The photoelectric effect occurs when there are electron emissions in a given material. This effect is usually produced in metallic materials which are exposed to electromagnetic radiation, such as light.
When this happens, this radiation rips electrons off the surface. In this way, the electromagnetic waves involved with this phenomenon transfer energy to electrons.
Learn more about electrons and the Electromagnetic waves.
What are Photons?

Photoelectric Effect Scheme
Photons are tiny elementary particles that have energy and mediate the photoelectric effect. Photon energy is calculated by the following formula:
E = h.f
Where,
AND: photon energy
H: proportionality constant (Planck's constant: 6.63. 10-34 J.s)
f: photon frequency
In the International System (SI), the photon energy is calculated in Joule (J) and the frequency in Hertz (Hz).
read Planck's constant.
Who discovered the Photoelectric Effect?
The photoelectric effect was discovered in the late 19th century by the German physicist Heinrich Hertz (1857-1894). At the beginning of the 20th century, the scientist
Albert Einstein, studied more deeply about this effect, contributing to its modernization. With that, Einstein won the Nobel Prize.According to Einstein, the radiation energy would be concentrated in a part of the electromagnetic wave, and not distributed over it, as stated by Hertz.
Note that the discovery of this effect was essential for a greater understanding of the light.
applications
In photoelectric cells (photocells), light energy is transformed into electrical current. Several objects and systems use the photoelectric effect, for example:
- televisions (LCD and plasma)
- the solar panels
- the reconstitutions of sounds in the films of a cinematograph
- the urban lighting
- the alarm systems
- the automatic doors
- the control devices (counting) of the subways
Compton Effect
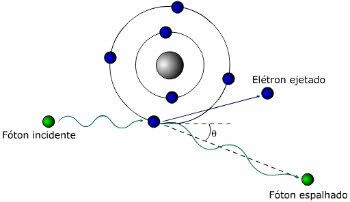
Compton Effect Scheme
Related to the photoelectric effect is the Compton effect. It occurs when a photon (X-ray or gamma-ray) decreases in energy when it interacts with matter. Note that this effect causes an increase in wavelength.
Entrance Exam Exercises with Feedback
1. (UFRGS) Select the alternative that presents the words that correctly complete the gaps, in order, in the following text related to the photoelectric effect.
The photoelectric effect, that is, the emission of ….. by metals under the action of light, is an experiment within an extremely rich physical context, including the opportunity to think about the functioning of the equipment. which leads to experimental evidence related to the emission and energy of these particles, as well as the opportunity to understand the inadequacy of the classical view of the phenomenon.
In 1905, when analyzing this effect, Einstein made the revolutionary assumption that light, until then considered a wave phenomenon, it could also be conceived as constituted by energetic contents that obey a distribution..., the quanta of light, later on called ….. .
a) photons – continuous – photons
b) photons – continuous – electrons
c) electrons - continuous - photons
d) electrons – discrete – electrons
Alternative and
2. (ENEM) The photoelectric effect contradicted the theoretical predictions of classical physics because it showed that the maximum kinetic energy of the electrons, emitted by an illuminated metallic plate, depends on:
a) exclusively from the incident radiation amplitude.
b) the frequency and not the wavelength of the incident radiation.
c) the amplitude and not the wavelength of the incident radiation.
d) the wavelength and not the frequency of the incident radiation.
e) the frequency and not the amplitude of the incident radiation.
Alternative and
3. (UFG-GO) A laser emits a monochromatic pulse of light with a duration of 6.0 ns, with a frequency of 4.0.1014 Hz and 110 mW power. The number of photons contained in this pulse is:
Data: Planck's constant: h = 6.6 x 10-34 J.s.
1.0 ns = 1.0 x 10-9 s
a) 2.5.109
b) 2.5.1012
c) 6,9.1013
d) 2.5.1014
e) 4.2.1014
Alternative to