O atomic ray of elements is a periodic property that determines the radius of an atom which varies depending on the element's position in the Periodic Table.
Thus, they can increase and decrease as the atomic number (Z) of the element that corresponds to the number of protons present in the nucleus of atoms.
In summary, the atomic radius corresponds to half the distance between the nuclei of two neighboring atoms, being expressed as follows:
r = d/2
whence:
r = radius
d = internuclear distance
Generally the atomic radius is measured in picometers (pm), sub-multiple of the meter (1 picometer=10-12 m.). Note that when the reference is not an atom but an ion, the radius found is the ionic radius.
Atomic Radius Variation
In the periodic table, the growth of the atomic radius can be seen in the following figure:
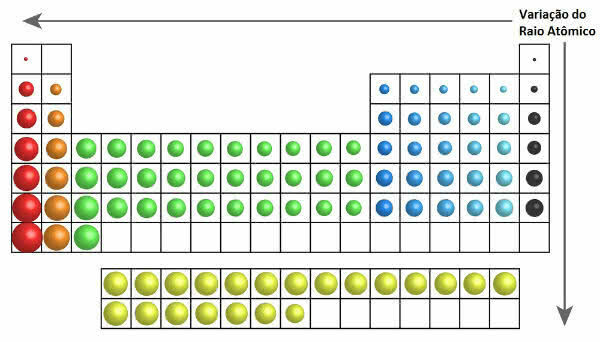 Atomic Radius Variation in the Periodic Table
Atomic Radius Variation in the Periodic Table
Thus, vertically (families or groups) the atomic radius increases from top to bottom. On the horizontal (periods), they increase from right to left.
See the inverse variation in Electronic Affinity and electronegativity.
Ionization Energy
THE ionization energy (or potential) it is also a periodic property that determines the energy required to shift an electron, which is expressed in electron volts (eV).
Read too: Periodic Properties.
Check entrance exam questions with a commented resolution in: Exercises on the Periodic Table.


