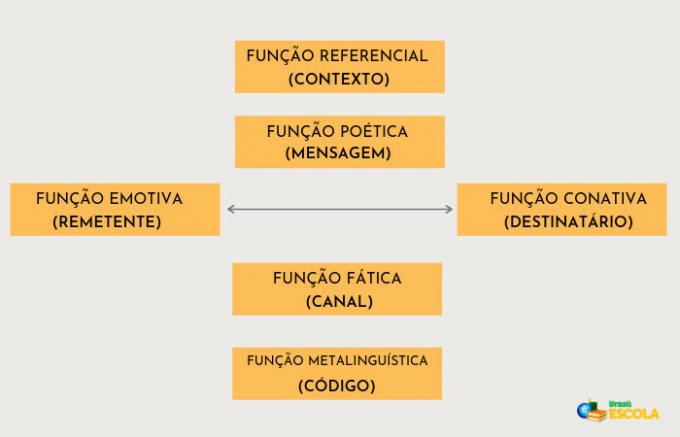
Language functions are related to the purpose of a text, which can have one or more functions. Thus, you can be (a) sender (a) of a text that exhibits emotions and, therefore, has an emotive or expressive function, or that values poetic elements and then presents a poetic function. But perhaps the purpose of the text is to inform you about something, through a clear and objective message, as it has a referential or denotative function.
But if you only intend to keep the communication channel active, you will be the sender of a text with a phatic or contact function. And if you want to highlight the language used, your text will have a metalinguistic function. However, be aware (a) when someone wants to convince you to do something, because the sender of the text is using the conative or appealing function.
Read too: What are figures of speech?
Emotional or expressive function

For you to identify this type of function in a text, it is necessary to observe if this text has
message sender's emotions or attitudes, that is, of the person who speaks or writes.Note this sentence and imagine that it was spoken by Bruno:
I was really happy when I won that ball.
Bruno is the one talking, because he uses the pronoun personal “I”. Furthermore, when he says he was very happy, Bruno, that is, the sender of the sentence, is expressing his emotion for winning a ball. So, we can say, with certainty, that this text has an emotive or expressive function.
poetic function
if you find one text with characteristics of poetry, it has poetic function. If a text has figurative meaning or sound features, as rhyme, assonance (repeat of vowels) or alliteration (repeat of consonants), it is a poetic text.
Read the poem below The House, by the Brazilian writer Vinicius de Moraes:
it was a house
Very funny
had no roof
there was nothing
no one could
not enter it
because in the house
There was no floor
no one could
Sleep on the Net
because the house
had no wall
no one could
pee
because potty
there was no
But it was done
with great care
in Rua dos Bobos
Number zero.
The poem has rhymes. Thus, “funny” rhymes with “nothing” and “network” with “wall”, for example. Furthermore, the text has a figurative sense. After all, is the house really a house? It seems not, since it has no roof, floor, or wall.
See too: What are the differences between poetry, poem and sonnet?
Referential or denotative function
The denotative sense is the contrary to the figurative sense. In a figurative sense, the word “heart” can mean love, for example. But in the denotative sense, heart it is an organ. Therefore, texts that present this type of meaning have a referential or denotative function.
See this excerpt from the text “Why are most leaves green”?:
In the leaves of vegetables there are cells with small structures that are called chloroplasts. Inside these structures we find a pigment called chlorophyll. This substance is capable of absorbing blue, violet and red wavelengths, as well as reflecting green light, giving the plant this coloration.
You may have noticed that there is no figurative sense in this text fragment. This is because is a text that intends to inform about something,so he needs to be clear. Thus, the words are all in a denotative sense, they have no other sense than their original meaning.
phatic or contact function

Texts that have the phatic or contact function present messages that are only expressed to keep the communication channel active. These are texts that only serve to keep the conversation from ending.
Read this dialogue between a boy and a girl who only know each other by sight:
- Hey!
- Hey!
"Are you okay?"
- Nice!
- Well!
— É!
As you noticed, the two are just saying things to maintain a communication. Maybe, from then on, one of them will say something that can really lead to a good chat. Otherwise, their conversation will soon be interrupted.
metalinguistic function
THE metalinguistic function is centered on language itself, that is, in the code used to express the message. For example, poetry that talks about poetry, a painting that shows someone painting, or even a film whose main theme is cinema.
See the lyrics titled Not identified, by Caetano Veloso:
I will make a song for her
A simple Brazilian song
To launch after carnival
[...]
I will make a love song
To record on a flying saucer
Not identified is a song that talks about a song.
Conative or appealing function
Texts that have this function are intended to convince or instruct you to do something. Usually they use imperatives. This can be seen, for example, in an advertising message that uses certain words to convince us to buy a product.
Another example is a ticket:
Lucas, feed the dog before going to school.
In this note, Lucas' father asks his son to feed the dog. For this, he uses the verb “to give”, in the imperative, in order to convince or instruct the child to perform the requested action.
Read too: What are the differences between prescriptive and injunctive texts?
Language functions and communication

After reading about each of the language's functions, you've noticed that every message has a specific purpose:
- express an emotion,
- value the poetic language,
- say something clearly and objectively,
- keep the communication channel going,
- talk about the language itself or
- convince someone.
Thus, the efficiency of communication depends on several elements:
- Message: what is said, written or expressed.
- issuer: the author of the message.
- receiver: who receives the message.
- Channel: message transmission medium.
- Code: language used in the message.
- Context: situation in which the message is produced.
So let's read this note again:
Lucas, feed the dog before going to school.
Now let's point out, in this text, each of the elements of communication:
- Message: “Lucas, feed the dog before going to school”.
- Sender: Lucas' father.
- Receiver: Lucas.
- Channel: piece of paper.
- Code: colloquial language.
- Context: familiar and informal.
However, for communication to be, in fact, efficient, the message must have a goal, which is precisely the function of language. But beware! One function does not exclude the other. This means that the same text can have more than one language function.
Summary of language functions
- Emotional or expressive function: displaying the message sender's emotions or attitudes.
- Poetic function: expose and enhance the poetic elements.
- Referential or denotative function: present an objective message.
- Phatic or contact function: keep the communication channel active.
- Metalinguistic function: highlighting the language used.
- Conative or appealing function: to convince or instruct the recipient of the message.
- Communication elements:
- Message.
- Issuer.
- Receiver.
- Channel.
- Code.
- Context.
solved exercises
Question 1 - (AND EITHER)
The biosphere, which brings together all the environments where living beings develop, is divided into smaller units called ecosystems, which can be a forest, a desert and even a lake. An ecosystem has multiple mechanisms that regulate the number of organisms within it, controlling their reproduction, growth and migrations.
DUARTE, M. The curious guide. São Paulo: Companhia das Letras, 1995.
The function of language predominates in the text
A) emotional, because the author expresses his feelings towards ecology.
B) factual, because the text tests the functioning of the communication channel.
C) poetic, because the text draws attention to language resources.
D) conative, because the text seeks to guide the reader's behavior.
E) referential, because the text deals with conceptual notions and information.
Resolution
Alternative E. As it is informative, the text must be clear and objective. Therefore, the referential function stands out, because its sense is denotative, there is no figurative sense in this text.
question 2 - (AND EITHER)
Small concert turned song
No there is no reason to lie or hide
The pain that was greater than my heart is capable of
No, there's no reason to keep singing just to explain
Those who never knew how to love will never understand
oh i will come back to me
go alone like that
Until consume me or consume all this pain
Until I felt the heart capable of love again
VANDRÉ, G. Available in: http://www.letras.terra.com.br. Accessed on: June 29 2011.
In Geraldo Vandré's song, there is the manifestation of the poetic function of language, which is perceived in the artistic and creative elaboration of the message, through sound and rhythmic combinations. By analyzing the text, however, one can also see the strong presence of the emotive or expressive function, through which the issuer
A) imprints on the song the marks of his personal attitude, his feelings.
B) conveys objective information about the theme that the song is about.
C) seeks to persuade the recipient of the song to adopt a certain behavior.
D) seeks to explain the language used to build the song.
E) aims to verify or strengthen the efficiency of the message conveyed.
Resolution
Alternative A. It is possible to identify, in the song, marks of the sender's personal attitude and feelings, which characterizes the emotive or expressive function. These marks are evidenced in the verses: “The pain that was greater than my heart is capable”, “Oh, I'm going back to me", "Going alone like this", "Until it consumes me or consumes all this pain", "Until I feel the heart capable of love".