The Pauling Diagram, also known as the Energy Diagram, is the representation of electronic distribution through power sub-levels.
Through the scheme, the chemist Linus Carl Pauling (1901-1994) suggested something beyond what was already known regarding the distribution of electrons from the atoms of chemical elements.
To improve the mood, Pauling proposed the energy sub-levels. Through them, it would be possible to arrange the electrons from the lowest to the highest energy level of an atom in its ground state.
Electronic distribution by Linus Pauling
According to the model proposed by Pauling, the electrosphere is divided into 7 electronic layers (K, L, M, N, O, P and Q) around the atomic nucleus, each of which allows a maximum number of electrons, which are 2, 8, 18, 32, 32,18 and 8, respectively .
At electronics distribution the energy sublevels, showing the lowest energy electron first until reaching the highest energy electron.
| Electronic Layers | Maximum Number of Electrons | Energy Sublevels | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | K | 2 and- | 1s2 | |||
| 2 | L | 8 and- | 2s2 | 2p6 | ||
| 3 | M | 18 and- | 3s2 | 3p6 | 3d10 | |
| 4 | N | 32 and- | 4s2 | 4p6 | 4d10 | 4f14 |
| 5 | O | 32 and- | 5s2 | 5p6 | 5d10 | 5f14 |
| 6 | P | 18 and- | 6s2 | 6p6 | 6d10 | |
| 7 | Q | 8 and- | 7s2 | 7p6 |
Layer K has only one sublevel(s), layer L has two sublevels (s and p), layer m has three sublevels (s, p and d) and so respectively.
The s sublevels allow up to 2 electrons, while the p sublevels allow up to 6 electrons. Next, the d sublevels allow up to 10 electrons, while the f sublevels allow up to 14 electrons.
Note that the sum of the electrons behaved in each sublevel per electron shell results in the maximum number of electrons in each of the 7 shells.
K: s2 = 2
L and Q: s2 + p6 = 8
M and P: s2 + p6 + d10 = 18
N and O: y2 + p6 + d10 + f14= 32
It was then that Pauling discovered the increasing order of energy:
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p6 6s2 4f14 5d10 6p6 7s2 5f14 6d10 7p6
From there, the diagonal arrows appear in the diagram to make the electronic distribution of the elements:
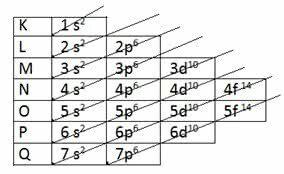 Pauling diagram
Pauling diagram
Example of electronic phosphorus distribution 15P:
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3
like up to 3s2 we already had a total of 12 electrons (2 + 2 + 6 + 2), we only need 3 more electrons from the 3p sublevel6.
Thus, we can get the required amount of electrons, as long as it is not greater than 6, which is the maximum number that the 3p sublevel6 behaves.
Read too Valencia layer and Quantum Numbers.
Solved Exercises on Electronic Distribution
question 1
(Unirio) “Dental implants are safer in Brazil and already meet international quality standards. The great leap in quality took place in the process of making titanium screws and pins, which make up the prostheses. Made with titanium alloys, these prostheses are used to fix dental crowns, orthodontic appliances and dentures, in the bones of the jaw and jaw.” (Jornal do Brasil, October 1996.)
Considering that the atomic number of titanium is 22, its electronic configuration will be:
a) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3
b) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5
c) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2
d) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d2
e) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6
Correct alternative: d) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d2.
The Linus Pauling diagram for the distribution of electrons in titanium is:
question 2
(ACAFE) Considering any generic M element, which has 1s electronic configuration2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d5, it can be said that:
I. its atomic number is 25;
II. has 7 electrons in the last shell;
III. has 5 unpaired electrons;
IV. belong to the 7A family.
The statements are correct:
a) I, II and III only
b) I and III only
c) II and IV only
d) I and IV only
e) II, III and IV only
Correct alternative: b) I and III only.
I. CORRECT Counting the number of electrons in the electronic distribution we see that 25 were used. Hence, the atomic number is 25 and corresponds to the chemical element manganese.
II. WRONG. The last layer, that is, the outermost layer has 2 electrons, being the 4s2.
III. CORRECT The unpaired electrons are in the d sublevel, which holds up to 10 electrons, but in the electronic distribution of manganese only 5 electrons have been assigned to the sublevel.
IV. WRONG. Manganese is located in the 7B family and in the 4th period.
question 3
(UFSC) The number of electrons in each sublevel of the strontium atom (38Sr) in ascending order of energy is:
a) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2
b) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 4p6 3d10 5s2
c) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 5s2
d) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4p6 4s2 3d10 5s2
e) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3p6 3s2 4s2 4p6 3d10 5s2
Correct alternative: a) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2.
The Linus Pauling diagram for the distribution of strontium electrons is:
Test your knowledge even more! Also resolve:
- Exercises on Electronic Distribution
- Exercises on the Periodic Table