THE Cold War is how we know the political-ideological conflict fought by the United States (USA) and the Soviet Union (USSR) between 1947 and 1991. This conflict placed two powers of different ideological orientation in the dispute for international supremacy.
Americans represented the capitalism and the Soviets represented the communism. The Cold War never generated a direct armed conflict between the Americans and the Soviets, but it did result in a series of small ones. indirect conflicts, in addition to promoting a dispute between these countries in areas such as the economy.
Read more:Understand how the 1917 Revolution turned Russia into a communist nation
Causes of the Cold War
The reasons that started the Cold War are the subject of intense debate among historians, and the reasons raised try to justify whether this conflict was an American or a Soviet invention. In any case, it is considered the starting point of the Cold War the speech of HarryTruman, President of the United States, who in 1947 held one said that it was his nation's role to fight to defend “free peoples” against the spread of communism.
This speech started the call DoctrineTruman, that is, the set of measures taken by the Americans with the objective of containing the advance of communism in Europe. This is because, in countless parts of Western Europe, communism showed itself as a great political force that had real chances of occupying power in these countries.
An indication in this regard was brought by historian Eric Hobsbawm, who indicated that the French prime minister warned the Americans, in 1946, that their country was in danger of elect communists to power, if the postwar French economy continued to be so bad|1|. Other countries in which the communists showed great political strength were Italy and Greece, for example.
Eric Hobsbawm also argues that the Cold War was based on a belief that the age of catastrophe had not come to an end and that capitalism was still under threat|2|. Thus, it was only natural that, in Western societies, communism was seen as a threat to capitalist values.
The fear was that the expansion of communism would threaten the values of capitalism and turn against societies. but Hobsbawm claims that the post-war Soviet Union was not an expansionist nation, it was in ruins. after Second World War and had assumed a paperdefensive in the late 1940s and early 1950s|3|.
The Soviet Union, in turn, sought ensure control under its sphere of influence, as had been foreseen in agreements between the Allies at the end of World War II. Thus, the countries invaded by the Red Army, throughout the conflict, were quickly converted into communist regimes satellite to Moscow.
Features
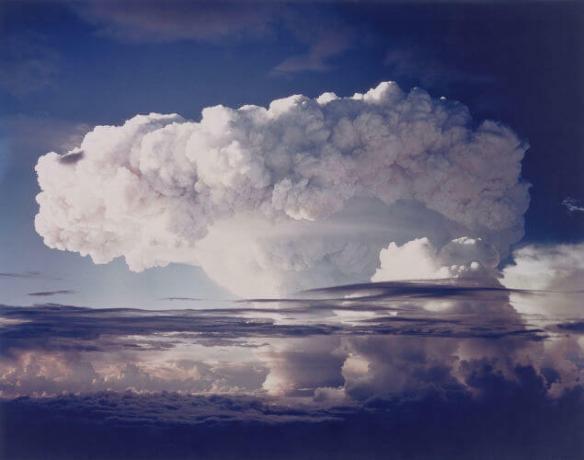

Hydrogen bomb test conducted by the United States in the 1950s. The arms race was one of the features of the Cold War.
The Cold War had repercussions in the world in different ways throughout the 20th century, of which we will highlight a few below:
Polarization of the world into two strictly defined ideological fields;
Arms race;
Space race;
Strong performance of espionage services;
Realization of economic investments in allied countries;
Indirect interference in marginal areas of the planet.
Also access: Understand the conflict that divided Spain during the 1930s
Outstanding events of the Cold War
The Cold War was marked by the strong fear caused by the possibility that a nuclear conflict waged by the United States and the Soviet Union would bring about the annihilation of humanity. There were moments of tension, but this direct conflict never came to pass. This is because, above all, the two Cold War powers promoted numerous efforts to avoid for a conflict to happen.
chinese revolution
The Chinese Revolution was the result of the victory of the Chinese Communist Party, led by Mao Tse-tung against nationalists, supported by the United States and led by Chiang Kai-shek in the Chinese Civil War in 1949.
With the victory, China became a communist nation, and the strategic defeat of the Americans in China caused the Americans to invest in development of countries such as Japan and Korea to impede the advance of communism and reduce Chinese influence in these countries. locations.
Korean War
THE Korean War it was a conflict between South Korea and North Korea, between 1950 and 1953. This conflict was a result of the division of the Korean peninsula, promoted by the Allied powers during World War II. As a result, the north came under Soviet influence and the south under American influence.
North Korea started to organize itself militarily and he promoted the invasion of the southern part of the peninsula with the aim of unifying it under his command. The Americans intervened in the conflict to help the South Koreans and, over the course of three years, neither side managed to rise above the other. An armistice was signed with the division between the Koreas remaining until today.
In this conflict, American intelligence knew of the existence of Soviet soldiers fighting for the North Koreans, but as part of the efforts had been made to avoid direct conflict, the issue remained a state secret and no action was taken by the Americans.
read more: Discover the revolution that gave rise to the first communist country in the Americas
Missile Crisis in Cuba
It was one of the most tense moments of the Cold War – if not the greatest. It began in 1962, when the United States discovered that the Soviet Union was installing a missile base in Cuba. Soviet missiles in Cuba did not pose much of a threat to the United States, but they would have negative repercussions for the image of the American president John F. Kennedy, so he intervened in the situation.
The Americans threatened the Soviet Union with war and the voltage arising from this led the Soviets to withdraw their missiles from Cuba. In contrast, the Americans did the same for their installed base in Turkey.
Vietnam War

American planes in action during the Cold War.
Conflict between 1959 and 1975 between North Vietnam and South Vietnam, each side seeking to unify the country under its rule. The civil war between the two sides started in 1959 and, from 1965, it had the direct participation of American troops.
The American participation in this conflict was extremely unpopular and resulted in the departure of the country in 1973, by decision of RichardNixon. the americans went defeated in that conflict, and Vietnam was unified under the command of the communists (supported by the Soviets) in 1976.
1979 Afghanistan War
Conflict fought between 1979 and 1989, in which Soviet troops invaded Afghanistan to defend the communist government threatened by fundamentalist rebels. The Afghan War was extremely costly and painful for the Soviets, and the Afghan rebels were financed and militarily trained by agents of the American government. In 1989, the Soviets withdrew their troops Afghanistan and, shortly thereafter, the communist government was overthrown by the rebels.
Also access: Understand how the Cold War interfered with Nicaraguan politics
Marshall Plan and Comecon
At the beginning of the Cold War, back in the 1940s, the Americans created the Marshal Planthere. This plan is designed exclusively for contain the spread of communism. The Marshall Plan consisted basically of providing large sums of money for the purpose of financereconstruction countries destroyed by World War II and to promote their economic development.
The biggest beneficiaries were countries in Western Europe, such as the United Kingdom, France and West Germany, and in Asia, such as Japan, Taiwan and South Korea. In response to the Marshall Plan, the Soviets founded the start (Council for Mutual Economic Assistance), a plan aimed at promoting the economic development of countries under Soviet influence.
NATO and Warsaw Pact
The existing military tension in the context of the Cold War led the nations of each bloc to organize themselves into large blocks of military cooperation in case of conflict. Thus, the US-led bloc joined the nato (North Atlantic Treaty Organization), created in 1949. The communist bloc, in turn, organized itself in the Warsaw Pact. Both blocks had as an essential feature the mutual defense. Thus, aggression against one member of the blocks was understood as aggression against everyone.
Germany in the Cold War

In blue is the territory of West Germany (allied to the US) and in red is the territory of East Germany (allied to the USSR).
Germany in the Cold War was a separate chapter in the political-ideological dispute that marked this period. At the end of World War II, Germany was devastated and its territory was invaded and Divided among the allied powers: USA, USSR, UK and France. The nascent ideological dispute meant that neither side gave up the German territory that ended up permanently divided.
This division led to the emergence of two Germanys:
German Democratic Republic (RDA), also known as GermanyEastern. It joined the communist bloc.
Federal Republic of Germany (RFA), also known as Germanywestern. It joined the socialist bloc.

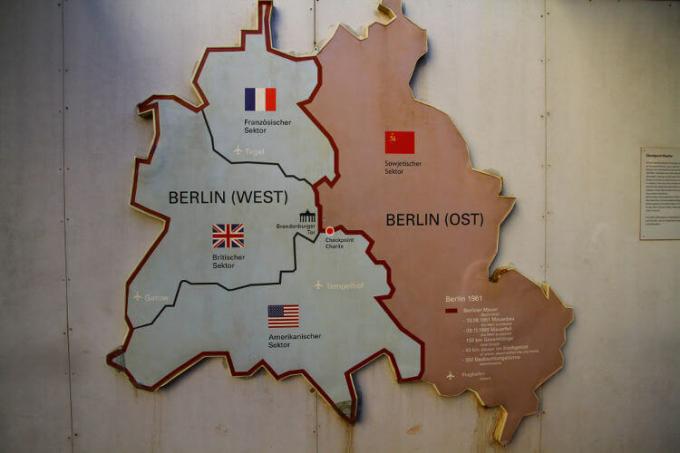
Map of the division of Berlin after World War II. The red part was East Berlin and the light part was West Berlin.**
This division was also reflected in Berlin, as the economic and strategic importance of this city made it the capital of both Germanys. With that, West Berlin became a capitalist piece embedded within communist territory. Throughout the 1940s and 1950s and the large number of people moving from East Berlin to West Berlin caused the Soviets to build a wall.

Image of the Berlin Wall, which separated East Berlin and West Berlin.
O Berlin Wall was built in 1961, by order of NikitaKhrushchev and walterUlbricht, leaders of the Soviet Union and East Germany, respectively. The construction of the wall took place around the perimeter of West Berlin, isolating it and was created to prevent East German citizens from fleeing for there. For 28 years, it symbolized the polarization of the Cold War world.
Also access: Understand the history of the conflict that resulted from the Yugoslav fragmentation
End of the Cold War

Mikhail Gorbachev, leader of the Soviet Union in the late 1980s and considered responsible for the country's economic opening.***
The Cold War ended with the dissolution of the Soviet Union in December 26, 1991 and it was the result of a strong political and economic crisis that dragged on in the communist bloc throughout the entire 1980s. The crisis of the socialist bloc originated in the 1970s and the lack of actions to reverse it aggravated the situation, making the maintenance of this bloc unsustainable.
First, in the 1970s, the Soviet economy clearly demonstrated to be backward. in relation to the great Western powers. Food production in the Soviet Union was insufficient, industry was unproductive, and important social indicators, such as life expectancy, stagnated or began to fall.
The rise in the value of oil created a false idea of prosperity in the 1980s and prevented necessary reforms for the Soviet economy from happening. The high bureaucracy of the economy, impeded society's access to technologies and forms of development of the Soviet economy, and the very high corruption in the high ranks of the Soviet Union aggravated the problem.
To make matters worse, the Soviet Union had to spend large sums of money on the 1979 Afghanistan War and in the containment of damages caused by the nuclear accident at the Chernobyl plant, in 1986.
The bad economic situation created dissatisfaction not only in the Soviet Union but throughout the communist bloc. THE lackinfreedom it's the authoritarianism present in the communist bloc expressed opposition reactions in places such as East Germany, Poland, Czechoslovakia, etc. In the late 1980s, drastic changes took place in Poland and East Germany, for example.
In November 1989, the berlin wall fell and the process of reunification of germany, completed in 1990. Poland elected a non-communist government, in 1989, and, in the Soviet Union, Mikhail Gorbachev began to promote reforms and the economic opening of the country through the Glasnot and perestroika.
Soon, the nations that formed the USSR began to demand their independence, and the continuation of the crisis led Gorbachev to resign on December 25, 1991. The next day, the dissolution of the Soviet Union was declared. The countries that formed the Soviet Union organized themselves in the Commonwealth of Independent States (CEI) and carried out their transition to capitalism.
|1| HOBSBAWM, Eric. Age of Extremes: The Brief 20th Century 1914-1991. São Paulo: Companhia das Letras, 1995, p. 228.
|2| Idem, p. 228.
|3| Idem, p. 229.
*Image credit: Vincent Grebenicek and Shutterstock
**Image credit: Yasemin Olgunoz Berber and Shutterstock
***Image credit: Konstantin Gushcha and Shutterstock
Take the opportunity to check out our video lesson related to the subject: