Vector quantities represent everything that can be measured (measurable) and needs direction and direction. Vector quantities differ from scalar quantities in that they need meaning.
This relationship with mode, direction, and direction is called a vector. In mathematics, a vector is a line that has a direction. For example, from point A to point B and is represented by vet(AB).
Vector quantities and scalar quantities
Scalar quantities take on a complete sense from their measure (modulus). This is what happens with quantities such as: time, temperature, mass and volume.
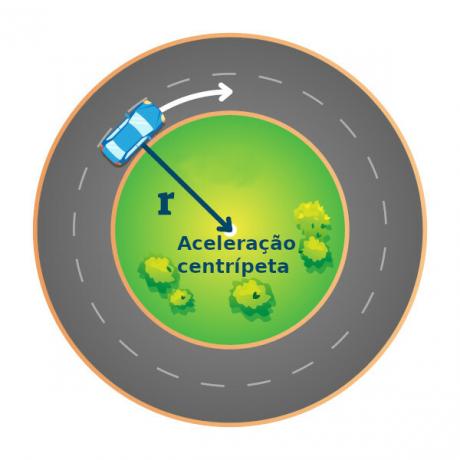
Other physical quantities need, in addition to the module, a sense and a direction to be understood. These are called vector quantities.
The vector is an oriented line that has a direction, a direction and a magnitude. It is the way to represent vector quantities.

Examples of vector quantities
Some examples of physical magnitudes that need meaning and direction are:
| Vector greatness | Definition | Unit of measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Distance traveled by a body over a period of time. | m/s; cm/s, km/h… |
| Acceleration | Rate of change of speed. | cm/s2 (Gal); m/s2… |
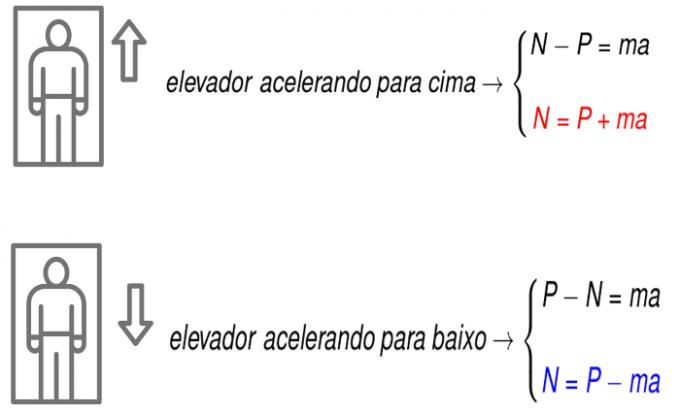
| Strength | Entity responsible for the movement or deformation of a body. | N, kgf, dyne, lbf... |
| Electric field | Force field caused by the action of electrical forces. | N/C, V/m... |
| Magnetic field | Field of action of magnetism created by a magnetic charge. | A/m, Oe |
Interested? See too:
- Vectors: addition, subtraction and decomposition
- Acceleration
- Normal force
- Electric field
- Magnetic field