Hematosis is the exchange of respiratory gases.
Generally speaking, it is the gas exchange between organisms and the environment.
Where does hematosis occur?
According to the place where the hematosis occurs, aerobic respiration can be of the following types:
Skin aerobic respiration, when hematosis occurs in the integument. This type of breathing is characteristic of land animals in wet environments. In this case, it is called tissue hematosis.
Aerobic tracheal respiration, when hematosis occurs in the tracheas. It happens to insects.
gill aerobic respiration, when hematosis occurs in the gills. It is typical of most aquatic animals. is called branchial hematosis.
And if it occurs in the lungs, it is called pulmonary aerobic breathing, characteristic of land animals. In this case, the exchange of gases takes place in the pulmonary alveoli, being called pulmonary or alveolar hematosis.
How does hematosis occur?
Hematosis occurs when oxygen-rich air from breathing reaches the pulmonary alveoli.
Each lung has approximately 150 million alveoli.
You alveoli they are sac-like structures located at the end of the bronchioles. They are covered by blood capillaries, in which blood circulates in close proximity to the air that has been inhaled.
Upon reaching the alveoli, oxygen diffuses into the blood from the capillaries. Meanwhile, carbon dioxide, present in the blood of capillaries, diffuses into the alveoli.
Thus, the hematosis occurs due to diffusion of oxygen gas from the air of the alveoli to the blood of the capillaries. And the same happens with carbon dioxide, however, in the opposite direction.
- The blood that comes out of the lungs is rich in oxygen, being called arterial blood.
- The blood that reaches the lungs is rich in carbon dioxide, being called venous blood.
When oxygen gas passes into the blood, it enters the red blood cells, where it binds with hemoglobin and forms oxy-hemoglobin. In this form, oxygen gas passes throughout the body and reaches the blood capillaries of the tissues.
In fabrics, the O2 it dissociates from oxyhemoglobin and diffuses into the fluid that bathes the cells.
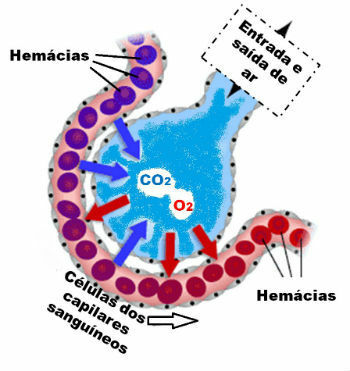
The process of hematosis in the pulmonary alveoli. The exchange of gases with blood capillaries.
Cells use the O2 for cellular respiration. During this process, carbon dioxide molecules are created that diffuse into the fluid that bathes the cells and are absorbed by the blood capillaries.
From there, the CO2 may remain in plasma or associate with hemoglobin.
However, most of the CO2 reacts with water inside the red blood cells and forms carbonic acid (H2CO3), which dissociates into H ions+ and bicarbonate ions (HCO3-).
Bicarbonate ions are essential to control blood acidity.
Learn more aboutRespiratory system.
How important is hematosis?
- Ensures tissue oxygenation;
- Allows the performance of cellular respiration;
- Produces bicarbonate ions that control blood acidity
Check issues with commented resolution inexercises on the respiratory system.

