THE division is the mathematical operation used to separate the elements of a set in smaller sets, that is, to divide an amount into equal parts. The division makes it possible to resolve different types of everyday situations, so it is important to understand its functioning in order to apply it properly.
Read too: What is fraction?
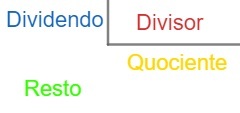
Parts and elements of the division
Suppose you have 6 jellybeans and your wish is to give some to each of your 2 friends. Let's initially interpret the idea through a drawing:
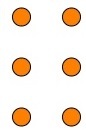
If we group the candies in two by two, each person will receive the same amount.
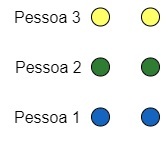
See that what we just did was to divide the 6 bullets by 3 people and we found 2 as an answer, that is, the answer of this division is 2. To represent a division, let's use the key method. Look:
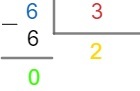
Each part of the division has a name: the number6it's called dividend, the number 3 is called divider, the number 2 é called quotient and0 is calledin rest. In general, we have the division as follows:
There is a method that facilitates the division process, the Euclid's algorithm. The method states that the dividend is equal to the divisor multiplied with the quotient added to the rest, in other words:
And in fact this occurs, see that:
dividend = divider · quotient + rest
6 = 3 · 2+ 0
See too: The importance of zero in division
Division step by step
To perform a division, we must use the call Euclid's algorithm, that is, we must imagine a number (quotient) that, when multiplied with the divisor, is equal to or as close as possible to the dividend.
If you find a number whose multiplication equals the dividend, the division ends. Now, if the number you found came very close to the dividend, you must subtract the dividend from the multiplication result and continue with the process. Follow the examples below!
Example 1
Divide the number 153 by 3.
Step 1 -Arm the operation using the key method. Note that the number 153 is relatively high compared to the number 3, which makes our job of finding a number that, multiplied by 3, is equal to 153 difficult, so we will take the digits of 153 until it is possible to division.

Step 2 -Let's now perform the division of the number 15 by the number 3, that is, we must find a number that, multiplied by 3, is equal to 15 or comes as close as possible. For now, number three will not be operated. When we finish dividing 15 by 3, let's lower the 3 of the dividend.
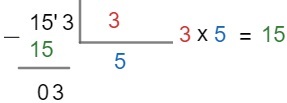
Step 3 – The remainder of the division equals 3. If it is still possible to perform the division, continue the process of thinking of a number that, multiplied by 3, equals 3. If the remainder of the division equals zero, then the division is over.
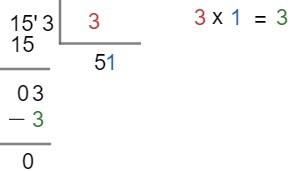
So dividing 153 by 3 equals 51.
153 ÷ 3 = 51
Example 2
Divide the number 55 by 2.
Step 1 – Let's arm the division operation using the key method.
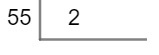
Step 2 – Let's now consider only the first digit of the dividend and then think of a number that, multiplied by 2, equals 5.

Step 3 – Now we should divide the remainder of the division by 2. In the multiplication table for number 2, we have that 2 x 7 = 14, like this:
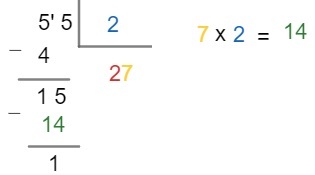
Step 4 – Note that the remainder is non-zero, which means that the division is not over yet. But note that it is not possible to divide the number 1 by 2. In these cases, we must add a zero to the remainder and a comma to the quotient and then perform the division:
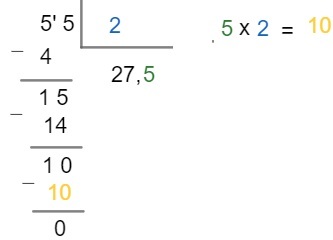
Therefore, 55 ÷ 2 = 27.5.
division with decimal numbers
To split between two decimal numbers, we must first check which of the numbers has the most decimal places between the dividend and the divisor. When checking which has the most decimal places, we must multiply it by a power of 10 (10; 100; 1000; 10000; …) until the comma disappears and continue dividing normally. Observation: if we multiply the dividend by a number, we must also multiply the divisor and vice versa.
Example 3
Divide the number 0.55 by 0.02.
The first step is to count the decimal places of the dividend and the divisor.
0.55 → 2 decimal places
0.02 → 2 decimal places
Therefore, we must multiply both by 100, as both have two decimal places. If they had three decimal places, we would multiply by 1000 and so on.
0.55 x 100 = 55
0.02 x 100 = 2
So dividing 0.55 by 0.02 is the same as dividing 55 by 2. As we have already performed the operation, we saw that the result is equal to 27.5.
Example 4
Divide the number 0.01 by 0.1.
0.01 → 2 decimal places
0.1 → 1 decimal place
We must take into account who has the most decimal places, so we must multiply the dividend and the divisor by 100.
0.01 x 100 = 1
0.1 x 100 = 10
Therefore, dividing 0.01 by 0.1 is the same as dividing 1 by 10. Note that it is not possible to perform this division, so we must add a “zero-colon” to the quotient and a zero to the dividend.

Therefore, 0.01 ÷ 0.1 = 0.1
Also access: Is there division by zero?
Signal game in division
When we are going to perform the division between two whole numbers, we must take into account the signs of the numbers that are being divided. The Signal Game Table applies to both division and multiplication of whole numbers. Look:
first number sign |
second number sign |
result sign |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
- |
- |
- |
+ |
- |
- |
- |
+ |
Example 5
Divide the numbers (–55) and (2).
First we must perform the operation with the signals. Note that the sign of the first number is negative and the second positive is positive. Looking at the table, we have that less with more is less. We also know that 55 ÷ 2 = 27.5.
(– 55) ÷ (2) = – 27,5
solved exercises
question 1 – Marcos will make a trip of 521 kilometers. To make the journey more secure, he decided to do it in two stages. How many kilometers will Marcos travel per day?
Resolution:
The total trip is 521 kilometers and will take place in two days. To determine the number of kilometers driven per day, we must divide these numbers.
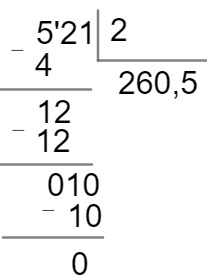
Marcos will therefore travel 260.5 kilometers per day.