O adipose tissue is a kind of connective tissue which presents as its main feature cells specialized in fat storage (lipids). Despite what it may seem to common sense, it is an important tissue for our body, being power supply.
Adipose tissue can be classified into two main types: unilocular and multilocular. In this text, we will find out more about it, emphasizing its main characteristics, types and functions they play in our body.
Know more:Main tissues of the human body - epithelial, connective, muscular and nervous
Fatty tissue characteristics
Adipose tissue is a special connective tissue that has typical cells called adipocytes or fat cells.
Adipocytes are cells capable of storing lipids in their interior without causing any damage to them. The amount of fat inside an adipocyte is usually large, which leads to a movement of the cell nucleus to a more peripheral region.

adipose tissue is found in large amounts of the human body. In a woman, it can correspond to 20% to 25% of her body weight, while in a man, 15% to 20%.
Types of adipose tissue
Adipose tissue can be classified into two groups: common, yellow or unilocular adipose tissue and brown or multilocular adipose tissue. Now let's see the main characteristics of each of them:
Common, yellow or unilocular adipose tissue
It presents adipocytes with only a big drop of fat inside your cytoplasm. As the drop of fat increases, the adipocyte also increases in size. The unilocular adipose tissue presents great vascularity.
It is called yellow adipose tissue, as it has white to dark yellow fat. This color is achieved thanks to the deposition of carotenes, which dissolve in fat and are obtained by food. Therefore, the individual's diet is important in determining the color of this tissue.
The unilocular adipose tissue is found just below our skin, forming the adipose panicle. The panicle, in adults, develops more in some parts of the body than in others, in newborns, however, it has an almost uniform thickness throughout the body.
Among the functions that can be attributed to the unilocular adipose tissue, we can mention the energy storage, a organ protection and support, and its role as thermal insulator. This tissue also stands out for the production of some substances, such as leptin, which has, among other functions, a role in appetite reduction.
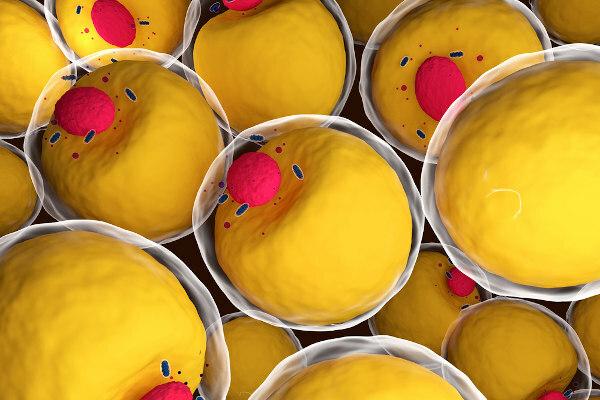

Brown or multilocular adipose tissue
It has, in its cells, several droplets of fat in the cytoplasm, unlike the unilocular, which has only one large drop. The adipocytes of brown adipose tissue also have mitochondria inside. The large amount of them together with the great vascularization give this tissue a brown look.
Multilocular adipose tissue is found, in greater quantity, in newborns and in hibernating animals. Its main function is the production of heat, thus helping to maintain the temperature. In hibernating animals, this tissue is commonly called hibernating gland.
Read more: What is hibernation - phases, doubts and importance of this process
Adipose tissue functions
Fat tissue has some important functions in the human body. See the table below, with some of them:
Adipose tissue functions |
|