The spleen is one of the organs of the lymphatic system with the body's defense function and acting in blood circulation.
It is approximately 13 cm long and up to 200 g in weight. It has a dark red color and a soft, spongy consistency.
The organ is located in the upper left part of the abdomen, behind the stomach and under the diaphragm.

Spleen Functions
The main functions of the spleen are:
- Filter microorganisms and foreign particles from the blood, like viruses and bacteria. It acts as a "sponge" in filtering the blood.
- To produce lymphocytes and plasma cells that synthesize antibodies.
- Make blood reserve in case of heavy bleeding. The organ can store up to 250 ml of blood.
- remove the Red Cells damaged or aged.
Spleen Anatomy
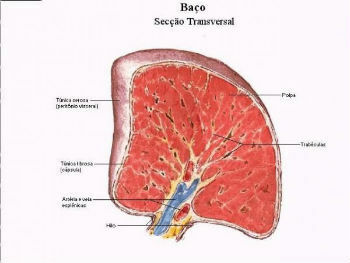
The spleen is covered by a fibrous capsule and formed by the splenic pulp, where the white pulp and the red pulp are found.
- White pulp: Formed by lymphoid tissues, it produces white blood cells (T and B lymphocytes) that participate in the body's immune system.
- Red pulp: Formed by blood tissue that filters the blood and removes foreign particles and microorganisms.
Learn more, read also:
- Human Body
- Lymphatic system
What causes pain in the spleen?
In some infectious conditions, the spleen can swell and cause pain. An example is the mononucleosis disease, when in an attempt to expel the virus from the body, the spleen increases the production of lymphocytes, becoming larger and causing swelling.
Other diseases can also affect the spleen and compromise its function and integrity. Examples:
- blood diseases
- Cirrhosis
- Disorders in lymphatic organs
- Lymphoma
- Cancer
- Anemia
- Hepatitis
- Leukemia
Curiosity about the spleen
The spleen is not a vital organ in the body. In cases of illness, it can be removed by surgery called a splenectomy.
When this happens, other organs take over some of the functions of the spleen. However, the function of eliminating microorganisms and impurities from the blood can be seriously compromised.
Read too:
- Organs of the human body
- Organs of the human body without which you can survive

