Mutualism is ecological relationship between individuals of different species, in which both are benefited by the interaction. By occurring between individuals of different species, is a relationship called interspecific, and, because it benefits everyone involved, it is called harmonic relationship.
Know more:What is species?
Mutualism is an interspecific and harmonic ecological relationship. |
Types of Mutualism
They exist different types of mutualism. Generally, in textbooks, mutualism is classified into two types: mandatory and optional. In obligatory mutualism, the relationship between individuals is obligatory for the survival of at least one of those involved, in the optional mutualism, the participants in the interaction can live in a independent.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Mutualism can be further classified into defensive, trophic and dispersive.
In defensive mutualism, it is observed that one of those involved provides protection to the other individual, while the protected individual generally provides food.
In trophic mutualism, what is observed is that each organism is responsible for providing a importantnutrient to the other.
In dispersive mutualism, we have the interaction between plants and animals, in which animals act by dispersing seeds or transporting pollen and earning in return food such as nectar and fruit.
MUTUALISM | ||
Types |
Features |
Examples |
mandatory mutualism |
Relationship in which individuals have a mandatory relationship. If interrupted, at least one of those involved may not survive. |
Lichen |
optional mutualism |
A relationship in which participants benefit but can live independently. |
Established interaction between hermit crab and sea anemone. |
Trophic Mutualism |
A relationship in which those involved provide each other with specific nutrients. |
lichen and mycorrhizae. |
defensive mutualism |
Relationship in which one of the involved promotes the defense of the other and receives food from it. |
Interaction established between ants and acacias. |
dispersive mutualism |
Established relationship between animals and plants, in which the animal guarantees the transport of pollen or seed and receives food in exchange. |
Established interaction between birds and some fruit plants. |
Mutualism and protocooperation
The termprotocooperationis used by some authors to indicate an ecological relationship in which individuals of different species are associated so that both are benefited, but this relationship not compulsory for the survival of those involved.
Some authors, however, prefer to use the expression optional mutualism replacing the term protocooperation, thus dealing with two concepts related to the same ecological relationship.
Read more: Cologne, an ecological relationship
Examples of Mutualism
The following are some examples of mutualism:
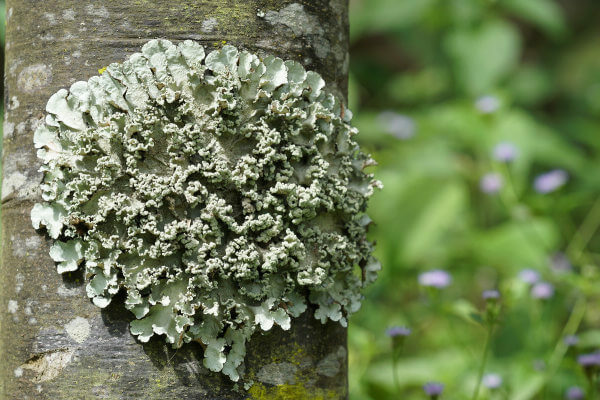

Lichens are associations between fungi and algae or fungi and cyanobacteria.
Lichen: Lichens are a mutualistic association established between a fungus and a photosynthetic microorganism (algae or cyanobacteria). THE seaweed or cyanobacteria is responsible for providing organic compounds to the fungus, while the fungus ensures the proper environment for the development of the photosynthetic organism, protecting and retaining it Water and mineral salts.

Note in the photo the nodules formed in the roots of the legumes.
genus bacteria Rhizobium and legumes: At bacteria like Rhizobium establish mutualism with legumes. In these plants, bacteria form nodules that help to provide a greater amount of nitrogen for the vegetable. Plants, in turn, provide nutrients from the process of photosynthesis for bacteria.
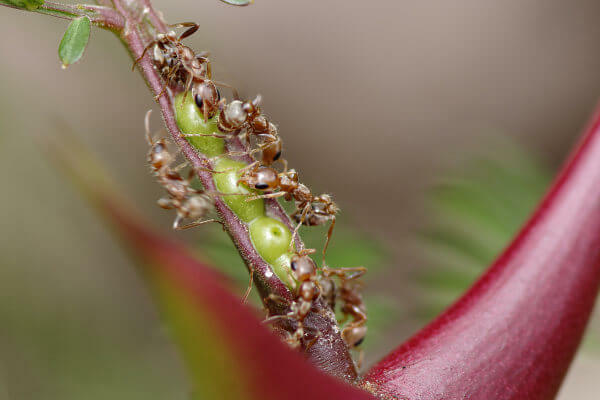

Ants protect the acacia while the plant provides nutrients for the ants.
Ants and acacias: Some ants live in acacias, plants that have hollow spines that shelter the animal. Ants get food from the acacia and, in turn, provide protection to the plant, as they attack herbivores, rid the plants of fungus and also cut other plants that grow close to it.
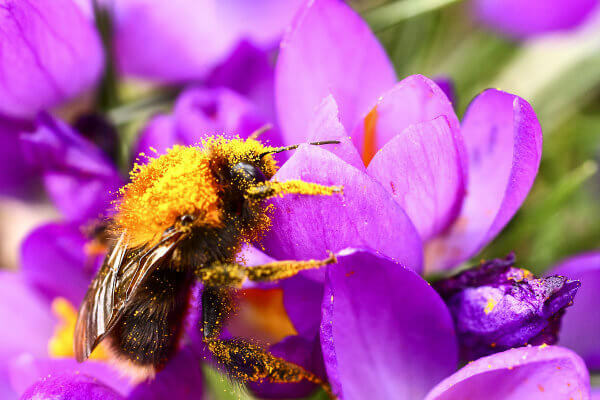

Pollination is essential for the reproduction of flowering plants.
Flowering plants and pollinators: Many species with flowers have adaptations to attract pollinators. Pollinators ensure the transport of pollen from one plant to another, promoting its reproduction, and in exchange obtain nectar for its food.
Read too:what is pollination?
→ Exercise solved
Check out an exercise that addresses mutualism:
|
(Mackenzie) Many living beings live in association with other beings of other species, maintaining harmonious relationships with them (mutualism) or inharmonious relationships (parasitism). The following relationships: Rhizobium, mycorrhizae and lichen are: a) all cases of mutualism. b) two cases of mutualism and one of parasitism. c) two cases of parasitism and one of mutualism. d) two cases involving algae and one involving bacteria. e) two cases involving bacteria and one involving fungus. |
Resolution: Letter A. Bacteria of the genus Rhizobium show a mutualistic relationship with plants of the legume family. In this relationship, the bacterium supplies the plant with nitrogen and the plant supplies the bacterium with the carbohydrates necessary for its development. In the case of mycorrhizae, we have an association between fungi and vegetable roots. Fungi, in this case, help to improve the transfer of minerals to plants and plants provide organic nutrients for the fungus.
Finally, we have lichens, which are associations between fungi and cyanobacteria or algae. In this relationship we observe that photosynthetic microorganisms promote the supply of organic compounds for the fungi, while the fungi provide a suitable environment for your development.
By Ma. Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SANTOS, Vanessa Sardinha dos. "Mutualism"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/mutualismo.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.