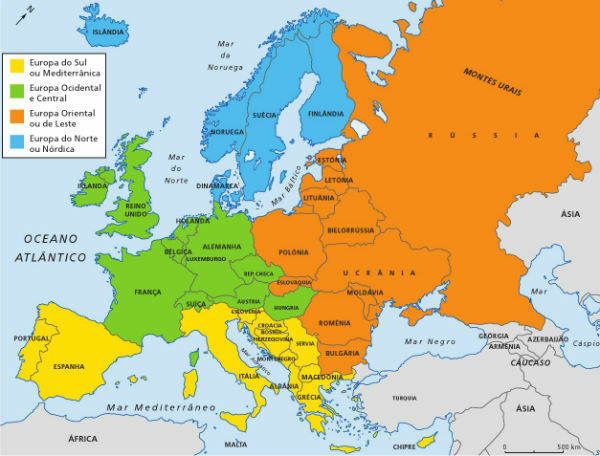 Map with the different regions of the European continent. In orange, Eastern Europe.
Map with the different regions of the European continent. In orange, Eastern Europe.
Eastern European Countries
- Albania
- Belarus
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Czech republic
- Croatia
- Georgia
- Slovakia
- Estonia
- Hungary
- Kosovo (discussed recognition)
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Macedonia, Republic of Macedonia (or Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia/FYROM)
- Moldavia
- Montenegro
- Poland
- Romania
- Russia
- Serbia
- Ukraine
Eastern European Cities
Currently, several cities in Eastern Europe are undergoing a process of discovery by their own neighbors and tourists from around the world.
All of them attract for the incredible cultural offer and also the prices cheaper than other capitals like London or Paris.
In this way, we see it as Prague, capital of the Czech Republic; Budapest, the capital of Hungary and recently Zagreb, the capital of Croatia, are increasingly popular with travellers.
Summary
Eastern European countries are grouped according to their cultural and historical characteristics.
Usually, they bring together countries that came under the influence of the Orthodox Church and have the language of Slavic origin.
Many of them like Serbia, Montenegro, Croatia were dominated by the Turkish-Ottoman Empire. That is why we find a large number of Muslims established there for several centuries.
In turn, regions such as Hungary, Czech Republic and Slovakia were part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. They have a culture close to the West, despite not having been occupied by the Roman Empire.
First World War
After World War I, the Empires that dominated this region fell apart.
Several peoples are now achieving their independence. The Kingdom of Yugoslavia is created, and the countries Austria, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, Albania, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania and Poland are created.
The Cold War and Eastern Europe
After World War II, the region was liberated from the Nazis by the Soviets. So these nations adopted the socialism as a government regime.
They also signed the Warsaw Pact in 1955 in order to establish a union and a defense system similar to that of the NATO.
The only exception was Yugoslavia which did not align itself with Soviet policy although it was socialist.
In any case, the expression “Eastern Europe” was widely used to designate the countries of the continent that had adopted socialism as a government regime.
Due to the isolation and influence of the Soviet Union in these countries, former British Prime Minister Winston Churchill called this process the Iron Curtain.
Fall of the Berlin Wall (1989)
In 1989, with the fall of the Berlin Wall, socialist regimes fell one after another in Eastern Europe. With the exception of Romania and Yugoslavia, the transition was carried out peacefully.
In Romania, there was a dispute between the former socialist leaders, the army and the people. The popular uprising bombed buildings in Bucharest and ended with the leader Nicolai Ceausescu and his wife Elena Ceausescu arrested and shot.
The former Yugoslavia would plunge into a bloody conflict where each of the nations of the former socialist republic wished to constitute a sovereign country.
The 90's were especially hard, as these nations had to move from a state economy to a market economy.
Currently, some of the former Eastern European countries are part of the European Union making the term obsolete.
There are more texts on this topic for you:- Berlin Wall
- End of USSR
- Europe
- European Union
- European countries
Entrance Exam Exercises
1. (UFMG) Considering the territorial fragmentation of the former Yugoslavia, it is CORRECT to state that this process:
a) it was a consequence of the clashes between the different nationalities that, until then, made up the country.
b) resulted from the fall of the Monarchy, responsible for the political unity and territorial integrity of the country.
c) resulted from the struggle of Serbia, supported by Bosnia, against Montenegro, with a predominantly Muslim population.
d) derived from the Federation's resistance to Tito's policy, which transformed the country into a Social Democratic Republic.
The) It was an unfolding of the clashes between the different nationalities that, until then, made up the country.
2. (FATEC-2007) In eastern countries recently incorporated into the European Union, the automobile industry increased from 310 thousand jobs in 2000 to 400 thousand in 2006. Payrolls increased 62% in Slovakia, which already has 58,400 people in the sector, and 41% in the Czech Republic, which has another 111,000. In Poland employment increased by 25% to 111,000 people; in Hungary, 32%, to 44 thousand; and in Slovenia, 31%, to 9,200. ( http://noticias.uol.com.br/midiaglobal/lavanguardia, accessed on March 27, 2007)
The economic picture expressed in the news is correctly complemented with the following data:
a) the entry of these Eastern European countries into the European Union, under the same conditions as the older members, gives them great competitive advantages, as they have lower production costs, attracting investments industrial.
b) these new members of the European Union take advantage of the high industrial growth rates in the richest countries in Europe in the recent decades, such as Germany and France, presenting themselves as areas of expansion of the automobile industry in the interior of Europe.
c) the presence of the State, as an economic agent with a large participation in the economy of Eastern European countries, is a important attractive factor for multinational industries to settle there, as they are dependent on capital state-owned.
d) the fact that they belong to the European Union makes these new member countries real “entrance doors” for markets with greater purchasing power, causing industries in developing countries to look for them there if install.
e) because such eastern European countries were essentially agricultural in the period when they were under the dominion of the Union Soviet, the current governments of those promote policies to attract industries, waving subsidies and few charges labor.
a) The entry of these Eastern European countries into the European Union, under the same conditions as the older members, gives them great competitive advantages, as they have lower production costs, attracting investments industrial.

