You transgenic foods they correspond to genetically modified foods (GM), that is, they are those in which the DNA is modified.
These foods are produced in the laboratory using artificial genetic engineering techniques. Thus, embryos are altered as they receive a gene from another species.
Transgenic Food Production: the issues discussed
There is much debate about the effectiveness of these types of “artificial” foods, since in nature many of them did not reproduce in this way.
There is controversy about the nutrients it contains, as well as their ethical, economic, social and political implications.
THE genetic engineering and the commercialization of genetically modified foods is considered a promising area for offering a perspective of innovation to conventional plant breeding.
This is because the manipulation of genetic material from plants and other living beings contributes, above all, to obtaining less perishable, healthier and safer foods.
Transgenic tests aim to develop plants and animals that are more resistant to diseases, pests, pesticides and climate change, thus increasing productivity.
On the other hand, there is controversy about the nature of such foods. This factor is related to the short- and long-term health effects of humans and animals. In other words, aiming for profit at the expense of health, which could be a big problem in the future.
Legislation on Transgenic Food
According to current legislation, the identification label on transgenic foods is mandatory in order to alert the consumer about what he is consuming.
In Brazil and the European Union, product labels with up to 1% of transgenic components are presented.

Decree No. 4.680 of 2003 requires companies to display information whenever the food has more than 1% of transgenic ingredients, even if it cannot be detected by laboratory testing.
This requirement is also valid for foods originating from animals fed with transgenic feed such as milk, eggs, and meat.
The standardized symbol is represented by a T inside a yellow triangle and must be inserted on the food packaging.
Transgenic Food in the World
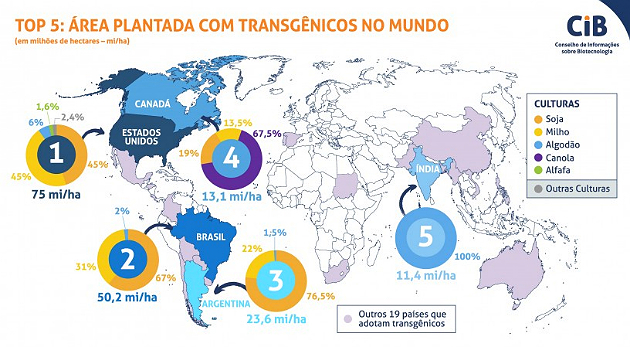
In many countries, the consumption of transgenic food is legal, while in others, its adherence is far from being effective.
In the latter case, we can mention Japan, whose commercialization of genetically modified foods is rejected.
The countries that lead the production of transgenic food are the United States, Argentina, Canada, China, in addition to Brazil.
In the world, the food produced in greater quantity is corn, soy, cotton and canola. The most prevalent crop on the planet is herbicide-resistant soy.
Transgenic foods of animal origin can also be modified. In 2012, the US company “food and Drug administration” (FDA) approved the consumption of the first genetically modified animal, a type of salmon.
Transgenics in Brazil
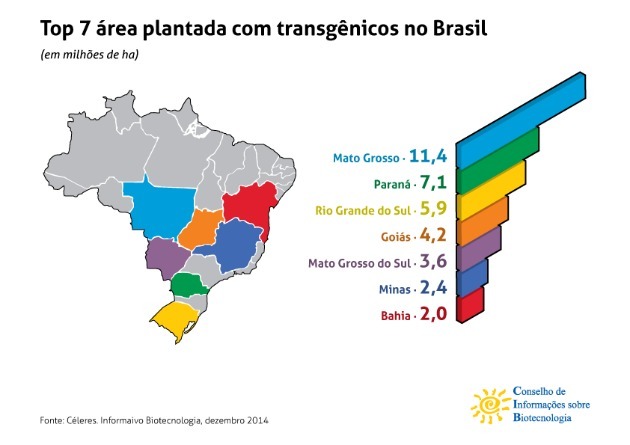
In 2017, in Brazil, 50.2 million hectares (ha) were occupied with transgenic crops, mostly soy. As a result, the country became the second largest producer of transgenics in the world, only behind the United States.
Brazil stands out for having commercially launched, in 2015, the first genetically modified organism fully developed in the country: a herbicide tolerant soy, the result of a partnership between the Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation (Embrapa) and the German company Basf.
Advantages and Disadvantages of transgenic foods
Transgenic foods have a series of advantages and disadvantages, including:
Advantages of transgenic foods
- Greater productivity;
- Cost reduction;
- Increased nutritional potential of food;
- Plants more resistant to pests (insects, fungi, viruses, bacteria) and pesticides, insecticides and herbicides;
- Increased plant tolerance to adverse soil and climate conditions;
- Reduction in the use of pesticides.
Disadvantages of transgenic foods
- Development of diseases (allergic reactions, cancer, etc.);
- Environmental imbalance (soil, water and air pollution, disappearance of species, loss of biodiversity, seed contamination, etc).