Circular motionuniform is a type of movement that occurs with velocityclimbconstant along a trajectory of shape Circular. Despite receiving the adjective uniform, this movement is accelerated, since the change in the velocity vector direction implies the existence of a centripetal acceleration of radial direction, whose direction points to the center of the curve.
See too: uniform movement – formulas, concepts, exercises
Introduction to uniform circular motion
uniform circular motion (MCU) is one in which a particle moves along a circular path of constant radius. In this type of movement, both the scalar speed as to angular velocity are constant, but the movement isaccelerated, since in this type of trajectory it is necessary to have an acceleration, which points in the direction of the radius, always towards the center of the curve, called centripetal acceleration.
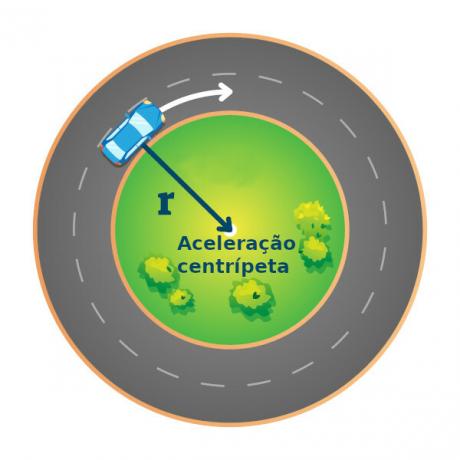

Since the trajectory covered in the MCU é Circular,
the space traversed (ΔS) by the particle can be calculated from a arc of circumference, so that a complete turn has a length equal to 2πR, where R represents the magnitude of the radius of this circle.The scalar velocity v do uniform circular motion, in turn, is calculated by the ratio between the spacetraveled (ΔS) and the breakintime (Δt), as shown below:

In the formula above, it is possible to separate the angular quantities from the spatial quantities. By doing this, another formula for the velocityclimb. Such a formula shows that the modulus of the scalar velocity in which the particle moves can be calculated from the product between the velocityangular (ω) and the path radius (R).
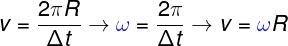
THE velocityangular is commonly called frequencyangular and also from pulsation. Its unit of measure is the radian per second (rad/s). However, since the radian is a angle measure, and not a physical quantity, the unit of measurement of angular velocity, strictly speaking, is the s-1, which is equivalent to hertz (Hz).
Angular velocity is also related to two other important quantities for circular movements: frequency (f) and period (T). The frequency, whose unit of measure is also the Hz, indicates the amount of rotations that a particle performs every second, while the period indicates the time required for this particle to go one lap complete. Thus, frequency and period are inversely proportional and related quantities. Watch:
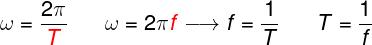
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Centripetal acceleration on the MCU
THE centripetal acceleration is the one that always point to the center of the curve performed by a particle in circular motion. This acceleration can be produced by a traction, frictional force, magnetic force, among others.
Just like the scalar acceleration, centripetal acceleration is measured in m/s². However, the physical meaning of centripetal acceleration is different from the meaning of scalar acceleration. While the latter indicates the variation of velocity magnitude, centripetal acceleration indicates a variation in speed direction, thanks to the character vector of velocity in circular motion.
THE formula used to calculate the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration of a particle in MCU is as follows:
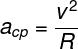
Read too: Circular movement: MCU and MCUV
Solved exercises on uniform circular motion
Question 1 —Determine the angular velocity of a particle that develops a uniform circular motion on a trajectory of uniform radius equal to 0.5 m, with a constant speed of 2.0 m/s.
a) 1.5 rad/s
b) 3.0 rad/s
c) 4.0 rad/s
d) 1.0 rad/s
Resolution:
Based on the information provided by the exercise statement, we will calculate the angular velocity.
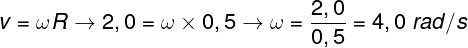
According to our calculations, we found that the angular velocity of this particle is equal to 4.0 rad/s, so the correct alternative is letter C.
Question 2 — A particle in uniform circular motion completes 2 turns on a circumference with a radius equal to 2.0 m, in a time interval of 4.0 s. Determine the period and frequency of this movement.
a) 0.5 Hz and 2.0 s
b) 0.4 Hz and 4.0 s
c) 4.0 Hz and 2.0 s
d) 2.0 Hz and 4.0 s
Resolution:
The statement states that the particle completes 2 rounds in 4.0 seconds, which indicates that it takes 2.0 s to complete each round. This result, therefore, is the period. The frequency, in turn, is defined by the inverse of the period and must be equal to 1/2, that is, 0.5 Hz, so the correct alternative is letter a.

*To download the mind map in PDF, Click here!
By Rafael Hellerbrock
Physics teacher