Decomposition is the transformation of a material into smaller parts, that is, a substance is transformed into other substances, chemically speaking.
The waste decomposition time depends on its composition and size and, therefore, varies from one material to another. Furthermore, it is related to factors of nature, such as temperature, humidity, soil type, etc.
See some examples below.
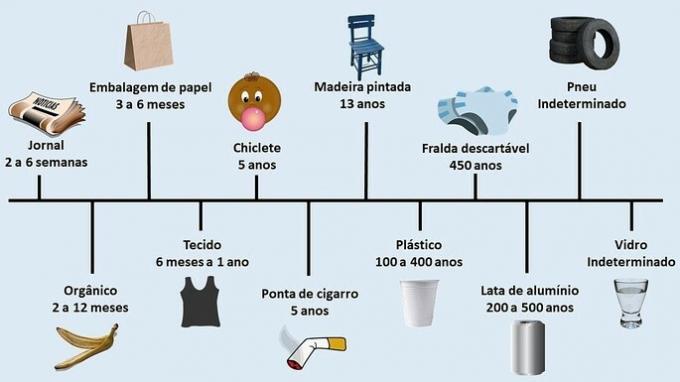
20 common waste materials and decomposition time
| Garbage | Time |
|---|---|
| Rubber | Undetermined time |
| Fruit peel (organic waste) | 2 to 12 months |
| chewing gum | 5 years |
| Leather | 50 years |
| Paper packaging (cardboard) | 3 to 6 months |
| Disposable diaper | 450 years |
| cigarette filter | 5 years |
| Pet bottle | 100 years |
| Newspaper | 2 to 6 weeks |
| Aluminum can | 200 years |
| Wood (painted) | 13 years |
| Metal | 100 years |
| Nylon | 30 years |
| Paper | 3 months |
| Stacks | 100 to 500 years |
| Plastic | 400 years |
| Tire | undetermined time |
| bottle caps | 100 to 500 years |
| Cotton fabric (cloth) | 1 year |
| Glass | undetermined time |
From the examples presented, food, fabric and paper waste are considered biodegradable products, due to the short time needed to be decomposed. The products commonly produced in the environment by the decomposition of food are: carbon dioxide (CO
2), water (H2O), methane (CH4) and ammonia (NH3).Non-biodegradable materials, which take a long time to decompose, exist in large quantities. The best solution for them is recycling, as in the case of glass, the decomposition time is indeterminate.
The time, usually too long, for a waste material to degrade is just one of the problems that the accumulation of waste can cause to the environment. Environmental, social and health problems can be caused by incorrectly produced and discarded waste.
Contamination of soil and groundwater, appearance of disease vector animals and even an imbalance in the ecosystem, as occurs in the oceans due to the excess of discarded plastic, are common due to the amount of garbage that produces.
Learn more about types of garbage.
3R's Principle: What can you do for the environment?
Reduce, reuse and recycle these are actions we can take to help the environment and reduce the amount of waste produced.
To cut back, for example, you can choose to have your own shopping bag instead of picking up several plastic bags from the market each time you go to the store. A good practice is also to have your own cup with you, at work for example, and to avoid using disposable cups.
To apply reuse you can encourage the consumption of second-hand clothes. We often have a piece in good condition, which no longer fits us or we simply don't like it anymore. Don't leave it in the closet for too long, look for someone who would like to have it.
Recycling allows new materials not to start from scratch in the manufacturing process and, therefore, generate savings in energy, water and other inputs.
Aluminum, common in soda cans, has a high cost production process. When aluminum cans are recycled, savings of up to 90% are generated if the metal comes from mining.
Complement your studies by also reading about:
- Selective collect
- Recycling
- environmental education