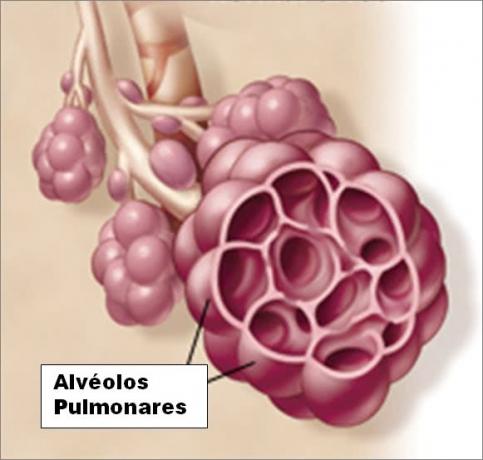
The pulmonary alveoli are tiny air sacs present in the lungs, surrounded by blood capillaries and a thin membrane.
They are located where the thin branches of the bronchi end.
The alveoli can be isolated or in groups, forming the so-called alveolar sacs.
In each lung there are millions of alveoli. They are responsible for the spongy appearance of the lungs.
Histology of pulmonary alveoli
The alveoli are lined with a layer of epithelial cells, called type I pneumocyte and type II pneumocyte.
Type I pneumocytes are squamous cells with a small amount of cytoplasm. This feature facilitates the passage of gases.
Type II pneumocytes are oval, bulky cells. This type of cell produces a lipoprotein secretion, called a surfactant.
The function of the surfactant is to keep the alveoli open and help diffuse gases across the alveolar membrane.
Also read aboutLungs and Lung Breathing.
Function of pulmonary alveoli
The main function of the pulmonary alveoli is to be the place where gas exchange takes place between air and blood, the bruise.
Upon reaching the alveoli, the oxygen it diffuses into the blood from the capillaries. Meanwhile, carbon dioxide, present in the blood of capillaries, diffuses into the alveoli.
Hematosis is the diffusion of gases, due to the different degree of concentration of each one.
You may also be interested in:
- Respiratory system
- Exercises on the Respiratory System
- Silicosis


