Regardless of how countries and regions work out the form and names of their addresses, there is a worldwide standard for locating any location on the earth's surface: geographic coordinates. They, in turn, are composed of a system that brings together the latitudes and longitudes.
Thus, any point located on the Earth's surface area is positioned at a specific latitude and longitude.
THE latitude it is always the distance, in degrees, from any point on the earth's surface to the Equator. This imaginary line is important because it is at the exact distance between the two poles of our planet. Thus, everything north of the Equator has positive latitudes, and everything south has negative latitudes.
The measurement of latitudes ranges from 0º to 90º to the north and from 0º to -90º to the south.
THE longitude, in turn, is the distance, in degrees, of any point on Earth in relation to the Greenwich Meridian, which divides the planet into the Eastern and Western hemispheres. Thus, everything east of Greenwich has positive longitudes, and everything west of Greenwich has negative longitudes.
Longitude measurements range from 0º to 180º to the east and from 0º to -180º to the west.
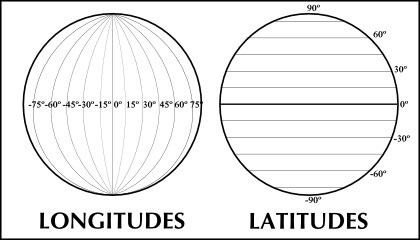
Didactic illustration of latitudes and longitudes
Remember that the Parallels and Meridians they are different from latitudes and longitudes in that, while they constitute the measure in degrees, they are the very imaginary lines of the Earth itself. Some well-known Earth parallels have specific latitudinal locations, which is the case of the Tropic of Capricorn, which has a latitude of 23.37º South.
The geographic coordinates, therefore, are nothing more than a combination of the Earth's latitudes and longitudes, allowing the formation of a network capable of locating all areas. This system is very important and used by military organizations, airlines, mariners, travelers and many others.
By Me. Rodolfo Alves Pena