Transesterification is the chemical reaction that takes place between an ester and an alcohol, with the formation of a new ester and alcohol.
Depending on the type of substance that reacts with the ester, we have the following types of transesterification:
- alcoholysis: Reaction between alcohol and ester;
- Acidolysis: Reaction between ester and carboxylic acid;
- interesterification: Reaction between two esters.
Mechanism
Transesterification to obtain oils occurs by mixing vegetable oil or animal fat with a simple alcohol in the presence of catalysts. As a result, biodiesel and glycerin originate.
The main use of transesterification is for the production of biodiesel. In this case, vegetable oils are obtained from soybeans, sunflowers, peanuts, castor beans, cotton or palm oil.
Transesterification occurs from one mole of triglyceride and three moles of alcohol. As described in the reaction below:
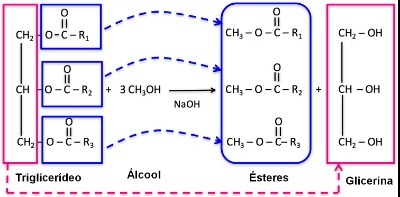
During the reaction, triglycerides are transformed into fatty acid monoesters, which make up biodiesel.
Furthermore, glycerin also appears as a by-product of the reaction.
For the production of biodiesel, the methanol and ethanol are the most used alcohols, being methanol the most efficient for the process.
Reaction catalysts can be acids or bases. Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is one of the most used.
In the case of biodiesel production, after the reaction it is necessary to separate the components in the mixture, through the decant. In the upper phase is biodiesel and in the lower phase is glycerin.
In some cases, it is also necessary to remove excess alcohol from the mixture, which is done by evaporation or distillation.
Read too:
- esters
- esterification
applications
As we have seen, the main application of transesterification is to obtain the biodiesel. It is a natural product with low pollutant content, representing an alternative to replace diesel oil.
However, the glycerin obtained in the process also has a high commercial value and is used by the cosmetic and drug industry.
Transesterification is also used to produce polymers. An example is obtaining polyethylene terephthalate (PET) used in the manufacture of plastic bottles.
Learn more about the Chemical reactions.