Electrolysis is a non-spontaneous chemical reaction which involves an oxidation-reduction reaction, which is caused by an electrical current.
For electrolysis to take place, the electrical current involved must be continuous and have a sufficient voltage.
For the ions involved to have freedom in the movement they perform, electrolysis can occur by fusion (igneous electrolysis) or by dissolution (electrolysis in solution).
Electrolysis Applications
Many materials and chemical compounds are produced from the electrolysis process, for example:
- aluminum and copper
- hydrogen and chlorine in cylinder
- costume jewelry (galvanization process)
- pressure cooker
- magnesium wheel (car hubcaps).
Laws of Electrolysis
The Laws of Electrolysis were developed by the English physicist and chemist Michael de Faraday (1791-1867). Both laws govern the quantitative aspects of electrolysis.
THE first law of electrolysis has the following statement:
“The mass of an element, deposited during the electrolysis process, is directly proportional to the amount of electricity that passes through the electrolytic cell”.
Q = i. t
Where,
Q: electric charge (C)
i: electric current intensity (A)
t: time interval of passage of electric current (s)
THE second law of electrolysis has the following statement:
“The masses of various elements, when deposited during electrolysis by the same amount of electricity, are directly proportional to their chemical equivalents”.
M = K. AND
Where,
M: substance mass
K: proportionality constant
AND: gram equivalent of substance
Learn more in the article: Faraday's constant.
Classification
The electrolysis process can occur through melting or dissolution:
Igneous Electrolysis
Igneous electrolysis is that which is processed from a molten electrolyte, that is, by the process of Fusion.
As an example, let's use NaCl (Sodium Chloride). When we heat the substance to 808 °C, it fuses and the ions present (Na+ and Cl-) start to have greater freedom of movement, in the liquid state.
when the electric current passes into the electrolytic cell, the Na cations+ they are attracted by the negative pole, called the cathode. Already the anions of Cl-, are attracted by the positive pole, or the anode.
In the case of Na+ a reduction reaction occurs, while in Cl-, there is a reaction of oxidation.
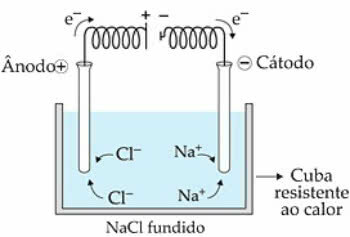
Scheme of Igneous NaCl Electrolysis
Aqueous Electrolysis
In aqueous electrolysis, the ionizing solvent used is water. In aqueous solution, electrolysis can be performed with inverted electrodes or active (or reactive) electrodes.
Inert electrodes: the water in the solution ionizes according to the equation:
H2O ↔ H+ + OH-
With the dissociation of NaCl we have:
NaCl → Na+ + Cl-
Thus, the H cations+ and on+ can be discharged at the negative pole, while OH anions- and Cl- can be discharged at the positive pole.
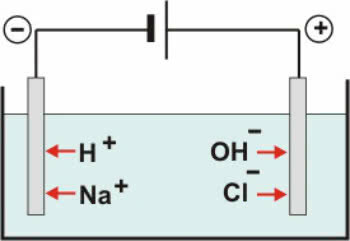
NaCl Aqueous Electrolysis Scheme
In cations there is a reduction reaction (cathodic reduction), while in anions, an oxidation reaction (anodic oxidation).
So we have the electrolysis reaction:
2 NaCl + 2 H2O → 2 In+ + 2 OH- + H2 + Cl2
From this, we can conclude that NaOH molecules remain in solution, while H2 is released at the negative pole and the Cl2, on the positive pole.
This process will result in the equivalent equation:
2 NaCl + 2 H2O → 2 NaOH + H2 + Cl2
Active Electrodes: in this case, the active electrodes participate in the electrolysis, however, they suffer corrosion.
As an example, we have the electrolysis in aqueous solution of copper sulfate (CuSO4):
CUSO4 → Cu2 + OS 2-4
H2O → H+ + OH-
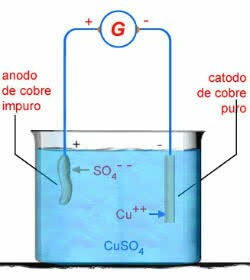 CuSO Aqueous Electrolysis Scheme4
CuSO Aqueous Electrolysis Scheme4
In this case, the copper anode will corrode:
Ass0 → Cu2+ + 2e-
This is because, according to the standard potentials of the electrodes, the electric current has an easier time removing the electrons from the Cu0 than the OS 2-4 or from oh-.
Therefore, at the negative pole, the following electrolysis reaction occurs:
2e- + Cu2+ → Cu
On the positive pole, we have the electrolysis reaction:
Cu → Cu2+ +2e-
Finally, when we add the two electrolysis equations, we have zero as a result.
Want to know more about the topic? Read the articles:
- Ion, Cation and Anion
- Chemical reactions
- Oxidation Reactions
Battery and Electrolysis
Electrolysis is based on an inverse phenomenon to that of the battery. In electrolysis, the process is not spontaneous, as it happens in batteries. In other words, electrolysis converts electrical energy into chemical energy, while the cell generates electrical energy from chemical energy.
know more about Electrochemistry.
Exercises
1. (Ulbra-RS) Metallic potassium can be produced by the igneous electrolysis of potassium chloride. From that statement, tick the correct alternative.
a) Electrolysis is a process that involves oxidation-reduction and reduction reactions motivated by electrical current.
b) Igneous electrolysis of potassium chloride takes place at room temperature.
c) Potassium is found in nature in the reduced form (K0).
d) The electrolysis reaction is one that takes place with the help of ultraviolet radiation.
e) In the process of electrolysis of potassium chloride, to obtain metallic potassium, the transfer of electrons from potassium to chlorine occurs.
Alternative to
2. (UFRGS-RS) In the cathode of an electrolysis cell there is always:
a) Metal deposition.
b) A reduction half-reaction.
c) Production of electric current.
d) Release of hydrogen gas.
e) Chemical corrosion.
Alternative b
3. (Unifor-CE) The following propositions are related to electrolysis:
I. Electrolysis reactions occur with consumption of electrical energy.
II. Aqueous glucose solutions cannot be electrolyzed because they do not conduct an electrical current.
III. In the electrolysis of saline solutions, metallic cations undergo oxidation.
We can say that only:
a) I is correct.
b) II is correct.
c) III is correct.
d) I and II are correct.
e) II and III are correct.
Alternative
4. (FEI-SP) Two Chemistry students performed BaCl electrolysis2; the first watery and the second fiery. Regarding the result, we can say that both obtained:
a) H2 it's the2 at the anodes.
b) H2 and Ba at the anodes.
c) Cl2 and Ba on the electrodes.
d) H2 at the cathodes.
e) Cl2 at the anodes.
Alternative and
5. (Vunesp) "Pool without Chemistry” is an advertisement involving water treatment. It is known, however, that the treatment consists of adding sodium chloride to the water and passing this water through a container equipped with copper and platinum electrodes connected to a lead car.
a) Based on this information, discuss whether the ad message is correct
b) Considering the inert electrodes, write the equations of the reactions involved that justify the previous answer.
a) The ad message is not correct, as there will be formation of chemical products.
b) 2 NaCl + 2H2O → 2 NaOH + H2 + Cl2 (reaction that forms chlorine, useful in the treatment of pool water)
2 NaOH + Cl2 → NaCl + NaClO + H2O (reaction that forms NaClO, a strong bactericide)