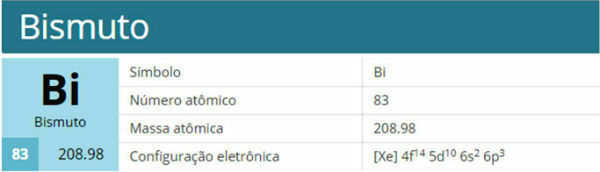
Bismuth is a chemical element with the symbol Bi, atomic number 83, atomic mass 208.9 u. It belongs to group 15 and family 5A.
In nature, bismuth is infrequent, which increases its market value. It has several types of uses in industries and even for human health.
Chemical and physical characteristics
Bismuth is solid at room temperature, having a low melting point.
It is characterized as a fragile and brittle metal, with a pinkish hue and an iridescent color.
It is the most diamagnetic metal on the periodic table, meaning it is repelled by strong magnetic fields.

In nature, in addition to its elemental form, it is also found in the form of the following minerals: bismutinite (Bi2s3) and bismite (Bi2O3).
It can also be found associated with silver, zinc and lead.
The countries with the greatest abundance of bismuth are Peru, Mexico, Bolivia and China. In Brazil, the amount of bismuth is extremely low, which prevents its exploitation.
A peculiar feature is that despite being a heavy metal, its salts do not present toxicity and can be used for numerous activities.
Despite this, both bismuth and its salts can cause some types of liver damage. Also, it can remain in the kidneys for years. Some cases of bismuth poisoning have already been reported.
applications
Because bismuth salts are non-toxic, they are used in the manufacture of medicines and cosmetics, such as eye shadows, blush and hair dyes.
An important pharmaceutical application is in the composition of drugs to combat peptic ulcers caused by the bacteria Helicobacter pylori.
Bismuth salicylate is used in medicines against diarrhea, stomach pain and indigestion.
Bismuth is also used in soldering and in the manufacture of metal alloys. In this case, it is mixed with aluminum, copper or iron.
Its low melting point makes it used in fire prevention systems. As the ambient temperature increases, the bismuth metal alloy melts and activates the water release system in place.