The cerebellum is an organ of the nervous system.
It is found between the brain and brainstem, connected to the thalamus and spinal cord through many nerve fibers.
The name cerebellum comes from Latin and means small brain.
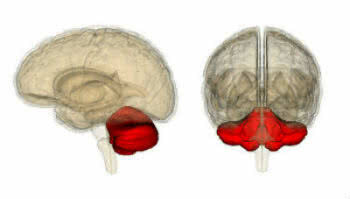
Location of the cerebellum in the brain
Anatomy and Histology
Anatomically, one can distinguish in the cerebellum the vermis and two cerebellar hemispheres (right and left):
The vermis is located in the middle part, it constitutes a narrow band that connects the two hemispheres.
The cerebellar hemispheres are its larger lateral masses. The two hemispheres have transverse folds called leaves. Thus, the cerebellum is formed by a large number of leaves made up of nervous tissue.
The cerebellum is composed of a central part of white matter, covered by a thin layer of gray matter, which represents the cerebellar cortex.
Roles
- Maintenance of balance and posture;
- Control of muscle tone;
- Adjustments of body movements;
- Motor learning.
Learn more about others Organs of the human body.
Illnesses
When the cerebellum is injured, the main symptoms that may appear are:
- Ataxia: incoordination of movements;
- loss of balance;
- Changes in posture and gait;
- Decreased muscle tone;
- Disorders in speech and eye movement;
Examples of diseases: Vermis syndrome and Friedreich's Ataxia, an inherited degenerative disease.
To gain more knowledge, see also:
- brain
- Nervous system
- Exercises on the Nervous System

