Oxidation is the chemical reaction in which atoms, ions or molecules lose electrons. It also causes an increase in the number of oxidation (nox).
The term oxidation was initially created to denote reactions in which oxygen was the reactant. However, it was found that in some cases, they occurred in the absence of this element. As the term was already widely known, it continued in use.
Oxidation reactions occur simultaneously with reduction reactions. Therefore, they are called redox, in which electrons are transferred.
In redox reactions, the oxidizing agent is the one that accepts electrons, undergoing reduction. The reducing agent loses electrons and undergoes oxidation.
Oxidation Examples
Iron Oxidation
Rust is the oxidation of iron. All metals can undergo oxidation. It occurs due to the contact of metals with air and water. Initially, the corrosion which is the wear of the metal due to oxidation. Then, it forms the rust.
See the reaction of redox for rust formation:
- Fe(s) → Fe2+ + 2e-. At this stage, the iron loses two electrons, undergoes oxidation
- O2 + 2 H2O + 4e- → 4OH-. O reduction2
- 2Fe + O2 + 2H2O → 2 Fe(OH)2. General Equation - Fe(OH)2 is the Iron Hydroxide, responsible for the brown color of the rust.
To protect iron and steel from oxidation, the galvanizing technique can be used. It consists of metallic zinc coating. However, it is an expensive process, making it unfeasible in some cases.
Thus, the hulls of ships and metallic platforms receive blocks of metallic magnesium that prevent the oxidation of iron. Magnesium is considered a sacrificial metal and needs to be replaced from time to time when it wears out.
Painting can also protect the metal from oxidation, but it is not as effective.

Rust
Also read about Stainless steel and Metal alloys.
Oxidation in Organic Chemistry
In addition to metals, oxidation can also occur with Hydrocarbons, especially the alkenes. Organic oxidation has four forms: combustion, ozonolysis, mild oxidation and energy oxidation.
Combustion
THE combustion it is a chemical reaction of a substance with oxygen, which culminates in the production of light and heat. Oxygen is called oxidizer. The substance with carbon is the fuel.
Oxygen has the function of oxidizing the fuel, it is the oxidizing agent of combustion.
Combustion can be complete or incomplete. Know the difference between the two ways:
- Complete combustion: Occurs when there is sufficient oxygen supply. At the end of the reaction, carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O).
- Incomplete combustion: There is not enough oxygen supply, they form carbon monoxide (CO) and water (H2O).
Ozonolysis
In this type of reaction, ozone is the reagent that causes alkenes to oxidize. The breakage of the double bond of alkenes occurs and the formation of carbonyl compounds, such as aldehydes and ketones.
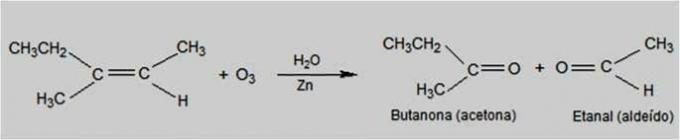
Ozonolysis Reaction
mild oxidation
Mild oxidation occurs when the oxidizing agent is a compound such as potassium permanganate (KMnO4), present in an aqueous solution, diluted and cooled, neutral or slightly basic.
This type of oxidation occurs using the Baeyer Test, used to differentiate alkenes from isomeric cyclans.
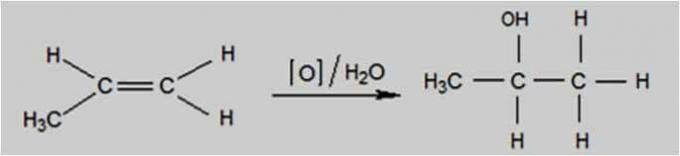
Mild Oxidation Reaction
Energy Oxidation
In this type of oxidation, potassium permanganate is found in a hotter and more acidic environment, making the reaction more energetic. Energetic oxidizing agents can break the double bond of alkenes.
Depending on the structure of the alkene, ketones and carboxylic acids can be formed.
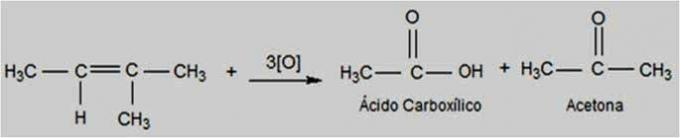
Energy Oxidation Reaction
Want to know more? Also read about Electrochemistry.

