You Brazilian biomes represent areas of great extension that are constituted by a complexsetinecosystems, presenting featuressimilar such as vegetation, fauna, soil, climate. These features vary depending on the localizationgeographic of these regions.
Even if these biological communities have different characteristics, they can be part of the same biome, given that they live under similar environmental conditions. According to the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics, Brazil has six biomes. Are they:
Amazon |
Caatinga |
thick |
Atlantic forest |
pampa |
wetland |
Read too: Vegetation of Brazil
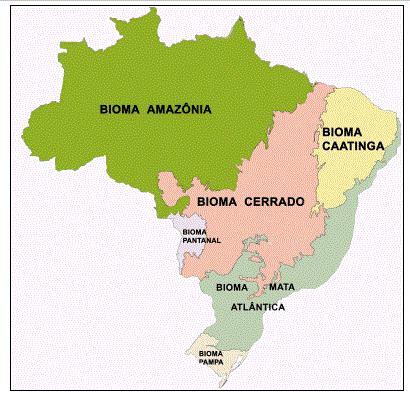
Map of Brazilian Biomes

Map of Brazilian biomes, according to the IBGE classification.
See too: Types of maps
Types of Brazilian Biomes
1) Amazon Biome

The Amazon biome comprises the area of several countries and it contains the largest tropical forest in the world.
O Amazon biome constitutes an area of approximately 4,196943 km2, occupying about 49.3% of the Brazilian territory. In this biome is found the largest tropical forest in the world, the
Amazon rainforest. This forest extends across nine countries in South America, but its largest portion is located in Brazil. It's a biome that understandseveralecosystems, therefore presenting a hugebiodiversity. In Brazil, the area of this biome is delimited by the "Legal Amazon".→Main characteristics of the Amazon biome
- Vegetation
- It is divided into dry land forest (higher strata, not flooded), floodplain forest (areas flooded for a period) and igapó forest (Lower strata, flooded most of the year).
- The appearance of the vegetation gives, when viewed from above, a continuous layer of crowns, which makes it difficult for light to enter, meaning that there is little undergrowth in this biome.
- Climate
- The prevailing climate is equatorial (hot and humid).
- the temperature suffers fewvariation throughout the year.
- - It has high air humidity and rainfall. Rainfall varies between 1,500 mm and 2,000 mm.
Read too: Why does it rain a lot in the Amazon?
- The fauna of the Amazon is mainly represented by the jaguar, pink dolphin, hyacinth macaw, armadillo and snakes such as the jararaca.
- The flora of the Amazon has around 30,000 species. Among the best known, it is possible to highlight the water lily, which is characteristic of the igapós forests.
- Hydrography
- THE biggerbowlhydrographic of the world is found in this biome, holding approximately 20% of the planet's fresh water, the Amazon Basin.
- The main river that drains this biome is the Amazon River, the largest in the world in terms of water volume.
- Ground
- The soil of the Amazon biome is normally sandy.
- has a humus layer from the deposition of vegetation, fruits and animal remains.
- Only 14% of the territory is fertile and suitable for agricultural activities.
2) Cerrado Biome

The Cerrado is considered the Brazilian savannah.
O Cerrado Biome is known as the savannaBrazilian, being the second largest biome in the country and also the second largest biome in South America. It constitutes an area of approximately 2,036,448 km2, representing about 23.9% of the Brazilian territory. It is a biome that presents different phytophysiognomies (aspect/feature of a plant community), due to the many biogeographic contacts with other biomes.
know more: Why is the Cerrado considered Brazil's water tank?
→ Main characteristics of the Cerrado
- Vegetation
- Features formationssavanna, forest and countryside.
- The species range from arboreal, shrub and vine vegetation, which are distributed among the strata: woody and herbaceous.
- Usually the trees have trunksdevious, reaching up to 20 meters.
- One of the identifying characteristics of this biome is related to its color. It presents shades of green, yellow and brown due to discoloration caused by intense sunlight.
- About two hundred species native to the Cerrado have medicinal potential, such as the pacari and the ruffian.
- Climate
- The predominant climate in this biome is the tropical seasonal. Features twoseasons well defined: dry winters and rainy summers.
- The average temperature throughout the year is 25 ºC, varying in some periods.
- Rainfall rates range from 1,200 mm to 1,800 mm. The rainy season starts in October and ends in April, starting the driest period.
- Fauna and Flora
- The fauna of the Cerrado, although not fully known, is represented by the maned wolf, toucan, giant anteater, puma, pampas deer, among others.
- There are about 837 species of birds, 185 species of reptiles, 194 species of mammals and 150 amphibians in the Cerrado.
- The flora is represented by ipe, barbatimão, jatobá, pequi, cagaita, among others. It is estimated that in the Cerrado there are ten thousand species of plants already identified.
- Hydrography
- The Cerrado is considered baby cribof thesprings from the main rivers in Brazil.
- The biome comprises nine of the twelve Brazilian hydrographic basins, according to IBGE.
- The Cerrado also understands the regioninbig onesaquifers, like Guarani and Bambuí.
- Ground
- Cerrado soils are very porous and permeable, making them suitable for the leaching process (erosion that occurs due to washing of the surface layer).
- have fewfertility and are usually acids.
- The colors of the Cerrado soils have reddish tones.
3) Caatinga Biome

The Caatinga is an exclusively Brazilian biome and is located in a very dry region.
O Caatinga biome represents about 9.9% of the Brazilian territory, with an area of approximately 844,453 km2. It is also known as the semi-arid steppe savanna, according to the IBGE. The Caatinga, the only biome exclusivelyBrazilian, it is quite degraded, mainly due to the incorrect and irrational use of its soils.
→ Main characteristics of the Caatinga biome
- The vegetation of the Caatinga is adapted to the dry climate, a characteristic known as xeromorphism. Plants have mechanisms of storageinWater, so that they survive long periods of drought.
- Plant species lose their leaves in the dry season.
- The trees present trunkscrooked and usually are low, represented by bushes and cactuses.
- Climate
- The predominant climate in the Caatinga is the semiarid, responsible for numerous particular characteristics of this biome.
- Rainfall rates vary between 200 mm and 1000 mm per year.
- The average temperature varies between 27 ºC and 32 ºC throughout the year.
- Several regions are punished due to highinsolation in the region.
- Fauna and Flora
- The fauna and flora of the Cerrado show miscellaneousspeciesendemic (which only exist in this region).
- The fauna of the Caatinga is represented by animals such as the alligator-do-papo-amarelo, boa constrictor, blue macaw, armadillo, capuchin monkey, agouti, among others.
- the fauna is richinbiodiversity, featuring about 178 mammals, 591 birds, 177 reptile species, 79 amphibians, 241 fish and 221 bee species.
- The flora is represented by species such as mandacaru, juazeiro, umbu, xiquexique, bromeliads, macambira, among others.
- The flora is mainly determined by the characteristics of the soil and rainfall.
- Hydrography
- The hydrography of the Caatinga is characterized by presenting riversflashing (rivers that disappear during the dry season). Compared to intermittent rivers, in the Caatinga region, there are few perennial rivers (rivers that flow throughout the year).
- The sources of the rivers of this biome are generally found in mountain ranges and plateaus.
- Due to low rainfall, the water tables present in the Caatinga region have volumereduced.
Read more:What are the characteristics of the São Francisco Basin?
- According to the Brazilian System of Soil Classification, the soils of the Caatinga range from shallow to deep.
- They are richinminerals, however poor in organic matter.
- The most common soils in this biome are shallow and stony, with color ranging from red to gray.
4) Atlantic Forest Biome

The Atlantic Forest has a dense and continuous forest.
OAtlantic Forest biomehas about 1,110,182 km2, occupying approximately 13% of the Brazilian territory. This biome extends over almost the entire CoastofBrazil. Due to the colonization of Brazil, this biome has undergone and is undergoing an intense process of deforestation, leaving around 10% of the native forest.
also know: Deforestation in Brazil
→ Main features of the Atlantic Forest:
- Vegetation
- The Atlantic Forest consists of Foresttropical, full of phytophysiognomies such as mangroves, restingas and rainforests (broad and perennial vegetation).
- The trees are medium and large.
- The treetops form a dense and continuous forest, reaching up to 60 meters in altitude.
- Climate
- The predominant climate in the Atlantic Forest is the tropicalhumid.
- At temperatures usually are high, also presenting high pluviometric indices.
- THE air humidity it is high, with few dry spells.
- Due to its extension, this biome also encompasses regions with a subtropical and high-altitude tropical climate.
- Fauna and Flora
- The Atlantic Forest fauna is represented by species such as toucans, jaguars, sloths, tamarins, among others.
- This biome has around 850 species of birds, 370 species of amphibians, 200 species of reptiles, 270 species of mammals (39% are endemic) and 350 species of fish.
- The flora is represented by species such as wildflowers and bromeliads and has around 20 thousand species of plants, of which around 8 thousand are endemic.
- Hydrography
- Covers the area of eight watersheds, fed by rivers such as the São Francisco, Paraíba do Sul and Paraná River.
- The Atlantic Forest also includes one of the largest aquifers in the world: the Guarani Aquifer.
- Ground
- The Atlantic Forest soils are mostly acid, shallow and shallow.
- They are usually quite permeable, therefore moist, however poorinnutrients due to the low incidence of solar rays, which are prevented from reaching the ground by vegetation.
- The high precipitation makes them prone to leaching processes.
5) Pantanal Biome

The Pantanal Biome is considered one of the largest wetlands in the world.
O Pantanal biome has an area of approximately 150,355 km2, occupying about 1.8% of the Brazilian territory. It is considered oneof thebiggerplainsfloodedofworld, due to its flat terrain, and it is the smallerbiomeofparentsinextensionterritorial. Because it is influenced by biomes such as the Amazon and Cerrado, the Pantanal biome has great biodiversity.
→ Main characteristics of the Pantanal
- Vegetation
- There are several types of vegetation in the region comprised by the Pantanal.
- Cerrados, woods, savannas and swamps are found.
- The vegetation is not closed, presenting fieldsopen, varying according to topographic characteristics.
- In flooded areas, it is common to find speciesaquatic, like the water lily.
- Climate
- The climate that prevails in the Pantanal is the tropical, with characteristics of continentality, hot and humid.
- There are periods of drought and rain.
- THE thermal range it is high, with temperatures ranging between 0ºC and 40ºC, with an annual average of 25ºC.
- Fauna and Flora
- The fauna of the Pantanal is represented by species such as the marsh deer, the marsh alligator and the tuiuiú.
- About 132 species of mammals, 463 species of birds, 113 species of reptiles, 41 species of amphibians and 263 species of fish are found.
- The flora of the Pantanal is represented by water lilies, water hyacinth, orchids, among others.
- Approximately 2,000 species of plants are found, normally from other biomes, according to the Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation (Embrapa).
- Hydrography
- The hydrographic basin that covers the Pantanal region is the Paraguay River basin.
- The main rivers that feed the region are: Rio Paraguai and Rio Cuiabá.
- Ground
- During periods of flooding, part of the Pantanal plain is flooded, and the soil is not able to absorb all the water.
- The soil consists of deposition of rock fragments coming from higher altitude areas.
- They are waterproofs and present lowfertility.
6) Pampa Biome

The Pampa biome has undergrowth known as native grasslands.
O Pampa biomeit is a region of plains composed mainly of native fields. It covers an area of 176,496 km2, occupying about 2.1% of the Brazilian territory. It is also known as Campos Sulinos and is found only in the state of Rio Grande do Sul.
→ Main features of the Pampa biome
- Vegetation
- The vegetation of the Pampa consists of grasses, mostly. It presents uniform grassland vegetation.
- It presents two types of phytophysiognomies: clean fields (shrubs) and dirty fields (without the presence of shrubs)
- Represented by an herbaceous mat, which reaches up to 50 centimeters.
- Climate
- The predominant climate in the Pampa biome is the seasoned, with cold subtropical characteristics.
- The annual average temperature is 19ºC.
- Presents the four well-defined seasons.
read more: Types of climate in Brazil
- Fauna and Flora
- The fauna is represented by species such as pampas deer, guinea pig, rhea, partridge, among others.
- The biome has about 100 species of mammals and approximately 500 species of birds.
- The flora is represented by species such as aloe vera, native clover and carpet grass.
- The biome has about 3,000 species of plants.
- Hydrography
- The Pampa biome covers an area of two hydrographic basins: the Southern Coastal Basin and the Rio da Prata Basin.
- Features highpotentialhydroelectric and has plenty of rivers navigable.
- Ground
- The soils of the Pampa biome are from lowfertility, sandy and conducive to leaching processes.
- Due to the intense agricultural practices in the region, much of this biome is suffering from devastation.