The spine or backbone is the central axis of the body responsible for supporting our bipedal position.
It also constitutes an important communication axis between the central and peripheral nervous system, through the spinal cord, contained in the spinal cord channel.
The spine is also made up of soft tissues such as muscles, ligaments, capsules, tendons and discs, and these structures are responsible for the flexibility of the spine.
 Spine
Spine
Spinal Anatomy
vertebrae
The vertebrae are stacked on top of each other, thus forming the vertebral column.
The smallest are the cervical, followed by the thoracic, which are of medium size. While the lumbar vertebrae, located at the bottom of the spine, are the largest.
The spine extends from the base of the skull to the caudal end of the trunk. The sacral vertebrae are fused and form the sacrum bone, just as the coccygeal vertebrae form the coccyx.
The pelvis is the base of the spine, where the lower limbs articulate. Superiorly, the spine articulates with the occipital bone of the skull and, inferiorly, with the iliac bone.
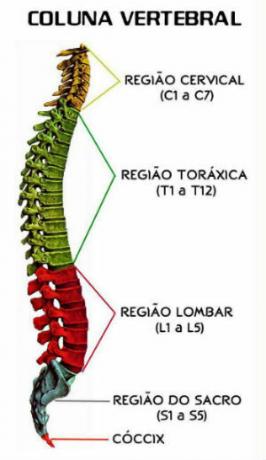
THE spinal column consists of 33 vertebrae interspersed by intervertebral discs, featuring the following division:
- Cervical Vertebrae: 7 vertebrae;
- Dorsal or thoracic vertebrae: 12 vertebrae;
- Lumbar Vertebrae: 5 vertebrae;
- sacral vertebrae: 5 fused vertebrae;
- Coccygeal Vertebra: 4 fused vertebrae.
 spinal division
spinal division
With the exception of the 1st and 2nd cervical vertebrae, atlas (C1) and axis (C2), respectively, all vertebrae have 7 basic elements:
- Body;
- Thorny Process;
- Transverse Process;
- Joint Processes;
- Blades;
- Pedicles;
- Vertebral foramen.
 Vertebrae anatomy
Vertebrae anatomy
Read too:
- bones of the human body
- Human skeleton
- skeletal system
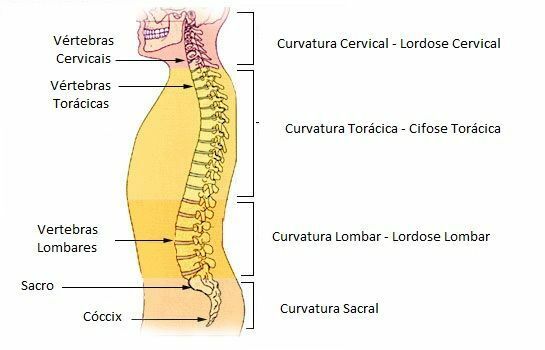
Spinal Curvatures
Viewed from the side, the spine has 4 curvatures considered to be physiological, that is, natural:
- Cervical lordosis (posterior concavity);
- Thoracic kyphosis (anterior concavity);
- Lumbar lordosis (posterior concavity);
- Sacrococcygeal kyphosis (anterior concavity).
Spinal curvatures
Illnesses
Some diseases are associated with the spine. Are they:
- kyphosis: Abnormal spinal deviation, causing the upper back to appear more rounded than normal.
- Lordosis: Excessive curvature of the spine.
- Disc herniation: Situation in which part of the intervertebral disc leaves its normal position and compresses the nerve portion of the spine.
- Scoliosis: Deformity in the curvature of the spine, which takes on an "s" or "c" shape.
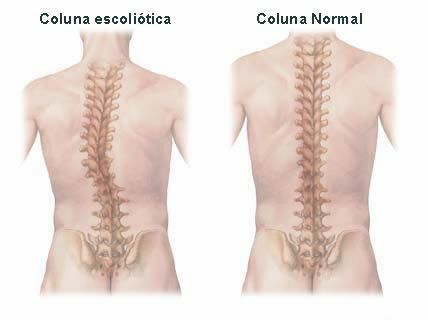 Scoliosis spine
Scoliosis spine
Know more:
- Human Body
- Locomotor System
- Nervous system