O pH of a solution indicates the content (measurement) of hydronium ions (H3O+) present in the middle. This content determines whether the analyzed solution has an acidic, basic or neutral character.
Observation: It is noteworthy that the hydronium content (H3O+ or H+) can be acquired simply in the laboratory using pH indicator tapes - which, however, do not have great accuracy in the measure - or by means of equipment called a peagometer, which, on the contrary, has great accuracy in measuring the pH of a solution.
Pedometer or potentiometer to measure the pH of a solution
To carry out the calculations involving pH of a solution, we can use the following logarithmic equation:
pH = - log [H3O+]
or
pH = - log [H+]
IMPORTANT: In calculations involving the pH of a solution, we always use the base 10 logarithm.
Mind Map: Calculating PH of Solutions

* To download the mind map in PDF, Click here!
From the logarithmic equation above, we can still use the following simplification (obtained by applying a logarithmic function) of this equation:
[H3O+] = 10-pH
Observation: The simplified expression above can only be used if the pH value is integer; otherwise, the logarithmic function must be used.
It is important to emphasize that the calculations involving the pH of a solution are always related to the pOH (hydroxylionic potential / OH-), since both potencies are based on the self-ionization of water (Kw = 10-14, a phenomenon in which water produces so much H+ how much oh-) and Ostwald's law of dilution (the more diluted a solution, the greater the amount of H cations+ ). Thus:
about water autoionization:
Kw = [H+]. [oh-], so pH + pOH = 14
law of Ostwald dilution(Through it, we can know how much a certain material ionizes or dissociates in water):
Ki = M.α2
Ki = Ionization constant of a substance in an aqueous medium;
M = molarity or molar concentration of the substance in the aqueous medium;
α2 = degree of ionization or dissociation of the material in the medium.
The classification of a solution as acidic, basic or neutral will have the following criteria (a 25 OÇ):
-
one solution will be neutral when the concentration of H+ is equal to the concentration of OH- or have a pH equal to 7.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
[H+] = [OH-]
one solution will be acidic when the concentration of H+ is greater than the OH concentration- or the pH is between 0 and 7.
[H+] > [OH-]
one solution will be basic when the concentration of H+ is less than the OH concentration- or the pH is between 7 and 14.
[H+] < [OH-]
See some examples of calculations involving the pH of solutions:
1º)Knowing that the concentration of hydronium in a coffee is equal to 1.10-5, what will be the pH present in this solution?
how to exercise provided the hydronium concentration for coffee, we can use the simplified pH formula:
[H3O+] = 10-pH
1.10-5 = 10-pH
10-5 = 10-pH
-5 = -pH
pH = 5
As the pH is less than 7, the solution is acidic.
2º) (UFU) What is the pH of a 0.045 mol/L acetic acid solution, assuming its Ki = 1,.10-5? Data: log 2 = 0.3; log 3 = 0.48.
Exercise data:
M = 0.045 mol/L
Ki = 1,8.10-5
log 2 = 0.3
log 3 = 0.48
How the exercise provided the molarity (M) and the ionization constant (Ki),initially let's determine the degree of ionization of the acid mentioned, because the concentration of hydronium (H3O+ or H+) is always the result of the multiplication between the molarity and the degree of ionization. Soon:
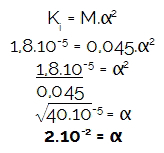
Next, let's calculate the amount of hydronium multiplying molarity of the acid by the degree of ionization found:
[H3O+] = M.α
[H3O+] = 0,045.2.10-2
[H3O+] = 0,09.10-4
[H3O+] = 9.10-4 mol/L
Finally, we put the hydronium concentration value in the logarithmic pH equation:
pH = - log [H3O+]
pH = - log 9.10-4
pH = 4 - log 9
pH = 4-log 32
pH = 4 - 2. (log 3)
pH = 4- (2.0.48)
pH = 4-0.96
pH = 3.04
As the pH is less than 7, the solution is acidic.
3º)(Cefet-PR) A 45 OC, the Kw of a neutral solution is equal to 4.10-4. So what is the pH value of this solution at this temperature? Log 2 data = 0.3.
How the exercise tells you the solution is neutral, soon [H3O+] is equal to [OH-]:

Finally, we put the hydronium concentration value in the logarithmic pH equation:
pH = - log [H+]
pH = - log 2.10-7
pH = 7 - log 2
pH = 7-0.3
pH = 6.7
As the pH is almost 7, the solution is neutral (as indicated in the exercise statement) because the temperature is 45 OÇ.
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
DAYS, Diogo Lopes. "Calculations involving pH of solutions"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/calculos-envolvendo-ph-solucoes.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.
Ostwald's law, ionization constant, molar concentration, degree of ionization, weak electrolyte, number of mol ionized, Friedrich Wilhelm Ostwald, monoacids, monobases.