When we are exercising or we are suffering from a very sunny day, we notice the sweat running down our face, don't we? O sweat it is a substance that, like many others in the body, is produced by glands.
Glands can be defined as structures formed by epithelial tissue able to produce useful substances for our body. These substances are traditionally called secretions and can be produced and released inside our body or out of it, as is the case with sweat.
All glands play a fundamental role in our survival, since the substances they produce perform the most varied functions. Sweat, for example, regulates our temperature so that it does not reach values that could put our health at risk. Substances produced by glands even act in growth, reproduction and metabolism, and are therefore essential for life.
The glands can be unicellular (formed by only one cell) or multicellular (formed by several cells). Single-celled glands are nothing more than secretory cells. A very common example are the so-called goblet cells present in the intestine.
Multicellular glands are the most commonly found in our body and can be classified into exocrine, endocrine and mixed. See the description of each of these types below:
Exocrine glands: They are those that produce secretion and release them through channels or ducts to internal cavities or to the outside of the body. As an example of these glands, we can mention the sweat and salivary glands. The latter releases its secretion (saliva) into the oral cavity, while the sweater releases sweat on the surface of the skin.
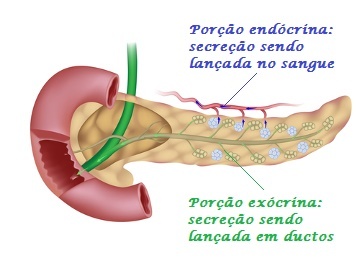
The pancreas is an example of a mixed gland. Watch!
Endocrine glands: Without the help of channels, these glands release their secretion directly into the blood. The secretions from the endocrine glands are called hormones. As an example, we can mention the thyroid, parathyroid, pituitary, adrenals, ovaries and testes.
Mixed glands: Glands are called mixed when an organ has both an exocrine and an endocrine portion. As an example, we can mention the pancreas, which produces pancreatic juice (exocrine portion) and the hormones insulin and glucagon (endocrine portion).
Take the opportunity to check out our video lesson on the subject:


