In humans, the transport of nutrients takes place thanks to the blood, which is carried by the cardiovascular system to all parts of the body. And in plants? How does this happen? Have you ever thought cHow does the plant transport substances through its body?
→ Vascular and avascular plants
We can classify plants into two main groups: vascular and avascular. in plants avascular, no specialized structure for conducting substances is found. In these plants, substances are passed from cell to cell, in a process called diffusion. As an example of avascular plants, we can mention the moss, a representative of the group of bryophytes.
Already in plants called vascular, there is a system that carries out the transport of substances. Products such as water, mineral salts and other substances go through fabrics conductors and move as a result of some processes, such as transpiration, which promotes the emergence of a force that moves water and mineral salts through the body of the plant. We can say, therefore, that in this group of plants there is a true vascular system.
→ Conductive fabrics
We know that two types of sap circulate in a plant: raw sap and elaborated sap. The raw sap is formed by water and mineral salts, and the elaborated sap presents, in addition to water, amino acids, sugars and other products. In addition to the difference in the constitution of the sap, each of these types of sap will be transported by a different tissue.
Raw sap is transported via xylem, and elaborated sap is transported by phloem. The raw sap always travels from the direction of the root, where water and salts are absorbed, to the other parts of the plant. The elaborated sap follows the opposite direction, ensuring that the nutrients produced by the plant are taken to all plant organs.
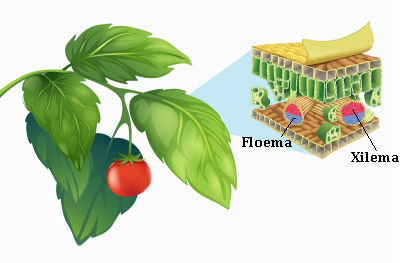
It is possible to observe the xylem and phloem in all plant organs of vascular plants
Xylem is a tissue that has several cell types, from which cells that are specialized in carrying water and mineral salts stand out. These cells are characterized by being killed at maturity. The phloem, in turn, also has cells specialized in conduction, but they are alive in adulthood.
Both xylem and phloem are present in all plant organs. This means that if you cut a sheet and look at it under a microscope, you can see conductive tissue. The same will happen if you analyze the root, stem and flower, for example. This distribution in all plant organs enables an efficient transport of substances throughout the plant organism.



