THE distillation it is one of the processes of separation of homogeneous mixtures that takes place through boiling, where the liquid is vaporized and then condensed. Thus, the mixtures that will be separated have different boiling points.
In other words, distillation is a physicochemical process of separation of mixtures that takes place through heating and cooling of the mixtures. When the mixture is heated, the substance that has the lowest boiling point, that is, the most volatile, is evaporated first.
Distillation is carried out in chemical laboratories and industries using specific equipment (condenser, thermometer, distillation, bunsen nozzle, beaker, heating mantle, fractionation column), for example, when separating water from alcohol or water from the salt.
A natural example of the distillation process is seen when water droplets condense on colder days. In addition, the so-called distilled beverages (cachaça, vodka, brandy, tequila, rum, whiskey) are produced through the fractional distillation process, used since ancient times.
Types of Distillation
Distillation can take place in two ways depending on the nature of the separate mixtures:
Simple Distillation
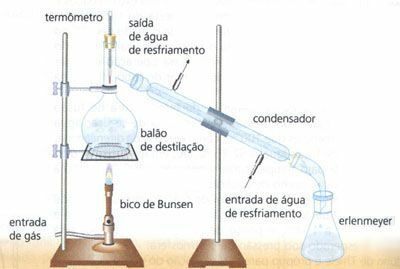 Simple Distillation
Simple Distillation
Separation of a homogeneous mixture of solid and liquid, eg water (H2O) of the salt (NaCl). In this way, the water is evaporated through heating, which passes through the condenser in the form of liquid (water droplets), from which the salt is retained and separated in a container called a water balloon. distillation.
Fractional Distillation
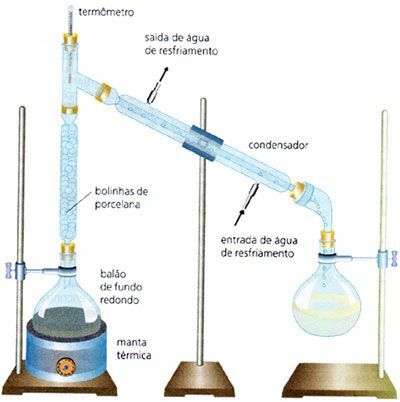 Fractional Distillation
Fractional Distillation
Widely used in industry, it is the separation of a homogeneous mixture of liquid and liquid, by example, water and alcohol (The boiling point of water is 100°C and the boiling point of ethyl alcohol is 78°C). It is carried out through mixtures that have very close boiling points. Unlike the simple distillation process, in this case there is a fractionation column.
Oil Distillation
To obtain petroleum products (gasoline, kerosene, fuel oil, paraffin, asphalt), the distillation process fractionated is used where the liquid with the lowest boiling point is separated first until reaching the liquid with the highest boiling point. boiling.
remember that the Petroleum it is a natural substance composed of several organic components, especially hydrocarbons (carbon and hydrogen molecules).
azeotropic distillation
Azeotropic distillation occurs when the separation of mixtures forms an azeotrope, that is, they have low volatility and point constant boiling points, which cannot be separated by the simple method of distillation, eg hydrochloric acid (HCL) and water (H2O).
Fun Facts: Did You Know?
Distilled Water (demineralized water) is a pure substance obtained through distillation and is generally used in the laboratory. Note that the water we drink is not pure, that is, it includes mineral salts. However, distilled water can be used for human consumption as well as for the treatment of some diseases, for example, kidney stones.
Complement your research by reading the articles:
- Melting and boiling point
- Liquefaction or Condensation
- Vaporization
- Separation of Mixtures
Check entrance exam questions with feedback commented on: exercises on mixing separation.