The Manaus Free Trade Zone (ZFM) is an industrial zone located in the north of the country. It comprises an area of 10,000 square kilometers.
Although most of it is located in the city of Manaus, in Amazonas, it also covers other Brazilian states: Acre, Rondônia, Roraima and Amapá.

Manaus Free Zone
The body responsible for the inspection and administration of the site is the Manaus Free Trade Zone Superintendence (SUFRAMA).
History and Objectives
The Manaus Free Trade Zone is an economic development model that was established in the city of Manaus in 1967 by Decree-Law 288.
In Brazil, this period was driven by the strong industrialization the country was undergoing after the government of Juscelino Kubitschek.
Still in the government of Juscelino Kubistchek Law No. 3173, of June 6, 1957, created a Free Zone in the city of Manaus, which in fact was only put into effect 10 years later with Decree-Law 288.
This decree altered and regulated the previous law and also increased the limits beyond the city of Manaus.
Excerpts from Law nº 3173, launched in the government of Juscelino Kubitschek
Art. 1st – A free zone for storage or deposit, storage, conservation, processing and removal of goods, articles and products is created in Manaus, capital of the State of Amazonas. of any nature, coming from abroad and intended for domestic consumption in the Amazon, such as interested countries bordering Brazil or bathed in the tributary waters of the river Amazons.
Art. 2nd – The Federal Government will demarcate, in the vicinity of the city, on the banks of the Negro River and in a place that meets the conditions of draft and berth satisfactory, an area of land not less than two hundred hectares, where the free zone will be located, with the facilities and services suitable for its operation.
§ 1 – The lands destined to the free zone created in this law will be obtained by donation from the Government of State of Amazonas or upon expropriation for public utility purposes, in accordance with the legislation in force.
Excerpts from Decree-Law 288 that established the current limits and objectives
“Art 1 The Manaus Free Trade Zone is an area of free trade in imports and exports and special tax incentives, established with the purpose of creating in the interior of the Amazon an industrial, commercial and agricultural center endowed with economic conditions that allow its development, in view of the local factors and the great distance, to which the consumer centers of their products.
Art 2 The Executive Branch will demarcate, on the left bank of the Negro and Amazonas rivers, a continuous area with a surface at least ten thousand square kilometers, including the city of Manaus and its surroundings, where the Free Trade Zone will be installed.
§ 1 The Free Zone area will have a maximum continuous length on the left banks of the Negro and Amazonas, fifty kilometers downstream of Manaus and seventy kilometers upstream of this City.
§ 2 The surface strip of rivers adjacent to the Free Zone, in the vicinity of its port or ports, is considered to be integrated in it, with a minimum extension of three hundred meters from the margin.
§ 3 The Executive Power, by decree and by proposal of the Free Zone Superintendence, approved by the Ministry of the Interior, may increase the area originally established or change its configuration within the limits established in paragraph 1 of this article."
When it was implemented, the main objective of the Zona Franca was to foster the economic development of the region.
In addition, it focused on integration between the Northern States and had the intention of promoting the occupation of that space. This is because the North region is the least populated in Brazil.
Advantages such as reduced customs duties, free trade area for imports, exports and tax incentives, attracted several national and foreign companies and industries to the area.
The free trade areas of the Manaus Free Trade Zone are: Tabatinga (AM; Macapá/Santana (AP); Guajará-Mirim (RO); Boa Vista and Bonfim (RR); Brasiléia, Epitaciolândia and Cruzeiro do Sul (AC).
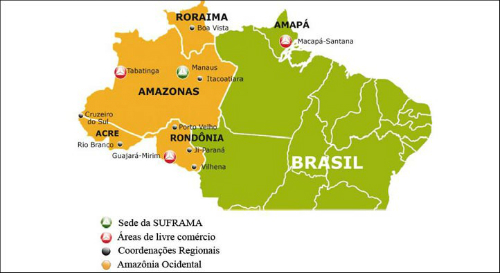
Map of Manaus Free Trade Zone with headquarters of Suframa, free trade areas, regional coordinations and Western Amazon
Currently, there are about 600 industries that sell different types of chemical, electronic, computer, automotive, etc. products. Some large industries have consolidated themselves in the area, such as Nokia, Siemens, Honda, Yamaha, etc.
Although the industrial hub is the most prominent, the Manaus Free Trade Zone also encompasses a commercial and an agricultural hub.
Importance of the Manaus Free Trade Zone
The Manaus Free Trade Zone has a strong economic impact on the region, as it employs more than half a million people.
Its creation was very important as it allowed the industrialization and development of the region, which until then was concentrated in the Southeast region of the country.
Integration between the states of the region has been consolidated over the years. In addition, it is noteworthy that it was essential to increase the population of the region, one of the smallest demographics in the country.
In February 2017, the Manaus Free Trade Zone celebrated its 50th anniversary. Despite the global crisis that began in 2008, this hub continues to stand out in the region's economy.
Curiosity
Besides Brazil, there are several countries that have a Free Trade Zone, for example, Chile, Portugal, Spain, France, China, etc.
Positive and negative points
The Manaus Industrial Zone has several advantages and disadvantages:
Benefits
- Commercial and economic development of the region
- Goods benefiting from tax incentives
- Reduced Customs Fees
- Benefits for companies and industries
- job and income generation
Disadvantages
- economic exhaustion
- High government spending
- Difficulty in selling products
Entrance Exam Questions
1. (UFPB-2009) Regarding the creation of a free zone in the city of Manaus, which sought to install an industrial pole in the North region, identify the factors on which this enterprise was supported:
1) Exemption from taxes on import of equipment.
2) Exploitation of specialized labor.
4) Installation of small and medium-sized companies, both domestic and foreign.
8) Export of products.
16) Destination of electronic products for consumers in the Northeast region of Brazil.
1: exemption from taxes on importing equipment; and 8: Export of products.
2. (Unesp) The following considerations refer to the city located on the map.
I. Its industrial hub is the result of a Decree-Law from the time of the military regime, therefore, imposed on Brazilian society.
II. Its companies carry out basic assembly operations, gradually incorporating nationally manufactured components.
III. Industrial production is heavily subsidized.
IV. The tax regime establishes unfair competition with producers from other regions of the country.
Check the correct alternative.
a) Textile Pole of Belém.
b) Industrial District of Santarém.
c) Manaus Free Trade Zone.
d) Porto Velho Steel Complex.
e) Petrochemical Zone of Palmas.
Alternative c: Manaus Free Trade Zone.
Read too:
- North region
- Northern States
- Economy of Brazil
- Northern Region Economy
- Industrialization in Brazil