O backwoods it is the largest northeastern sub-region that is located between the mid-north and the agreste.
It is a place that suffers from the great drought, a characteristic factor of the low rainfall.
Map and Location
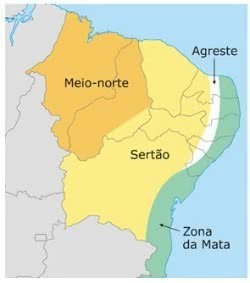
Map of northeastern sub-regions: mid-north, sertão, agreste and forest zone
The northeastern hinterland is a large region that covers all of Ceará and parts of the states of Piauí, Rio Grande do Norte, Paraíba, Pernambuco, Alagoas, Sergipe and Bahia.
Climate
The predominant climate of the hinterland is the semiarid climate with high temperatures throughout the year and irregular rainfall.
It is divided into two seasons, with rainy winter (December to June) and hot summer (July to November).
Due to its location, the region suffers from long periods of drought. Thus, there are winters that do not rain and can last for more than two years.
That's because the Borborema Plateau, located between the wild and in the forest zone, prevents the moisture from the ocean from reaching the region.
Therefore, the rainfall index is very low, which leads to several social and economic problems.
Relief, Vegetation and Fauna
The relief of the hinterland region is varied with plateaus, plateaus and mountains. The vegetation is marked by the biome of the caatinga, which includes undergrowth, thorny shrubs and small trees and gnarled trunks.

Cacti, typical plants of the caatinga
The cacti and bromeliads that have adapted to the conditions of the region stand out. Most of the plants lose their leaves, in order to survive with the lack of water.
Likewise, the animals were adapting to the conditions. In the sertão fauna, reptiles and various insects predominate.
rivers and soils
One of the most important rivers in the northeastern hinterland is the São Francisco River, of a perennial character. It has great importance for the population as it supplies the region.

São Francisco River, the most important in the northeastern hinterland
Other rivers are intermittent, that is, temporary, which disappear in some periods of the year. Examples are the Aracaju, Jaguaribe, Apodi and Açu rivers.
The soil in the region is shallow, stony and, for the most part, not very fertile. However, in some places, such as swamps, the humidity is higher and therefore the soil is more fertile.
Economy
Although a large part of the region is very arid, there are more humid places, such as marshes. There, agricultural activities are carried out, with emphasis on sugarcane, corn, cassava and bean plantations.
In addition, places closer to the São Francisco river are found fruit plantations. Extensive cattle raising with cattle raising is also an economic activity developed in wetter places.
Some urban centers are present in the region, such as Fortaleza (CE), Juazeiro do Norte (CE), Mossoró (RN), Petrolina (PE), Patos (PB), Vitória da Conquista (BA) and Juazeiro (BA). Thus, the local economy is also marked by industries, commerce and services in general.

Fortaleza (CE), the only capital located in the northeastern hinterland
However, it is noteworthy that the region has one of the highest rates of social and economic inequalities in Brazil.
Problems such as hunger, poor income distribution, misery and rural exodus are recurrent, above all, in the interior cities of the sertão.
Read more about the region:
- Northeast region
- wild
- Wood zone
- Northeast States
- Northeast Region Climate
- Northeast Region Economy
- drought in the northeast
- Drought Industry
Learn more about the northeast region, economy and climate:
