Money laundering is the expression created to name the introduction of dirty money into the financial system making it appear to have a legal origin.
It is a way of hiding the source of an illegally obtained asset. This can be the case of money from trafficking, prostitution, corruption, tax evasion and others.
The term “washing” refers to the idea of giving the appearance of being clean to a gain resulting from an illegal activity.
The expression arose in the 20s in the United States, when a chain of laundries was used to receive money for services rendered. It turns out that the laundry was just a front and will have been paid for the jobs it never did.
How does money laundering work?
Billing services never rendered or billing more than they should are ways to disguise the origin of the money.
A dealer who wants to deposit money from the traffic in the bank, for example, can transfer the amount to a shell company. This makes the deposit, without anyone suspecting its honest origin, after all, a company is paid for the work it performs.
A dealer could not do this, as he has no way of proving that the origin of the money is legal.
Accounts opened in the name of “oranges” are also widely used. “Oranges” are people who “lend” their name to open accounts and hide the true identity of their beneficiary. They do this in exchange for a good bonus.
These are just a few ways to hide the true origin of an asset, which can also be done through various operations. financial (with the aim of confusing the institutions), or even sending the money to tax havens, where bank secrecy is guaranteed.
See too: News that may fall into Enem and Vestibular
What are the stages of money laundering?
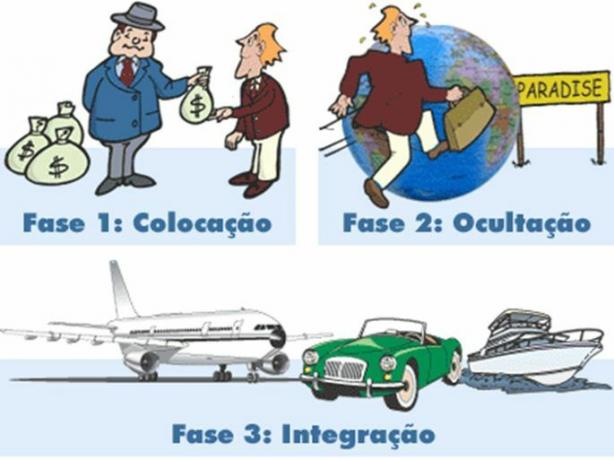
Money laundering results from the following three phases:
- 1st place - Introduce dirty money into the economic system in order to hide its origin.
- 2nd Concealment - Make it difficult to track the asset earned in a dirty way, moving that money through various financial transactions.
- 3rd Integration - Use the money that, at this stage, is already clean for a new economic circuit.
Money laundering prevention
The debate on the prevention of money laundering emerged in 1988 Vienna Convention.
Over the years, and with the improvement of crime, the authorities increasingly look for ways to reduce the entry of illicit money into the system.
For this, the legislation requires certain procedures. Examples are documentary proof of the origin of a deposit from a certain amount, or regular deposits, from the moment they reach a certain amount.
The FATF (Financial Action Group on Money Laundering/Financial Action Task Force on Money Laudering) is the body that recommends anti-money laundering measures for the entire world.
Each country has the obligation to adopt these measures according to its reality. From them, procedures and tools are implemented, such as:
- Customer knowledge (Know Your Customer - KYC)
- Risk rating
- Transaction monitoring
- Personal training
- Audit
Money Laundering Prevention Law
In Brazil, the COAF (Council for the Control of Financial Activities) is the body responsible for the prevention and inspection of money laundering.
This practice is configured as an independent crime since 1998 through Law No. 9613, of March 3, 1998, a law that was amended by Law No. 12,683, of 2012.